Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is the primary function of the acrosome in a sperm cell?
Which of the following is the primary function of the acrosome in a sperm cell?
- Dissolving the outer layer of the egg for fertilization. (correct)
- Facilitating the sperm's attachment to the uterine wall.
- Providing energy for the sperm's movement.
- Protecting the sperm's DNA from damage.
What is the correct sequence of events after an egg is released from the ovary?
What is the correct sequence of events after an egg is released from the ovary?
- Implantation, fertilization, menstruation.
- Fertilization, implantation, menstruation. (correct)
- Fertilization, menstruation, implantation.
- Menstruation, fertilization, implantation.
What is the main event that characterizes the beginning of the menstrual cycle?
What is the main event that characterizes the beginning of the menstrual cycle?
- Follicle development.
- Menstruation. (correct)
- Ovulation.
- Implantation.
Which of the following does NOT occur if fertilization of the egg takes place?
Which of the following does NOT occur if fertilization of the egg takes place?
Approximately how long is the typical menstrual cycle?
Approximately how long is the typical menstrual cycle?
What physiological change defines the onset of menopause?
What physiological change defines the onset of menopause?
During which stage of the menstrual cycle is the uterine lining at its thickest?
During which stage of the menstrual cycle is the uterine lining at its thickest?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating follicle development in the ovary?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating follicle development in the ovary?
What triggers ovulation during the menstrual cycle?
What triggers ovulation during the menstrual cycle?
What role does estrogen play in the menstrual cycle following menstruation?
What role does estrogen play in the menstrual cycle following menstruation?
How do the levels of estrogen and progesterone change at the beginning of the menstrual cycle?
How do the levels of estrogen and progesterone change at the beginning of the menstrual cycle?
What happens to the unfertilized egg if implantation does not occur?
What happens to the unfertilized egg if implantation does not occur?
Which of the following statements accurately compares sperm and egg cells?
Which of the following statements accurately compares sperm and egg cells?
What is the role of mitochondria in the middle piece of a sperm cell?
What is the role of mitochondria in the middle piece of a sperm cell?
When does the first menstruation typically occur in a female's life?
When does the first menstruation typically occur in a female's life?
Flashcards
Egg (Ovum)
Egg (Ovum)
The female gamete involved in sexual reproduction.
Sperm Cell
Sperm Cell
The male gamete involved in sexual reproduction, delivering genetic material to the egg.
Acrosome
Acrosome
A vesicle in sperm containing enzymes to dissolve the egg's outer layer, enabling fertilization.
Zygote
Zygote
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryo
Embryo
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantation
Implantation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstruation
Menstruation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Puberty
Puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menopause
Menopause
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen
Estrogen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone
Progesterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicles
Follicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- A sperm cell is motile, much smaller than an egg, and is divided into a head, middle piece, and a tail.
- The sperm head contains the haploid nucleus with the cell's genetic material and the acrosome, a vesicle with enzymes.
- Enzymes from the acrosome dissolve the jelly layer around the egg for fertilization.
- The sperm middle piece contains many mitochondria, producing energy for movement.
- A flagellum powers the sperm's movement.
- Sperm last for 2-3 days before disintegrating, while ova survive 24 hours.
- Typically, one egg is released from an ovary each month.
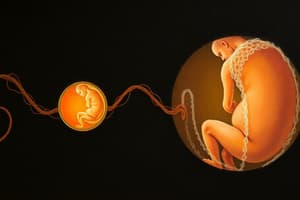
- Fertilization by a sperm results in a zygote, which divides and becomes an embryo.
- The embryo travels down the oviduct to the uterus.
- Implantation occurs when the embryo embeds in the uterine lining and attaches to the uterine wall.
- Before ovulation, the uterine wall prepares to receive an embryo, becoming thick, spongy, and vascularized to nourish the embryo with nutrients and oxygen.
- Unfertilized eggs die and exit the body through the vagina.
- If fertilization doesn't occur, hormone levels change, causing the endometrium to disintegrate and exit through the vagina (menstruation/period); unfertilized eggs do not attach to the uterus wall.
- Menstruation, the discharge of endometrial fragments and blood, occurs about once per month.
- The first menstruation happens at puberty shortly after first ovulation.
- Menstruation lasts about five days, after which the endometrium prepares for a potential embryo.
- The menstrual cycle is defined as the sequence of events from the first day of menstruation to the first day of the following menstruation; ovulation occurs in each cycle.
- The average menstrual cycle lasts 28 days but varies.
- Menstrual cycles occur regularly until menopause or pregnancy.
- Menopause is when the ovaries stop ovulating, menstruation stops, and the menstrual cycle ends, generally occurring between ages 45-55, after which a female can no longer have children.
- Events during the menstrual cycle are controlled by ovarian hormones (estrogen, progesterone) and pituitary hormones (FSH, LH).
- During menstruation, estrogen and progesterone levels are low.
- The pituitary gland then secretes FSH, which stimulates the development of several follicles, sacs within the ovaries where the eggs mature, containing supporting cells.
- Typically, only one follicle matures per cycle, while others disintegrate.
- Follicles release estrogen as they develop.
- Estrogen causes the uterine lining to grow and the endometrium to thicken and become spongy.
- When estrogen reaches a certain level, the pituitary gland releases a surge of LH and FSH.
- The LH surge triggers ovulation, where the mature follicle bursts, releasing the egg to the oviduct.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Sperm cells, smaller than eggs, have a head with a nucleus and acrosome, a middle piece with mitochondria, and a flagellum for movement. Fertilization results in a zygote, which develops into an embryo. The embryo implants in the uterine lining, which thickens to provide nourishment.