Podcast
Questions and Answers
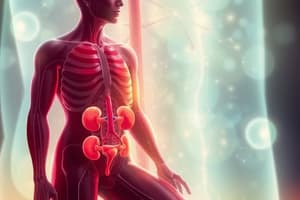
Where are the kidneys located in human beings?
Where are the kidneys located in human beings?
In the abdomen, one on either side of the backbone.
What is the primary biological process for the removal of harmful metabolic wastes from the body called?
What is the primary biological process for the removal of harmful metabolic wastes from the body called?
Excretion
List the components of the human excretory system.
List the components of the human excretory system.
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
How do unicellular organisms typically remove waste products?
How do unicellular organisms typically remove waste products?
What is the function of the urinary bladder in the excretory system?
What is the function of the urinary bladder in the excretory system?
How is urine produced in the human body?
How is urine produced in the human body?
In what way does the excretory system in humans compare to that of multicellular organisms?
In what way does the excretory system in humans compare to that of multicellular organisms?
What nitrogenous waste products are primarily filtered out of the blood in the kidneys?
What nitrogenous waste products are primarily filtered out of the blood in the kidneys?
Explain how the excretory processes in simple organisms differ from those in complex multicellular organisms.
Explain how the excretory processes in simple organisms differ from those in complex multicellular organisms.
Discuss the role of kidneys in the context of maintaining homeostasis in humans.
Discuss the role of kidneys in the context of maintaining homeostasis in humans.
In what ways do the ureters contribute to the efficiency of the human excretory system?
In what ways do the ureters contribute to the efficiency of the human excretory system?
Describe the process that occurs in the kidneys to convert blood into urine.
Describe the process that occurs in the kidneys to convert blood into urine.
What is the significance of the urinary bladder in human excretion?
What is the significance of the urinary bladder in human excretion?
How do the functions of human kidneys exemplify evolutionary adaptation in excretion?
How do the functions of human kidneys exemplify evolutionary adaptation in excretion?
Analyze the importance of nitrogenous waste removal for human health.
Analyze the importance of nitrogenous waste removal for human health.
Identify and explain the role of specialized structures within human kidneys involved in urine formation.
Identify and explain the role of specialized structures within human kidneys involved in urine formation.
Study Notes
Excretion Overview
- Excretion is the biological process for removing harmful metabolic wastes from the body.
- Organisms generate gaseous wastes during photosynthesis and respiration, along with nitrogenous materials that require elimination.
- Unicellular organisms typically use simple diffusion to expel waste into surrounding water.
- Complex multicellular organisms employ specialized organs for excretion.
Excretion in Human Beings
- The human excretory system consists of:
- Two kidneys
- Two ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
- Kidneys are situated in the abdomen on either side of the backbone.
- The kidneys filter waste products from the blood to produce urine.
- Urine is transported from the kidneys through ureters to the urinary bladder for temporary storage.
- Urine is released from the body through the urethra.
- Nitrogenous wastes, such as urea and uric acid, are specifically removed from blood by the kidneys, similar to how CO2 is expelled in the lungs.
- The kidneys contain basic filtration units that facilitate this waste removal process.
Excretion Overview
- Excretion is the biological process for removing harmful metabolic wastes from the body.
- Organisms generate gaseous wastes during photosynthesis and respiration, along with nitrogenous materials that require elimination.
- Unicellular organisms typically use simple diffusion to expel waste into surrounding water.
- Complex multicellular organisms employ specialized organs for excretion.
Excretion in Human Beings
- The human excretory system consists of:
- Two kidneys
- Two ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
- Kidneys are situated in the abdomen on either side of the backbone.
- The kidneys filter waste products from the blood to produce urine.
- Urine is transported from the kidneys through ureters to the urinary bladder for temporary storage.
- Urine is released from the body through the urethra.
- Nitrogenous wastes, such as urea and uric acid, are specifically removed from blood by the kidneys, similar to how CO2 is expelled in the lungs.
- The kidneys contain basic filtration units that facilitate this waste removal process.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
We have discussed earlier how plants take in simple compounds such as CO2 and photosynthesise energy stored in their chlorophyll-containing organs, namely leaves. The other kinds of raw materials needed for building plant bodies will also have to be taken up separately. For plants, the soil is the nearest and richest source of raw materials like nitrogen, phosphorus and other minerals. The absorption of these substances therefore occurs through the part in contact with the soil, namely roots. If the distances between soil-contacting organs and chlorophyll- containing organs are small, energy and raw materials can easily diffuse to all parts of the plant body. But if these distances become large because of changes in plant body design, diffusion processes will not be sufficient to provide raw material in leaves and energy in roots. A proper system of transportation is therefore essential in such situations. Energy needs differ between different body designs. Plants do not move, and plant bodies have a large proportion of dead cells in many tissues. As a result, plants have low energy needs, and can use relatively slow transport systems. The distances over which transport systems have to operate, however, can be very large in plants such as very tall trees. Plant transport systems will move energy stores from leaves and raw materials from roots. These two pathways are constructed as independently organised conducting tubes. One, the xylem moves water and minerals obtained from the soil. The other, phloem transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves where they are synthesised to other parts of the plant. We have studied the structure of these tissues in detail in Class IX. Transport of water