Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a major feature of simple epithelium?
What is a major feature of simple epithelium?
- Irregularly shaped cells
- Multiple layers of cells
- One layer of cells (correct)
- Cells with varying shapes
Which cell form is associated with simple epithelium?
Which cell form is associated with simple epithelium?
- Squamous (correct)
- Columnar
- Transitional
- Stratified
Where can simple squamous epithelium be found?
Where can simple squamous epithelium be found?
- Epidermis
- Bladder
- Sweat glands
- Lining of vessels (correct)
What is a main function of simple squamous epithelium?
What is a main function of simple squamous epithelium?
Which cell form is found covering the ovary and thyroid?
Which cell form is found covering the ovary and thyroid?
What is the main function of cuboidal epithelium?
What is the main function of cuboidal epithelium?
Where can simple columnar epithelium be found?
Where can simple columnar epithelium be found?
Which function is associated with simple columnar epithelium?
Which function is associated with simple columnar epithelium?
What characterizes stratified epithelium?
What characterizes stratified epithelium?
Where is stratified squamous keratinized epithelium found?
Where is stratified squamous keratinized epithelium found?
What is the main function of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium?
What is the main function of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium?
Which of the following contains stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium?
Which of the following contains stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium?
Where are sweat glands located?
Where are sweat glands located?
What is the function of cuboidal epithelium in sweat glands?
What is the function of cuboidal epithelium in sweat glands?
Where is transitional epithelium found?
Where is transitional epithelium found?
Which is a main function of transitional epithelium?
Which is a main function of transitional epithelium?
Where can stratified columnar epithelium be found?
Where can stratified columnar epithelium be found?
What is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
What is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
What is a major feature of pseudostratified epithelium?
What is a major feature of pseudostratified epithelium?
Where can pseudostratified epithelium be found?
Where can pseudostratified epithelium be found?
Which function is performed by pseudostratified epithelium?
Which function is performed by pseudostratified epithelium?
Which of the following is an example of simple epithelium distribution?
Which of the following is an example of simple epithelium distribution?
What type of epithelium is found in the serous lining of cavities?
What type of epithelium is found in the serous lining of cavities?
Which epithelium prevents water loss?
Which epithelium prevents water loss?
Which type of epithelium is mainly involved in distensibility?
Which type of epithelium is mainly involved in distensibility?
In what location would protection be the primary function of the epithelium?
In what location would protection be the primary function of the epithelium?
Which epithelium contains cilia?
Which epithelium contains cilia?
Which of the following is lined by simple cuboidal epithelium?
Which of the following is lined by simple cuboidal epithelium?
What kind of epithelium is the conjunctiva made of?
What kind of epithelium is the conjunctiva made of?
Which type of epithelium facilitates movement of the viscera?
Which type of epithelium facilitates movement of the viscera?
Which of the following structures contains nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which of the following structures contains nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What type of epithelium lines the gallbladder?
What type of epithelium lines the gallbladder?
Where is the peritoneum located?
Where is the peritoneum located?
Which function is associated with transitional epithelium?
Which function is associated with transitional epithelium?
What is the main function of the epithelium lining the trachea?
What is the main function of the epithelium lining the trachea?
Where are the ureters located?
Where are the ureters located?
Which function is performed by simple squamous epithelium?
Which function is performed by simple squamous epithelium?
Which of these is a location of stratified columnar epithelium?
Which of these is a location of stratified columnar epithelium?
What liquids are protected by stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium?
What liquids are protected by stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium?
What is a characteristic of stratified epithelium?
What is a characteristic of stratified epithelium?
Which of the following describes the shape of simple squamous epithelium?
Which of the following describes the shape of simple squamous epithelium?
Which of the following is the main function of pseudostratified epithelium?
Which of the following is the main function of pseudostratified epithelium?
Flashcards
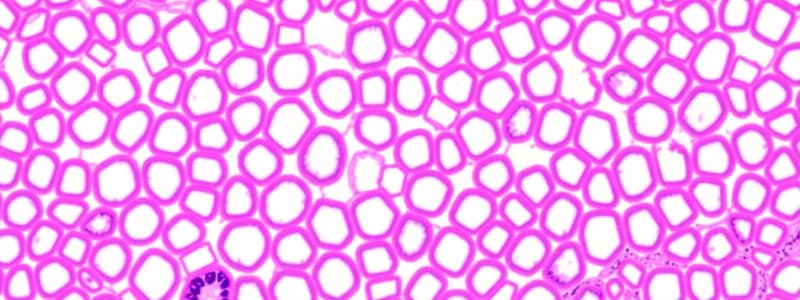
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Composed of a single layer of flattened cells.
Function of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Function of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Facilitates movement of viscera; active transport via pinocytosis; secretes biologically active molecules.
Distribution of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Distribution of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Lining of vessels (endothelium) and serous lining of cavities (mesothelium).
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Function of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Distribution of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Function of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Distribution of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Epithelium
Stratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
Function of Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
Distribution of Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium
Function of Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium
Distribution of Stratified Squamous Nonkeratinized Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Function of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Distribution of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Transitional Epithelium
Function of Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Transitional Epithelium
Distribution of Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Description of Pseudostratified Epithelium
Description of Pseudostratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Pseudostratified Epithelium
Function of Pseudostratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Pseudostratified Epithelium
Distribution of Pseudostratified Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Function of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distribution of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Distribution of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Simple Epithelium (One Layer of Cells)
- Squamous cells line vessels (endothelium) and serous cavities like the pericardium, pleura, and peritoneum (mesothelium).
- Squamous cells facilitate movement of the viscera (mesothelium), active transport via pinocytosis (mesothelium and endothelium), and secretion of biologically active molecules (mesothelium).
- Cuboidal cells cover the ovary and thyroid.
- Cuboidal cells function in covering and secretion.
- Columnar cells line the intestine and gallbladder.
- Columnar cells function in protection, lubrication, absorption, and secretion.
Stratified Epithelium (Two or More Layers of Cells)
- Squamous keratinized (dry) epithelium is found in the epidermis.
- Squamous keratinized epithelium provides protection and prevents water loss.
- Squamous nonkeratinized (moist) epithelium lines the mouth, esophagus, larynx, vagina, and anal canal.
- Squamous nonkeratinized epithelium provides protection, secretion, and prevents water loss.
- Cuboidal cells are located in sweat glands and developing ovarian follicles.
- Cuboidal cells function in protection and secretion.
- Transitional epithelium is found in the bladder, ureters, and renal calyces.
- Transitional epithelium's main function is protection and distensibility.
- Columnar epithelium is located in the conjunctiva.
- Columnar epithelium provides protection.
Pseudostratified Epithelium (Layers of Cells with Nuclei at Different Levels)
- Not all pseudostratified cells reach the surface, but all adhere to the basal lamina.
- Pseudostratified epithelium lines the trachea, bronchi, and nasal cavity.
- Pseudostratified epithelium functions in protection, secretion, and cilia-mediated transport of particles trapped in mucus out of the air passages.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.