Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of epithelial tissue is primarily involved in the secretion of hormones into the bloodstream?
What type of epithelial tissue is primarily involved in the secretion of hormones into the bloodstream?
- Exocrine Epithelium
- Nervous Epithelium
- Covering Epithelium
- Glandular Epithelium (correct)
Which of the following characteristics are true about epithelial tissues?
Which of the following characteristics are true about epithelial tissues?
- They have both apical and basal surfaces. (correct)
- They fit closely together to form continuous sheets. (correct)
- They have a rich blood supply.
- They do not have regenerative capacity.
What is the primary function of the cilia found on epithelial cells?
What is the primary function of the cilia found on epithelial cells?
- To facilitate movement of substances. (correct)
- To absorb nutrients.
- To provide structural support.
- To protect underlying tissues.
Which type of gland secretes products directly into ducts that lead to specific locations in the body?
Which type of gland secretes products directly into ducts that lead to specific locations in the body?
What is the role of the basement membrane in epithelial tissue?
What is the role of the basement membrane in epithelial tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
Which type of epithelial tissue would be most effective at providing a barrier against harmful substances?
Which type of epithelial tissue would be most effective at providing a barrier against harmful substances?
What is the primary type of function served by glandular epithelium?
What is the primary type of function served by glandular epithelium?
Study Notes
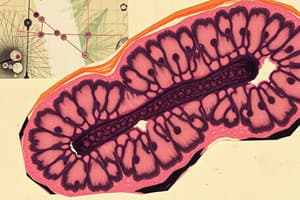
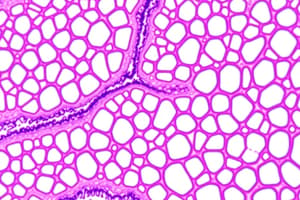
Epithelial Tissue - Protective Tissue
- Definition: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
- Histology: The study of tissues.
Covering/Lining Epithelium
- Location: Outer layer of skin & internal structures.
Glandular Epithelium
- Location: Glands of the body.
Functions
- Physical Protection:
- Protects organs from harmful substances.
- Found in skin & bladder.
- Absorption:
- Allows food products to be absorbed.
- Found in the small intestine & kidney.
- Sensory:
- Forms sensory receptors that send sensory responses to the brain.
- Examples:
- Rods & cones (eye)
- Taste buds (tongue)
- Secretion:
- Occurs in glands.
- Endocrine: Secretes product directly into the bloodstream.
- Affects the whole body.
- Examples: Thyroid & Pituitary glands.
- Exocrine: Secretes product into a duct, and then to its desired location.
- Affects a specific target area only.
- Examples: Sweat, earwax, and saliva glands.
Structure
- Cells fit closely together to form continuous sheets.
- Epithelial tissue sits upon and is supported by connective tissue.
- Avascular: No direct blood vessels, arteries, or veins.
- Innervated: Contact with nerves.
- High Regenerative Capacity: Epithelial tissue can repair itself.
Apical Surface
- Side exposed to the outside world or cavity of an organ.
- May contain microvilli or cilia.
- Microvilli: Increase surface area for absorption.
- Cilia: Move things & sensory function (skin/respiratory).
Basal Surface
- Anchored to the lower surface.
Basement Layer
- Composed of the basal lamina and reticular lamina.
- Basal Lamina: Joins epithelial to connective tissue, acting as a filter for substances.
Classification
- Number of layers: More layers = more protection. Single layer means substances pass through more easily.
- Presence of cilia: Cilia are involved in movement.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the fascinating world of epithelial tissue with this quiz. Learn about its definition, types, locations, and vital functions such as protection, absorption, sensory perception, and secretion. Test your knowledge on both covering/lining and glandular epithelium.