Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary component that assists in the attachment of the epithelial layer to the basement membrane?
What is the primary component that assists in the attachment of the epithelial layer to the basement membrane?
- Basal lamina components
- Adhesion proteins
- Cytoskeleton elements
- Extracellular matrix proteins (correct)
Which characteristic distinguishes epithelial tissues from other tissue types regarding blood supply?
Which characteristic distinguishes epithelial tissues from other tissue types regarding blood supply?
- Complete blood dependency
- Direct blood vessel attachment
- Absence of blood vessels (correct)
- Extensive vascularization
What role does extensive innervation play in epithelial tissues?
What role does extensive innervation play in epithelial tissues?
- Promotes adhesive properties
- Enhances nutrient absorption
- Detects environmental changes (correct)
- Facilitates rapid cell division
How do epithelial cells maintain their integrity when exposed to environmental damage?
How do epithelial cells maintain their integrity when exposed to environmental damage?
Which of the following best describes the structure of the basement membrane in epithelial tissues?
Which of the following best describes the structure of the basement membrane in epithelial tissues?
What is the primary reason epithelial tissues lack blood vessels?
What is the primary reason epithelial tissues lack blood vessels?
Which of the following best describes the function of the basement membrane?
Which of the following best describes the function of the basement membrane?
What is the significance of epithelial tissues being richly innervated?
What is the significance of epithelial tissues being richly innervated?
Why do epithelial cells have a high regeneration capacity?
Why do epithelial cells have a high regeneration capacity?
What are the primary components of the molecular layers in the basement membrane?
What are the primary components of the molecular layers in the basement membrane?
What is a primary function of epithelial tissue related to the body's surfaces?
What is a primary function of epithelial tissue related to the body's surfaces?
How does epithelial tissue act as a gatekeeper in the body?
How does epithelial tissue act as a gatekeeper in the body?
What role do glands, formed from epithelial cells, primarily serve?
What role do glands, formed from epithelial cells, primarily serve?
Which of the following statements best describes why epithelial tissues have no blood vessels?
Which of the following statements best describes why epithelial tissues have no blood vessels?
What is a crucial function of sensory nerve endings in epithelia?
What is a crucial function of sensory nerve endings in epithelia?
Select the characteristic of an epithelium that distinguishes it from connective tissues.
Select the characteristic of an epithelium that distinguishes it from connective tissues.
What defines a simple epithelium?
What defines a simple epithelium?
Which statement about stratified epithelia is true?
Which statement about stratified epithelia is true?
Which shape is NOT one of the classifications of epithelial cells at the apical surface?
Which shape is NOT one of the classifications of epithelial cells at the apical surface?
How are epithelia primarily categorized?
How are epithelia primarily categorized?
In which type of epithelium would you expect to find cuboidal cells?
In which type of epithelium would you expect to find cuboidal cells?
What is a primary functional characteristic of simple epithelial tissue?
What is a primary functional characteristic of simple epithelial tissue?
Which statement best describes stratified epithelial tissues?
Which statement best describes stratified epithelial tissues?
What type of epithelium resembles a brick wall?
What type of epithelium resembles a brick wall?
What characteristic defines a stratified epithelium?
What characteristic defines a stratified epithelium?
How are pseudostratified epithelium cells classified?
How are pseudostratified epithelium cells classified?
What role does the basal layer of a stratified epithelium play?
What role does the basal layer of a stratified epithelium play?
Which statement about the cells in a simple epithelium is true?
Which statement about the cells in a simple epithelium is true?
What distinguishes squamous cells from cuboidal and columnar cells?
What distinguishes squamous cells from cuboidal and columnar cells?
What is the primary structural characteristic of simple squamous epithelium?
What is the primary structural characteristic of simple squamous epithelium?
Which type of epithelium is classified as simple despite appearing layered?
Which type of epithelium is classified as simple despite appearing layered?
In what type of tissue is simple squamous epithelium most effective for gas exchange?
In what type of tissue is simple squamous epithelium most effective for gas exchange?
What happens to the cells in the apical layer of a stratified epithelium?
What happens to the cells in the apical layer of a stratified epithelium?
What structural resemblance does a stratified epithelium have?
What structural resemblance does a stratified epithelium have?
Which feature of the nucleus in simple squamous epithelium cells is notably described?
Which feature of the nucleus in simple squamous epithelium cells is notably described?
What is the function of simple squamous epithelium in the context of respiration?
What is the function of simple squamous epithelium in the context of respiration?
Which of the following terms describes the shape of cells in a stratified epithelium?
Which of the following terms describes the shape of cells in a stratified epithelium?
How does the structure of simple squamous epithelium contribute to its function?
How does the structure of simple squamous epithelium contribute to its function?
What is a key feature of the basal layer of stratified epithelium?
What is a key feature of the basal layer of stratified epithelium?
Which statement correctly describes squamous cells?
Which statement correctly describes squamous cells?
What is a distinguishing feature of cuboidal cells?
What is a distinguishing feature of cuboidal cells?
Which of the following best describes columnar cells?
Which of the following best describes columnar cells?
In what way do transitional cells differ from the other epithelial types?
In what way do transitional cells differ from the other epithelial types?
What feature characterizes simple squamous epithelium?
What feature characterizes simple squamous epithelium?
Which cell type is primarily found in the lining of the bladder?
Which cell type is primarily found in the lining of the bladder?
What is a common feature among the different types of epithelial cells?
What is a common feature among the different types of epithelial cells?
Which option correctly identifies the characteristics of cuboidal cells?
Which option correctly identifies the characteristics of cuboidal cells?
Why are transitional cells particularly suited for the bladder?
Why are transitional cells particularly suited for the bladder?
How do squamous cells differ from cuboidal and columnar cells?
How do squamous cells differ from cuboidal and columnar cells?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
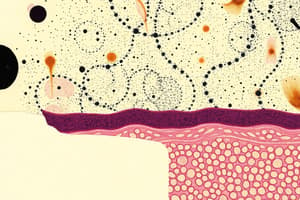
Attachment to a Basement Membrane
- Epithelial layers bind to a thin basement membrane at their basal surface, appearing as a single layer under light microscopy.
- Basement membrane consists of three molecular layers observable via electron microscopy, formed from both epithelial and connective tissue secretions.
- Composed of collagen, glycoproteins, and proteoglycans, these layers serve as a strong adhesive and selective barrier between epithelium and underlying tissue.
Avascularity
- Epithelial tissues are devoid of blood vessels.
- Nutrients are absorbed directly across the apical surface or through diffusion from blood vessels in the underlying connective tissue.
Extensive Innervation
- Epithelia are richly supplied with sensory nerves, enabling detection of environmental changes.
High Regeneration Capacity
- Epithelial cells divide frequently, allowing for rapid regeneration.
- Damage from environmental exposure leads to cell loss, with stem cells adjacent to the basement membrane continuously replacing lost cells.
Epithelial Functions
- Physical Protection: Shields external and internal surfaces from dehydration, abrasion, and damage from pathogens or chemicals.
- Selective Permeability: Acts as a barrier, regulating passage of substances in and out of the body, functioning as a "gatekeeper."
- Secretions: Specialized epithelial cells form glands to produce and secrete various substances, such as hormones and mucus.
- Sensations: Innervated epithelial tissues transmit sensory information (touch, temperature, pressure, pain) to the central nervous system.
Epithelial Classification
- Epithelia are categorized by cell layers (simple or stratified) and cell shape (squamous, cuboidal, columnar).
- Simple Epithelium: One layer of cells; primarily for filtration, absorption, or secretion.
- Stratified Epithelium: Two or more layers; provides structural support and protection against abrasion.
Cell Shapes
- Squamous Cells: Flat and wide, resembling floor tiles.
- Cuboidal Cells: Height equal to width, with spherical nuclei.
- Columnar Cells: Taller than wide, with oval nuclei oriented lengthwise.
- Transitional Cells: Can change shape based on stretching, found in areas like the bladder.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Comprises a single layer of flattened cells with centrally located, flattened nuclei.
- Ideal for rapid molecule and ion exchange, found in structures like alveoli in the lungs.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- One layer of block-shaped cells with centrally located spherical nuclei.
- Functions in absorption and secretion; found in glands and kidney tubules.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- A single layer of taller cells, featuring oval nuclei in the basal region.
- Includes nonciliated (with microvilli and goblet cells) for absorption and secretion, and ciliated variants that move mucus along surfaces.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- Appears layered but is a single layer with nuclei at varying levels.
- Contains ciliated and nonciliated forms; ciliated version houses goblet cells that trap foreign particles, lining respiratory pathways.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Multiple layers with only the basal layer in contact with the basement membrane.
- Provides protection against abrasion; may be keratinized (e.g., skin) or nonkeratinized (e.g., oral cavity).
Keratinized vs. Nonkeratinized
- Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Contains dead cells filled with keratin for protection, forms the epidermis of skin.
- Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Remains moist, found in areas like the oral cavity and esophagus, protecting against abrasion without keratin buildup.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.