Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following characteristics of epithelial cells is LEAST helpful in determining their classification?
Which of the following characteristics of epithelial cells is LEAST helpful in determining their classification?
- Cell dimensions
- Nuclear shape
- Cell shape
- Presence of reticular lamina (correct)
The apical domain of an epithelial cell is characterized by which of the following features?
The apical domain of an epithelial cell is characterized by which of the following features?
- Presence of collagen III fibers
- Exposure to the external environment or lumen (correct)
- Attachment to the basement membrane
- Specialized junctions for cell-cell adhesion
What is the primary function of tight junctions (Zonula Occludens) found on the lateral surface of epithelial cells?
What is the primary function of tight junctions (Zonula Occludens) found on the lateral surface of epithelial cells?
- To provide strong mechanical attachment between cells
- To facilitate communication between adjacent cells
- To anchor cells to the underlying basement membrane
- To seal the space between cells, preventing paracellular transport (correct)
The basement membrane, crucial for epithelial tissue support, consists of two layers with distinct origins. What are these two layers?
The basement membrane, crucial for epithelial tissue support, consists of two layers with distinct origins. What are these two layers?
Which component of the basement membrane is primarily responsible for providing an interaction site for cell adhesion molecules?
Which component of the basement membrane is primarily responsible for providing an interaction site for cell adhesion molecules?
How would disruption of claudin molecules within intestinal tight junctions affect intestinal function?
How would disruption of claudin molecules within intestinal tight junctions affect intestinal function?
What is the role of fibroblasts in relation to the basement membrane?
What is the role of fibroblasts in relation to the basement membrane?
An experiment reveals that epithelial cells are unable to adhere properly to their basement membrane. Which component of the basement membrane is MOST likely affected?
An experiment reveals that epithelial cells are unable to adhere properly to their basement membrane. Which component of the basement membrane is MOST likely affected?
A researcher is studying a sample of tissue and observes a distinct layer containing collagen III fibers beneath the basal lamina. Which structure is the researcher most likely observing?
A researcher is studying a sample of tissue and observes a distinct layer containing collagen III fibers beneath the basal lamina. Which structure is the researcher most likely observing?
A patient presents with symptoms of food poisoning. Tests reveal an enterotoxin that inhibits the function of claudin molecules. Which specific structure is directly affected by this enterotoxin?
A patient presents with symptoms of food poisoning. Tests reveal an enterotoxin that inhibits the function of claudin molecules. Which specific structure is directly affected by this enterotoxin?
Epithelial tissues rely on connective tissues for nutritional support due to which characteristic?
Epithelial tissues rely on connective tissues for nutritional support due to which characteristic?
Which structural feature of epithelial cells is most directly related to their ability to form selective barriers?
Which structural feature of epithelial cells is most directly related to their ability to form selective barriers?
If a tissue sample shows cells with distinct apical and basal surfaces, and is supported by connective tissue, which type of tissue is it most likely to be?
If a tissue sample shows cells with distinct apical and basal surfaces, and is supported by connective tissue, which type of tissue is it most likely to be?
How does the high mitotic rate observed in epithelial tissues contribute to their function?
How does the high mitotic rate observed in epithelial tissues contribute to their function?
Considering the classification of epithelia, what cellular characteristic distinguishes simple from stratified epithelium?
Considering the classification of epithelia, what cellular characteristic distinguishes simple from stratified epithelium?
Which of the following features is essential for classifying epithelium based on the shape of surface cells?
Which of the following features is essential for classifying epithelium based on the shape of surface cells?
How does the avascular nature of epithelial tissue influence its metabolic processes and overall thickness?
How does the avascular nature of epithelial tissue influence its metabolic processes and overall thickness?
Suppose a pathologist is examining a biopsy from a new organ. They identify a tissue lining a duct that appears to be multiple layers of cells, but all cells are in contact with the basement membrane. How should the tissue be classified?
Suppose a pathologist is examining a biopsy from a new organ. They identify a tissue lining a duct that appears to be multiple layers of cells, but all cells are in contact with the basement membrane. How should the tissue be classified?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of epithelial tissues?
Which of the following is NOT a primary function of epithelial tissues?
What is the role of innervation in epithelial tissue, given that it is avascular?
What is the role of innervation in epithelial tissue, given that it is avascular?
Which type of intercellular junction acts primarily as a seal to prevent the passive flow of substances between adjacent epithelial cells?
Which type of intercellular junction acts primarily as a seal to prevent the passive flow of substances between adjacent epithelial cells?
What is the primary function of gap junctions found on the lateral surface of epithelial cells?
What is the primary function of gap junctions found on the lateral surface of epithelial cells?
What type of protein is found within the core of both microvilli and stereocilia?
What type of protein is found within the core of both microvilli and stereocilia?
In Celiac disease, the immune reaction against gluten leads to the damage of which apical surface modification in the small intestine, resulting in malabsorption?
In Celiac disease, the immune reaction against gluten leads to the damage of which apical surface modification in the small intestine, resulting in malabsorption?
Which apical modification is longer, less motile than microvilli, and often exhibits branching?
Which apical modification is longer, less motile than microvilli, and often exhibits branching?
How do cilia differ structurally from microvilli?
How do cilia differ structurally from microvilli?
What is the primary function of the primary cilium found on some epithelial cells?
What is the primary function of the primary cilium found on some epithelial cells?
Based on the components of epithelial tissue, what characteristic is most important for its protective and barrier functions?
Based on the components of epithelial tissue, what characteristic is most important for its protective and barrier functions?
Epithelial tissue can be found lining internal organs and their ducts. What is a primary function this tissue performs in these locations?
Epithelial tissue can be found lining internal organs and their ducts. What is a primary function this tissue performs in these locations?
Considering the characteristics of epithelial tissues, which feature is most crucial for enabling rapid tissue repair and regeneration?
Considering the characteristics of epithelial tissues, which feature is most crucial for enabling rapid tissue repair and regeneration?
Flashcards
Nuclear Shape & Cell Shape
Nuclear Shape & Cell Shape
Epithelial cells' shape often mirrors the shape of their nucleus.
Epithelial Domains
Epithelial Domains
The apical domain faces the lumen or external environment, the basal domain rests on the basement membrane, and the lateral domain connects to adjacent cells.
Basement Membrane
Basement Membrane
A structure underneath the basal surface of epithelial cells that composed of the basal lamina and reticular lamina.
Basal Lamina Functions
Basal Lamina Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Lamina
Reticular Lamina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tight Junctions (Zonula Occludens)
Tight Junctions (Zonula Occludens)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin
Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Paracellular Pathway
Paracellular Pathway
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inhibition of Claudin Molecules
Inhibition of Claudin Molecules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Cells
Epithelial Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anchoring Junctions
Anchoring Junctions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gap Junctions (Nexus)
Gap Junctions (Nexus)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microvilli
Microvilli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Celiac Disease
Celiac Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stereocilia
Stereocilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cilia
Cilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary cilium
Primary cilium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissue
Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specialized Contacts
Specialized Contacts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Polarity
Epithelial Polarity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Connective Tissue Support
Connective Tissue Support
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avascular but Innervated
Avascular but Innervated
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelial Regeneration
Epithelial Regeneration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Covering or Lining Epithelia
Covering or Lining Epithelia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelium Classification (Layers)
Epithelium Classification (Layers)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epithelium Classification (Shape)
Epithelium Classification (Shape)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Squamous Cells
Squamous Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cuboidal Cells
Cuboidal Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Human Histology lecture MT120225, Unit 2: Epithelial Tissue is lectured at UST General Santos, School of Health Sciences, Department of Medical Technology, Second Semester A.Y. 2024-2025.
- At the end of this unit, the student must be able to identify and describe the various epithelial tissue types.
- Course content covers: Epithelial Cells, Epithelial Domains, Covering or Lining Epithelia, Secretory Epithelia and Glands, Transport Across Epithelia, and Renewal of Epithelial Cells.
Characteristic Features of Epithelial Cells
- Epithelial cells are characterized by their shape and dimensions.
- Nuclear shape corresponds roughly to cell shape.
Epithelial Cells: Squamous
- Simple squamous epithelial cells have a height less than their width (H < W) and can be found lining the alveoli of lungs.
Epithelial Cells: Cuboidal
- Cuboidal epithelial cells have a height equal to their width (H = W).
Epithelial Cells: Columnar
- Columnar epithelial cells have a height that is greater than their width (H > W).
Characteristic Features: Polarity & Domains
- Epithelial cells exhibit distinct polarity
- They have three domains which include the apical domain, basal domain, and lateral domain.
Epithelial Domains
- Consist of the Apical Domain, Lateral Domain, and Basal Domain.
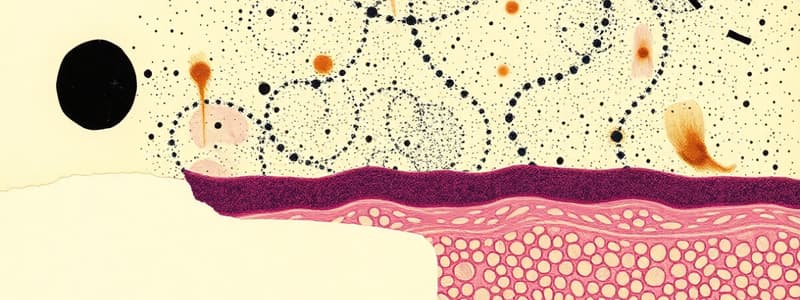
Basal Surface
- The basal surface rests on the basement membrane made up of the basal lamina (BL) and reticular lamina (RL).
Basal Lamina
- The Basal Lamina is 20-100 nm thick
- It is composed of glycoproteins, collagen, and proteoglycans.
- It is produced by epithelial cells and supports the overlying epithelium, acts as a semipermeable barrier, and provides an interaction site for many cell adhesion molecules.
Reticular Lamina
- The Reticular Lamina contains collagen III fibers
- They are produced by fibroblasts (connective tissue).
Lateral Surface
- Intercellular adhesion and other junctions exist on this surface.
- Tight/Occluding Junctions (Zonula Occludens) seal between adjacent cells and prevent passive flow of materials between cells.
- Anchoring Junctions serve as sites of strong cell adhesion.
- Gap Junctions (Nexus) are patches many connexons; they permit intercellular exchange of small molecules.
MEDICAL APPLICATION
- The enterotoxin secreted by Clostridium perfringens, which causes food poisoning, prevents maintenance of the tight juntion by inhibiting insertion of claudin molecules of intestinal cells, causing loss of tissue fluid into the intestinal lumen via paracellular pathway.
Apical Surface
- The apical surface contains microvilli, stereocilia, and cilia.
Microvilli
- Microvilli are finger-like cytoplasmic projections of epithelial tissue specialized for absorption.
- They are 1 μm long and 0.1 μm wide.
- They increase surface area by 20-30 fold
- The internal structure has a core of actin filaments and actin binding proteins.
MEDICAL APPLICATION
- Celiac disease leads to loss of microvilli brush border of the absorptive cells of the small intestine.
- It is caused by the immune reaction against wheat protein (gluten) during its digestion, which causes diffuse enteritis and malabsorption.
Stereocilia
- Stereocilia are seen on absorptive epithelial cells lining the male reproductive system and sensory cells of the inner ear.
- They have a core of actin filaments and actin binding proteins.
- Stereocilia are longer and less motile than microvilli and often have distal branching.
Cilia
- Cilia are long and larger than microvilli
- They are abundant on cuboidal or columnar cells
- They are 5-10 μm long and 0.2 μm.
- They contain microtubules internally
- Cilia exhibit beating patterns that move materials in one direction.
- The primary cilium, which is not motile, detects light, odor, motion, and the flow of liquid.
Covering or Lining Epithelia
- Tissue is a group of similarly specialized cells that work together to perform a specific function.
- Main functions include:
- Epithelial tissue has a small amount extracellular matrix and functions to line the surface/body cavities and grandular secretion.
- Connective tissue has an abundant amount of extracellular matrix and functions to support and protection tissues/organs.
- Muscle tissue has a moderate amount of extracellular matrix and functions to strong contraction body movements.
- Nervous tissue has very small amount of extracellular matrix and functions to transmission of nerve impulses.
Covering or Lining Epithelia: Epithelial Tissue Characteristics
- Epi upon + thele nipple
- Composed of closely aggregated polyhedral cells adhering strongly to one another and to ECM.
- Covers external surfaces of the body, line the internal cavities and the organs, form various organs and glands, and line their ducts.
Covering or Lining Epithelia: Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue
- Cellularity – in close contact with each other.
- Specialized contacts - have junctions for attachment and communication.
- Polarity - have apical, basal, and lateral surfaces.
- Supported by connective tissue - source of nutrients, metabolites, and oxygen.
- Avascular but innervated.
- Regeneration - high mitotic rate.
Covering or Lining Epithelia are Classified According to:
- Cell layers.
- Cell shape.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.