Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic of epithelium indicates it is made up of closely packed cells?
Which characteristic of epithelium indicates it is made up of closely packed cells?
- Polarity
- Pseudostratification
- Cellularity (correct)
- Avascularity
What type of epithelium is primarily involved in absorption and secretion?
What type of epithelium is primarily involved in absorption and secretion?
- Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Simple Columnar Epithelium (correct)
- Transitional Epithelium
- Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Which statement is true regarding the basement membrane of epithelium?
Which statement is true regarding the basement membrane of epithelium?
- It contains blood vessels that nourish the epithelium directly.
- It supports the epithelium by providing a surface for attachment. (correct)
- It consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells.
- It prevents the diffusion of nutrients.
Which type of epithelium has multiple layers to protect against abrasion?
Which type of epithelium has multiple layers to protect against abrasion?
What is a common feature of both simple cuboidal and simple columnar epithelium?
What is a common feature of both simple cuboidal and simple columnar epithelium?
What is a key characteristic of epithelial tissues?
What is a key characteristic of epithelial tissues?
Which of the following correctly describes a function of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following correctly describes a function of epithelial tissue?
How do epithelial cells differ from connective tissue cells?
How do epithelial cells differ from connective tissue cells?
What must be observed to classify epithelial tissue?
What must be observed to classify epithelial tissue?
What distinguishes epithelial tissue from the other three main types of tissue in the human body?
What distinguishes epithelial tissue from the other three main types of tissue in the human body?
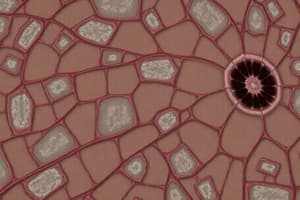
What primary function allows the urinary bladder to accommodate varying volumes without damage?
What primary function allows the urinary bladder to accommodate varying volumes without damage?
Which structures primarily provide a tight barrier within epithelial tissues?
Which structures primarily provide a tight barrier within epithelial tissues?
Which of the following describes the process by which liquids or gases are taken in by cells?
Which of the following describes the process by which liquids or gases are taken in by cells?
What is the primary difference between epithelial cells and endothelial cells?
What is the primary difference between epithelial cells and endothelial cells?
What role do nerve endings in epithelial cells serve?
What role do nerve endings in epithelial cells serve?
Which cellular feature helps certain epithelial cells in moving substances across surfaces?
Which cellular feature helps certain epithelial cells in moving substances across surfaces?
Which of the following statements about secretion and excretion is true?
Which of the following statements about secretion and excretion is true?
How do tight junctions contribute to epithelial functionality?
How do tight junctions contribute to epithelial functionality?
What distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from other types of epithelial tissues?
What distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from other types of epithelial tissues?
Which type of epithelium is characterized by cells that become flattened as they move from the basal to the apical layer?
Which type of epithelium is characterized by cells that become flattened as they move from the basal to the apical layer?
What is a primary function of stratified columnar epithelium?
What is a primary function of stratified columnar epithelium?
Which feature is unique to transitional epithelium?
Which feature is unique to transitional epithelium?
Which type of epithelium has an outermost layer consisting of cuboidal cells?
Which type of epithelium has an outermost layer consisting of cuboidal cells?
What is the primary role of mucous membranes?
What is the primary role of mucous membranes?
Which of the following components is NOT typically found in mucous?
Which of the following components is NOT typically found in mucous?
How many layers compose the serous membrane?
How many layers compose the serous membrane?
What is the function of hyaluronan released by fibroblasts in synovial membranes?
What is the function of hyaluronan released by fibroblasts in synovial membranes?
Which type of membrane is known as the skin?
Which type of membrane is known as the skin?
What characterizes the cutaneous membrane?
What characterizes the cutaneous membrane?
Which of the following best describes the serous fluid?
Which of the following best describes the serous fluid?
What type of glands produce the mucous found in mucous membranes?
What type of glands produce the mucous found in mucous membranes?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Epithelial Tissue
- Epithelial tissue covers all internal and external body surfaces
- It is made up of cells, closely packed and arranged in one or more layers
- Epithelial tissue is specialized to form the covering or lining of internal and external body surfaces
- Epithelial tissue is one of the four main tissue types:
- Muscle tissue
- Nerve tissue
- Connective tissue
- Epithelial cells are the most prolific of the four major tissue types
- Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue:
- It is avascular – without blood vessels, nutrients diffuse in from underlying connective tissue
- It has a good nerve supply
- Cells are tightly packed together
- Epithelial cells have rapid cell division
- Epithelial cells are characterized by:
- Cellularity - predominantly cells
- Polarity - cells have a defined apical and basal surface
- Supported by connective tissue - underneath the epithelial layer that provides structural support
- Avascular - lacks blood vessels
- Regenerative - constantly renewing itself
Epithelial Tissue Functions
- Epithelial cells provide:
- Protection - covering inner and outer linings of body cavities and organs
- Secretion - movement of material from one point to another (ex. chemicals from a cell or gland)
- Absorption - the process of a liquid, gas or substance being taken in
- Sensation - nerve endings provide signals for sensory sensations (ex. taste, sight, smell)
- Transcellular Transport - movement of substances (in and out of the cell) across the cell membrane
- Movement - some cells have cilia (sweep motion) that aid in moving substances
- Lubrication - mucous secretion helps to lubricate cavities and organs
Basement Membrane
- The basement membrane supports and protects the entire epithelial layer
- It is made up of two layers:
- Basal lamina - produced by the epithelial cells
- Reticular lamina - produced by the underlying connective tissue
Classification of Epithelium
- Epithelium is classified by:
- Number of cell layers (simple - one layer, stratified - more than one layer)
- Shape of cells (squamous - flattened, cuboidal - cube-shaped, columnar - tall and thin)
- Specializations (cilia, microvilli, keratinization)
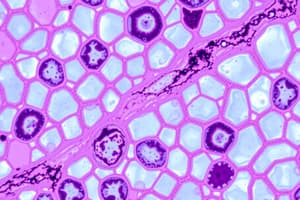
Simple Epithelium
- Simple Epithelium - single layer of cells
- Simple Squamous - single layer of flattened cells (facilitates the transfer of materials, found in lungs, blood vessels, and body cavities)
- Examples: lining of blood vessels, alveoli of lungs, lining of body cavities (serous membranes)
- Simple Cuboidal - single layer of cube-shaped cells (associated with absorption, secretion, and excretion)
- Examples: lining of kidney tubules, ducts of glands, covering of ovaries
- Simple Columnar - single layer of tall, thin cells (associated with absorption and secretion)
- Examples: lining of small intestine, stomach, and uterus
- Pseudostratified - appears to be stratified but all cells contact the basement membrane, contains cilia (helps move substances, protection)
- Examples: lining of trachea, respiratory tract, and portions of male reproductive tract
- Simple Squamous - single layer of flattened cells (facilitates the transfer of materials, found in lungs, blood vessels, and body cavities)
Stratified Epithelium
- Stratified Epithelium - multiple layers of cells
- Stratified Squamous - multiple layers of flattened cells, can be keratinized or non-keratinized (protection from abrasion)
- Examples: skin, lining of mouth, esophagus, and vagina
- Stratified Cuboidal - multiple layers of cube-shaped cells (limited distribution, protection)
- Examples: lining of ducts of some glands
- Stratified Columnar - multiple layers of cells with the uppermost layer being columnar (protection)
- Examples: lining of male urethra, and large ducts of some exocrine glands
- Transitional - multiple layers of cells with cells that change shape (stretching, protection)
- Examples: lining of urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra, lining of urinary tract
- Stratified Squamous - multiple layers of flattened cells, can be keratinized or non-keratinized (protection from abrasion)
Membranes
- Membranes - sheets of tissue composed of cells
- Mucous Membranes - line body cavities that are open to the external environment (protective function, secrete mucous)
- Examples: lining of mouth, nose, digestive tract, and urinary tract
- Serous Membranes - line closed body cavities (lubrication, reduce friction)
- Examples: lining of the pleura, pericardium, and peritoneum
- Synovial Membranes - line the cavities of freely moveable joints (lubrication, nourish cartilage)
- Examples: knee, shoulder, hip joints
- Cutaneous Membrane - aka skin - protective outer covering
- Examples: skin
- Mucous Membranes - line body cavities that are open to the external environment (protective function, secrete mucous)
Importance in Dentistry
- Understanding epithelial tissue and membranes is important in dentistry because these tissues are present in the mouth:
- Epithelium - lining of the oral cavity, gums, and teeth
- Membranes - mucous membranes (lining the mouth), and in the periodontal ligament
- Pathologies - understanding these tissues helps in the diagnosis and treatment of oral diseases.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.