Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the types of epithelial tissues with their descriptions:
Match the types of epithelial tissues with their descriptions:
Simple Squamous Epithelium = Thin, flat plates providing a smooth, low-friction surface Cuboidal Epithelium = Cube-shaped cells commonly found in glands Columnar Epithelium = Tall, column-like cells lining the digestive tract Stratified Epithelium = Multiple layers of cells providing protection
Match the functions of connective tissue with their corresponding roles:
Match the functions of connective tissue with their corresponding roles:
Support = Providing structure and shape to organs Transportation = Moving nutrients and waste products via blood Storage = Reservoir for energy in the form of fat Protection = Defending against pathogens and injury
Match the categories of muscle tissue with their characteristics:
Match the categories of muscle tissue with their characteristics:
Skeletal Muscle = Striated and voluntary muscle responsible for movement Cardiac Muscle = Striated and involuntary muscle found in the heart Smooth Muscle = Non-striated and involuntary muscle in hollow organs Multinucleated Muscle = Characteristic of skeletal muscle fibers
Match the specializations of epithelial tissue with their functions:
Match the specializations of epithelial tissue with their functions:
Match the types of connective tissue cells with their roles:
Match the types of connective tissue cells with their roles:
Match the following types of epithelial tissue with their characteristics:
Match the following types of epithelial tissue with their characteristics:
Match the following functions with their respective connective tissues:
Match the following functions with their respective connective tissues:
Match the following categories of muscle tissue with their descriptions:
Match the following categories of muscle tissue with their descriptions:
Match the following specializations of epithelial tissue with their functions:
Match the following specializations of epithelial tissue with their functions:
Match the following connective tissue cells with their roles:
Match the following connective tissue cells with their roles:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Tissues Overview
- Tissues consist of groups of cells with similar structures working together with intercellular matrix that fills gaps between cells.
- The matrix may contain unique substances, such as salts and fibers, contributing to tissue's distinct characteristics.
Types of Tissues
- Four main types: Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, Muscle tissue, Nervous tissue.
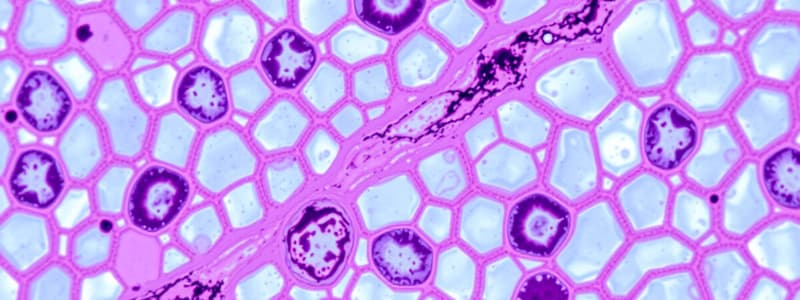
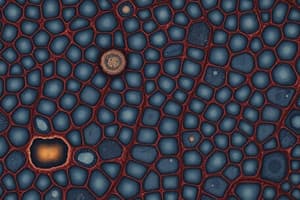
Epithelial Tissues
- Reside throughout the body, covering surfaces, lining cavities, and forming glands.
- Functions include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception.
- Cells are tightly packed with minimal intercellular matrix and supported by a basement membrane made of carbohydrates and proteins.
Shapes and Arrangements of Epithelial Cells
- Epithelial cells can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar.
- Arrangements include single (simple) or multiple layers (stratified).
Types of Epithelial Tissues
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: Flat and thin, providing a smooth, low-friction surface. Found in lungs (alveoli), blood vessels (endothelium), and lining of body cavities (mesothelium).
- Keratinized Epithelium: Contains keratin; this waterproofs and protects against abrasions, found in mammalian skin.
- Transitional Epithelium: Found in organs that stretch, like the bladder, ureters, and urethra.
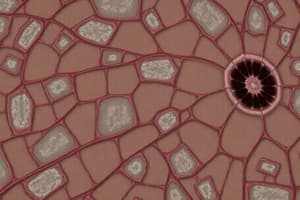
Connective Tissue
- Binds structures together, providing framework and support for organs with significant intercellular matrix and fewer cells.
- Functions include fat storage (adipose), transport (blood), disease protection, and tissue repair.
- Contains cells such as fibroblasts (extracellular matrix protein secretion), macrophages (pathogen destruction), and mast cells (histamine production).
Types of Connective Tissue
- Includes loose connective tissue, adipose tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue, elastic connective tissue, cartilage, osseous tissue (bone), and blood.
Muscle Tissue
- Composed of cells capable of contraction for body movement, characterized by high cellularity and extensive blood supply.
- Muscle fibers are elongated and arranged in bundles, containing contractile proteins actin and myosin.
Categories of Muscle Tissues
- Skeletal Muscle Tissue: Cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, under voluntary control.
- Cardiac Muscle Tissue: Branching fibers, single nucleus per cell, striated with intercalated disks, involuntary control.
- Smooth Muscle Tissue: Spindle-shaped fibers, single central nucleus, non-striated, involuntary control.
Nervous Tissue
- Located in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, responsible for coordinating body activities.
- Functions include stimulating muscle contractions, enabling consciousness, and processing emotions, memory, and reasoning.
Neurons and Glial Cells
- Neurons generate and conduct impulses and are essential for neural communication.
- Glial cells support neurons, insulating and providing nutrients, as well as protecting against bacterial invasion through phagocytosis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.