Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of epithelial tissues?
What is the primary function of epithelial tissues?
- Conducting electrical impulses
- Connection and support of other tissues
- Protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception (correct)
- Production of hormones
Which of the following is NOT one of the four main tissue types?
Which of the following is NOT one of the four main tissue types?
- Muscle
- Nervous
- Epithelial
- Endocrine (correct)
What characteristic of epithelial tissue refers to its distinct directional structures?
What characteristic of epithelial tissue refers to its distinct directional structures?
- Regeneration
- Polarity (correct)
- Specialized contacts
- Secretion
Which method is NOT typically used in studying tissue structure?
Which method is NOT typically used in studying tissue structure?
Glandular epithelia primarily function in which of the following?
Glandular epithelia primarily function in which of the following?
What is histology primarily concerned with?
What is histology primarily concerned with?
What is the role of the intestinal epithelium as a selective barrier?
What is the role of the intestinal epithelium as a selective barrier?
Which type of microscopy is used for examining thick tissue sections?
Which type of microscopy is used for examining thick tissue sections?
What is the primary function of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
What is the primary function of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
Where is transitional epithelium most commonly found?
Where is transitional epithelium most commonly found?
Which type of gland is classified as being externally secreting?
Which type of gland is classified as being externally secreting?
What distinguishes keratinized stratified squamous epithelium from nonkeratinized?
What distinguishes keratinized stratified squamous epithelium from nonkeratinized?
In which area of the body would you find stratified columnar epithelium?
In which area of the body would you find stratified columnar epithelium?
Which type of epithelium forms the moist linings of the esophagus and mouth?
Which type of epithelium forms the moist linings of the esophagus and mouth?
What characterizes glandular epithelia in general?
What characterizes glandular epithelia in general?
What is a common feature of both unicellular and multicellular glands?
What is a common feature of both unicellular and multicellular glands?
What is the primary function of hormones produced by endocrine glands?
What is the primary function of hormones produced by endocrine glands?
Which of the following glands is NOT considered an endocrine gland?
Which of the following glands is NOT considered an endocrine gland?
What is the basic structure of multicellular exocrine glands?
What is the basic structure of multicellular exocrine glands?
Which type of gland secretes substances via exocytosis as they are produced?
Which type of gland secretes substances via exocytosis as they are produced?
Which hormone-related structure is responsible for producing and releasing hormones directly into the bloodstream?
Which hormone-related structure is responsible for producing and releasing hormones directly into the bloodstream?
Which of the following is a characteristic of unicellular exocrine glands?
Which of the following is a characteristic of unicellular exocrine glands?
What is the primary difference between exocrine and endocrine glands?
What is the primary difference between exocrine and endocrine glands?
What term describes the secretion method for glands that accumulate their products until the cell ruptures?
What term describes the secretion method for glands that accumulate their products until the cell ruptures?
What is the primary function of the basement membrane in epithelial tissues?
What is the primary function of the basement membrane in epithelial tissues?
What type of epithelial cell shape is characterized as being tall and column-like?
What type of epithelial cell shape is characterized as being tall and column-like?
Which of the following statements about epithelial tissue is false?
Which of the following statements about epithelial tissue is false?
What is the role of the lateral contacts in epithelial cells?
What is the role of the lateral contacts in epithelial cells?
Which type of epithelium is classified by a single layer of flattened cells?
Which type of epithelium is classified by a single layer of flattened cells?
Which of the following statements best describes the significance of nerve innervation in epithelial tissues?
Which of the following statements best describes the significance of nerve innervation in epithelial tissues?
What causes epithelial cells to regenerate?
What causes epithelial cells to regenerate?
Which type of epithelial layer is best described as having varying shapes in each layer but classified by the shape of the apical layer?
Which type of epithelial layer is best described as having varying shapes in each layer but classified by the shape of the apical layer?
What is the primary function of the pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of the pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
Where is the ciliated variety of pseudostratified epithelium primarily found?
Where is the ciliated variety of pseudostratified epithelium primarily found?
Which characteristic distinguishes stratified epithelia from simple epithelia?
Which characteristic distinguishes stratified epithelia from simple epithelia?
What is the main protective role of stratified squamous epithelium?
What is the main protective role of stratified squamous epithelium?
How do basal cells in stratified epithelia contribute to tissue regeneration?
How do basal cells in stratified epithelia contribute to tissue regeneration?
What type of cells forms the outer layer in keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What type of cells forms the outer layer in keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which type of tissue is known for being more durable due to its protective role?
Which type of tissue is known for being more durable due to its protective role?
What type of epithelial tissue is found in the sperm-carrying ducts in males?
What type of epithelial tissue is found in the sperm-carrying ducts in males?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Epithelial Tissue
- Sheet of cells that covers body surfaces or cavities
- Examples: skin, digestive organs, and respiratory tract.
- Functions: protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception.
- Composed of two types:
- Covering and lining epithelia: found on external and internal surfaces.
- Glandular epithelia: Secretory tissue in glands.
- Epithelial tissue is selectively permeable, allowing some substances to pass through but not others.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissues
- Polarity: cells have an apical surface which faces the body exterior or cavity, a basal surface which is attached to a basement membrane, and a lateral surface which interacts with neighboring cells.
- Specialized contacts: Cells are tightly connected by junctions to form a continuous sheet.
- Supported by Connective Tissue
- All epithelia have a basement membrane
- Reinforces and resists stretching and tearing
- Defines epithelial boundary.
- Consists of two layers:
- Basal lamina: layer of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins.
- Reticular lamina: network of collagen fibers.
- All epithelia have a basement membrane
- Avascular but innervated
- No blood vessels.
- Nutrients and oxygen diffuse from connective tissue.
- Contains nerves.
- Regeneration
- Epithelial cells have high regenerative capacities.
- Stimulated by loss of polarity, broken lateral contacts, and damage from friction or hostile substances.
- Requires adequate nutrients and cell division for repair.
Classification of Epithelia
- Based on:
- Number of cell layers: Simple (single layer) or Stratified (two or more layers).
- Shape of cells: Squamous (flattened), Cuboidal (cube-shaped), Columnar (tall and column-like).
- Stratified epithelia are classified according to the shape of the cells in the apical layer.
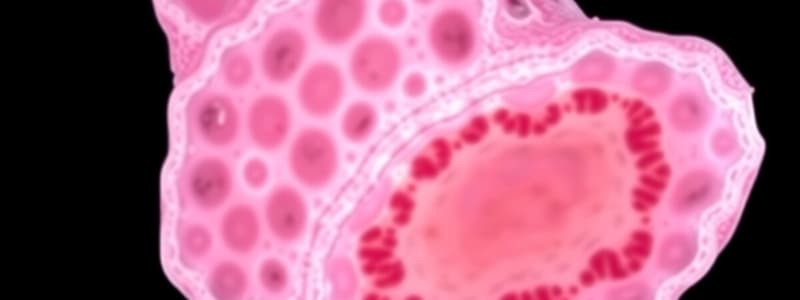
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm.
- Functions: Secrete substances, particularly mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action.
- Location: Ciliated variety lines the trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract; nonciliated type in males’ sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Thick epithelium composed of several cell layers.
- Basal cells are cuboidal or columnar and metabolically active.
- Surface cells are flattened (squamous).
- In the keratinized type, surface cells are full of keratin and dead.
- Basal cells are actively dividing and produce cells for the superficial layers.
- Function: Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion.
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
- Rare, found in ducts of larger glands.
- Typically only two cell layers thick, with other, more basal layers (e.g. squamous)
- Functions: protection and secretion.
- Location: Sweat glands, parotid glands, mammary glands.
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
- Limited distribution in the body, found in pharynx, male urethra, and lining some glandular ducts.
- Usually occurs at transition areas between two other types of epithelia.
- Only the apical layer is columnar.
Transitional Epithelium
- Found in urinary system organs (e.g., bladder)
- Cell shape can change depending on the degree of distention (stretching) of the organ.
- Relaxed state: Cells have rounded, dome-like shapes and multiple layers.
- Stretched state: Cells become thinner and squamous-like.
- Function: Permits distention of the urinary organs as they fill and empty.
Glandular Epithelia
- One or more cells that make and secrete an aqueous fluid called a secretion
- Classified by:
- Site of product release
- Endocrine: Secretes hormones internally (e.g., thyroid, pancreas).
- Exocrine: Secretes products externally (e.g., sweat, salivary glands).
- Relative number of cells forming the gland
- Unicellular: Single cell (e.g., goblet cells)
- Multicellular: Many cells (e.g., salivary glands)
- Site of product release
Endocrine Glands
- Ductless glands that secrete hormones.
- Hormones travel via lymph or blood to target organs, triggering specific responses.
- Examples: pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries/testes, thyroid and parathyroid glands, hypothalamus, adrenal glands.
Exocrine Glands
- Secrete products onto body surfaces or into body cavities through ducts.
- More numerous than endocrine glands.
- Examples: sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate, pancreas, and liver.
- Classified by:
- Structure:
- Unicellular: single cell (e.g., goblet cells).
- Multicellular: many cells.
- Mode of secretion:
- Merocrine: Secretion occurs by exocytosis (e.g., most sweat glands and pancreas).
- Structure:
Unicellular Exocrine Glands
- The only important unicellular glands are mucous cells and goblet cells.
- Found in epithelial linings of intestinal and respiratory tracts amongst columnar cells.
- Produce mucin, which dissolves in water to form mucus
- Mucus is a slimy protective and lubricating coating.
Multicellular Exocrine Glands
- Composed of a duct and a secretory unit.
- Supported by connective tissue which supplies blood and innervation.
- Connective tissue may form a capsule around the gland or extend into it, dividing it into lobes.
- Classified by:
- Structure: Shapes (simple, compound, tubular, alveolar, tubuloalveolar).
- Mode of secretion: Mechanisms of secretion (merocrine, apocrine and holocrine).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.