Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary functional distinction between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland?
What is the primary functional distinction between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland?
- The anterior pituitary primarily stores hormones produced by the hypothalamus, while the posterior pituitary synthesizes its own hormones.
- The anterior pituitary is composed of neuroendocrine cells, while the posterior pituitary contains mostly epithelial cells.
- There is no functional distinction; both lobes produce and secrete the same types of hormones.
- The anterior pituitary is composed of epithelial cells that produce and secrete hormones, while the posterior pituitary contains neuroendocrine cells that release hormones into the bloodstream. (correct)
Damage to the pineal gland is most likely to result in which of the following?
Damage to the pineal gland is most likely to result in which of the following?
- Absence of mood disorders.
- Sleep disturbances, insomnia, or irregular sleep patterns. (correct)
- Regular sleep patterns, including decreased episodes of insomnia.
- Increased regulation of the sleep-wake cycle.
What is the primary role of the blood-thymus barrier in the cortex of the thymus?
What is the primary role of the blood-thymus barrier in the cortex of the thymus?
- To regulate T cell activity within the medulla.
- To promote the secretion of thymopoietin and thymosin.
- To protect developing T cells. (correct)
- To facilitate the development of lymphatic tissue.
What is the MOST accurate description of the function of parafollicular cells (C-cells) in the thyroid gland?
What is the MOST accurate description of the function of parafollicular cells (C-cells) in the thyroid gland?
What is the MOST accurate function of the calcium-sensing receptors found on chief cells in the parathyroid gland?
What is the MOST accurate function of the calcium-sensing receptors found on chief cells in the parathyroid gland?
A patient presents with high blood pressure, diabetes, and depression. Dysfunction of which gland is MOST likely responsible?
A patient presents with high blood pressure, diabetes, and depression. Dysfunction of which gland is MOST likely responsible?
If glucagon is released from alpha cells in the pancreas because blood glucose falls below 100 mg/dL, which of the following processes is stimulated as a result?
If glucagon is released from alpha cells in the pancreas because blood glucose falls below 100 mg/dL, which of the following processes is stimulated as a result?
Which of the following BEST describes the functional relationship between estradiol and progesterone in the female reproductive system?
Which of the following BEST describes the functional relationship between estradiol and progesterone in the female reproductive system?
Which characteristic is associated with Type 1 Diabetes?
Which characteristic is associated with Type 1 Diabetes?
Which of the following is a typical manifestation of acromegaly caused by GH hypersecretion during adulthood?
Which of the following is a typical manifestation of acromegaly caused by GH hypersecretion during adulthood?
Which condition is MOST associated with iodine deficiency?
Which condition is MOST associated with iodine deficiency?
What is the MOST likely outcome of accidentally removing the parathyroid glands during a thyroidectomy?
What is the MOST likely outcome of accidentally removing the parathyroid glands during a thyroidectomy?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding individuals with Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding individuals with Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) is characterized by what?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) is characterized by what?
Besides melatonin production, what other function is associated with the pineal gland?
Besides melatonin production, what other function is associated with the pineal gland?
What is the primary functional role performed by helper T cells within the thymus?
What is the primary functional role performed by helper T cells within the thymus?
If a patient presents with increased nutrient breakdown, increased oxygen consumption, and heat production, which hormone's hypersecretion is MOST likely the cause?
If a patient presents with increased nutrient breakdown, increased oxygen consumption, and heat production, which hormone's hypersecretion is MOST likely the cause?
Which hormones are produced and released by the adrenal medulla in response to a stressful situation?
Which hormones are produced and released by the adrenal medulla in response to a stressful situation?
What is the effect of amylin, secreted by pancreatic beta cells, on gastric function and appetite?
What is the effect of amylin, secreted by pancreatic beta cells, on gastric function and appetite?
What role would testosterone play in a male approaching puberty?
What role would testosterone play in a male approaching puberty?
What typically causes individuals to be much shorter than average?
What typically causes individuals to be much shorter than average?
Promoting renal calculi (kidney stones) is seen in which disorder?
Promoting renal calculi (kidney stones) is seen in which disorder?
In cases of central precocious puberty, when do puberty changes begin in males?
In cases of central precocious puberty, when do puberty changes begin in males?
What is a key characteristic of Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome?
What is a key characteristic of Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome?
What is a symptom of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
What is a symptom of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
Mucosal neuromas are related to what disorder?
Mucosal neuromas are related to what disorder?
How do signals from the hypothalamus trigger hormone release in the posterior pituitary?
How do signals from the hypothalamus trigger hormone release in the posterior pituitary?
Which of the following processes is directly inhibited by somatostatin secretion from pancreatic delta cells?
Which of the following processes is directly inhibited by somatostatin secretion from pancreatic delta cells?
A benign tumor on the thyroid gland that can cause hyperparathyroidism is described MOST accurately by which of the following?
A benign tumor on the thyroid gland that can cause hyperparathyroidism is described MOST accurately by which of the following?
What is the primary function of pinealocytes within the pineal gland?
What is the primary function of pinealocytes within the pineal gland?
Damage to the thymus gland would MOST directly impair which of the following functions?
Damage to the thymus gland would MOST directly impair which of the following functions?
Which of the following BEST describes the role of regulatory T cells?
Which of the following BEST describes the role of regulatory T cells?
What is the MOST significant consequence of damage to the thyroid gland?
What is the MOST significant consequence of damage to the thyroid gland?
What is the primary target of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in regulating blood calcium levels?
What is the primary target of parathyroid hormone (PTH) in regulating blood calcium levels?
How do chief cells in the parathyroid gland respond to decreased blood calcium levels?
How do chief cells in the parathyroid gland respond to decreased blood calcium levels?
What is the primary role of mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex?
What is the primary role of mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex?
How do glucocorticoids, secreted by the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex, primarily affect the body?
How do glucocorticoids, secreted by the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex, primarily affect the body?
What is the function of acinar cells in the pancreas?
What is the function of acinar cells in the pancreas?
What is the primary role of estradiol in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary role of estradiol in the female reproductive system?
What is the main function of progesterone produced by the corpus luteum?
What is the main function of progesterone produced by the corpus luteum?
What is the underlying cause of Type II diabetes?
What is the underlying cause of Type II diabetes?
What is the primary cause of diabetes insipidus?
What is the primary cause of diabetes insipidus?
Excessive secretion of hormones from which zone of the adrenal cortex would MOST directly result in hypertension?
Excessive secretion of hormones from which zone of the adrenal cortex would MOST directly result in hypertension?
Which of the following pancreatic cell types is correctly paired with its hormone?
Which of the following pancreatic cell types is correctly paired with its hormone?
Which of the following is the MOST direct pathway through which light exposure influences melatonin production in the pineal gland?
Which of the following is the MOST direct pathway through which light exposure influences melatonin production in the pineal gland?
What is the primary role of circadian rhythm in regulating hormone production within the pineal gland?
What is the primary role of circadian rhythm in regulating hormone production within the pineal gland?
Which of the following immune cells of the thymus attacks and destroys targeted cells?
Which of the following immune cells of the thymus attacks and destroys targeted cells?
What is the primary effect of somatostatin, secreted by pancreatic delta cells, on gastric function?
What is the primary effect of somatostatin, secreted by pancreatic delta cells, on gastric function?
Which of the following is a direct consequence of hypersecretion of growth hormone (GH) during childhood?
Which of the following is a direct consequence of hypersecretion of growth hormone (GH) during childhood?
What is the MOST likely physiological outcome of hypothyroidism?
What is the MOST likely physiological outcome of hypothyroidism?
Which of the following is a characteristic sign of hyperthyroidism?
Which of the following is a characteristic sign of hyperthyroidism?
What is the MOST likely consequence of hypoparathyroidism on blood calcium levels and bone density?
What is the MOST likely consequence of hypoparathyroidism on blood calcium levels and bone density?
Which of the following conditions is MOST commonly associated with hyperparathyroidism?
Which of the following conditions is MOST commonly associated with hyperparathyroidism?
In Type II Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN), what is the MOST likely effect of a pheochromocytoma on blood pressure and heart rate?
In Type II Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN), what is the MOST likely effect of a pheochromocytoma on blood pressure and heart rate?
What is the MOST likely result of significant damage to the thymus?
What is the MOST likely result of significant damage to the thymus?
Which substances are co-secreted by pancreatic beta cells in response to elevated blood glucose levels after a meal?
Which substances are co-secreted by pancreatic beta cells in response to elevated blood glucose levels after a meal?
Which set of endocrine tumors is characteristic of Type 1 Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN1)?
Which set of endocrine tumors is characteristic of Type 1 Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN1)?
Flashcards
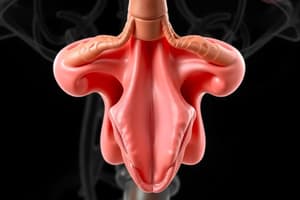
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
Divided into two main lobes, anterior and posterior, which produce different hormones.
Neuroendocrine cells
Neuroendocrine cells
Specialized nerve cells that release hormones into the bloodstream.
Pineal Gland
Pineal Gland
Receives signals from the optic nerve to regulate melatonin production and sleep patterns.
Circadian Rhythm
Circadian Rhythm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melatonin
Melatonin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thymus
Thymus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autoimmune Disorder
Autoimmune Disorder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicles (thyroid)
Follicles (thyroid)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Follicular cells (principal cells)
Follicular cells (principal cells)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parafollicular cells (C-cells)
Parafollicular cells (C-cells)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcitonin
Calcitonin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chief cells
Chief cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Gland
Adrenal Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cortex (adrenal)
Cortex (adrenal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medulla (adrenal)
Medulla (adrenal)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreas
Pancreas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Islets of Langerhans
Islets of Langerhans
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alpha cells (pancreas)
Alpha cells (pancreas)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Beta cells (pancreas)
Beta cells (pancreas)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breakdown of Glycogen
Breakdown of Glycogen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gonads
Gonads
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone
Testosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes
Diabetes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gigantism
Gigantism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pituitary dwarfism
Pituitary dwarfism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goiter
Goiter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid adenoma
Thyroid adenoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Precocious Puberty
Central Precocious Puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pinealocytes
Pinealocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Killer T cells
Killer T cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regulatory T cells
Regulatory T cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thymus Secretions
Thymus Secretions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thymus Lobe Composition
Thymus Lobe Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Follicles
Thyroid Follicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroid Capillaries
Thyroid Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parathyroid Gland Function
Parathyroid Gland Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chief Cells (Parathyroid)
Chief Cells (Parathyroid)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxyphil Cells
Oxyphil Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Cortex Functions
Adrenal Cortex Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zona Glomerulosa
Zona Glomerulosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zona Fasciculata and Reticularis
Zona Fasciculata and Reticularis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenal Medulla
Adrenal Medulla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acinar Cells
Acinar Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gonads Dual Function
Gonads Dual Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone Function
Progesterone Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type II MEN
Type II MEN
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Delta Cells
Pancreatic Delta Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thymus Function
Thymus Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Endocrine Histology
- The pituitary gland divides into the anterior and posterior lobes.
- Epithelial cells in the anterior lobe produce and secrete hormones.
- Neuroendocrine cells in the posterior lobe release hormones into the bloodstream.
- Signals from the hypothalamus reach the posterior pituitary via nerve cell axons/terminals.
- These signals trigger the release of hormones like oxytocin and vasopressin.
Pineal Gland
- Signals from the optic nerve help sense light and dark.
- This information regulates melatonin production and sleep patterns.
- Some nerve fibers travel from the optic nerve to the superior colliculi, spinal cord, sympathetic chain ganglion, and then the pineal gland.
- Melatonin production at night is regulated by the circadian rhythm, with serotonin as a precursor.
- The circadian rhythm is the internal clock that dictates when we feel awake and sleepy.
- Melatonin production is inhibited during the day when there is light, keeping humans alert.
- Melatonin production increases at night in the absence of light, signaling the body that it is time to sleep.
- Pinealocytes convert serotonin to melatonin.
- Damage to the pineal gland can cause sleep disturbances, insomnia, or irregular sleep patterns due to decreased melatonin levels, and mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Thymus
- Located behind the manubrium, above the heart.
- T cell maturation occurs.
- Killer T cells attack and destroy targeted cells, such as infected and cancerous cells.
- Helper T cells determine how the immune system reacts to threats.
- Regulatory T cells maintain immune tolerance, preventing autoimmune issues by stopping the immune system from attacking the body's own cells.
- Secretions include thymopoietin, thymosin, and thymulin, which ensure effective defense against infections and diseases, regulate T cell activity, and develop lymphatic tissue and T cells.
- The blood-thymus barrier in the cortex protects developing T cells.
- T cells decrease if the thymus is damaged, impairing infection and disease defense, weakening the immune system, and increasing cancer risk.
- A lobe is composed of a lobule, cortex, and medulla, separated by connective tissue trabeculae.
Thyroid Gland
- Located in the neck, it regulates metabolism and growth through hormone production.
- Follicles are composed of follicular cells (principal cells) that release TH (90% T4, thyroxine) and colloid.
- Parafollicular cells (C-cells) secrete calcitonin, which regulates calcium levels in the blood.
- Each follicle is surrounded by capillaries.
- TH increases nutrient breakdown, oxygen consumption, heat production, and promotes growth of bones, skin, hair, nails, and teeth and fetal nervous system development.
- Follicles are surrounded by capillaries that transport hormones into the bloodstream.
- Damage can cause hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, goiter, and metabolic issues.
Parathyroid Gland
- Monitors blood Ca2+ levels.
- Secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH) which regulates calcium levels in the blood.
- Chief cells release PTH when calcium levels are low, acting on bones, kidneys, and intestines to increase calcium.
- Chief cells have calcium-sensing receptors and a G protein system.
- The function of oxyphil cells is unknown, but they are larger than chief cells.
- More active cells producing and secreting PTH have darker cytoplasm.
- Damage can cause high BP, diabetes, depression, and other problems.
Adrenal Gland
- Regulates BP, stress response, and metabolism.
- The outer layer, cortex, is responsible for corticoid production.
- The zona glomerulosa produces mineralocorticoids like aldosterone, which regulate BP.
- The zona fasciculata and zona reticularis secrete glucocorticoids like cortisol, regulating metabolism and stress responses.
- The inner layer (medulla) has chromaffin cells (like postganglionic cells) that release catecholamines to regulate fight or flight.
Pancreas
- Islets of Langerhans are small clusters of cells.
- Alpha cells secrete glucagon between meals when blood glucose is below 100 mg/dL, acting on the liver to breakdown glycogen and conduct gluconeogenesis.
- Beta cells secrete insulin and amylin during and immediately following meals; amylin slows stomach emptying, promoting satiety.
- Delta cells secrete somatostatin, a regulator of glucagon and insulin secretion that lowers stomach acid and inhibits the release of the growth hormone GH.
- Acinar cells produce digestive enzymes that help break down food in the small intestine and absorb nutrients.
- Glucagon and insulin regulate blood sugar.
- Breakdown of glycogen into glucose occurs when the body needs a quick source of energy and blood glucose levels drop; this breakdown is called glycogenolysis, and it releases glucose into the bloodstream, further elevating blood sugar levels.
- Gluconeogenesis, glucose synthesis from fats and proteins, is increased during the production of glucose and raises blood sugar levels.
- In times of plentifully bound nutrients, insulin stimulates cells to absorb glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids for storage or metabolism, lowering blood glucose levels.
- Beta cells secrete insulin and amylin simultaneously.
- Amylin helps reduce spikes in blood glucose by slowing the emptying of the stomach, contributing to the feeling of fullness.
Gonads
- Ovaries and testes serve as both endocrine and exocrine glands.
- Sperm and eggs are part of the exocrine function, released into the reproductive tract.
- Estradiol, progesterone, and testosterone are key hormones involved in many processes.
- Estradiol, a form of estrogen, is produced by developing follicles in the ovaries, influencing menstruation and developing secondary sexual characteristics.
- Progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum of the ovaries; after ovulation, progesterone prepares the uterine lining for potential pregnancy by making it suitable for implantation of a fertilized egg.
- Interstitial cells in testes produce testosterone, which develops secondary male characteristics, such as promoting muscle mass and a deep voice, and also plays a role in sperm production.
Endocrine Disorders
- Diabetes affects blood sugar regulation.
- Type I diabetes is caused by no insulin production; it is an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks and destroys cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Type II diabetes is caused by insulin resistance, where the body produces insulin but does not respond to it well.
- Diabetes Insipidus is caused by ADH hyposecretion, where the body does not produce enough ADH, leading to a lot of urine production, which can lead to dehydration.
- "Insipidus" refers to the lack of sweetness of the urine in contrast to the sugary urine of diabetes mellitus.
- GH disorders are pituitary disorders that affect growth.
- Gigantism results from hypersecretion of growth hormone (GH) in childhood, leading to individuals who are much taller than average.
- Pituitary dwarfism is caused by GH hyposecretion during childhood, leading to individuals who are shorter than average.
- Acromegaly is caused by overproduction of GH during adulthood, causing thickening of bones and soft tissues, with noticeable effects on the hands, feet, and face.
- TH disorders affect the thyroid.
- Hypothyroidism is caused by the thyroid gland not producing enough TH, causing lowered metabolism, weight gain, and lethargy.
- Hyperthyroidism is caused by a thyroid gland producing too much thyroid hormone, causing an accelerated metabolism, weight loss, and an increased heart rate.
- Goiter is caused by a lack of iodine in the diet, causing the gland to be unable to synthesize TH. Without TH, the pituitary gland receives no feedback and acts as if the thyroid were understimulated, causing it to secrete extra TSH, which makes the thyroid produce more colloids. Accumulated colloid cannot be iodinated to make TH and produces visible swelling in the neck.
- Hypoparathyroidism, is when not enough PTH produced, which causes low blood Ca2+, increased bone density, and issues with muscle contraction especially the heart.
- A fatal tetany can result, which are suffocating spasms of muscles of the larynx which can happen in two to three days after a complication of thyroid surgery where the parathyroid was accidentally removed or degenerated from a cut-off blood supply.
- Hyperparathyroidism results from increased secretion of PTH, increasing blood calcium and can be caused by adenomas, which are benign tumors. Bones become soft, fragile, and deformed, also promoting the formation of renal calculi (kidney stones).
- Central precocious puberty is when the body matures earlier than normal, generally at the age of 8 for females and 9 years for males, and causes include early GnRH release, childhood obesity, brain/pituitary tumors, meningitis, cancer treatments, and genetics.
- Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome occurs when the body does not respond to androgens. People with AIS are "male" because they have XY chromosomes, but they don't have a scrotum or penis. The testes are undescended in the abdomen and produce normal male levels of testosterone, however, the target cells lack receptors for it. This causes them to not be able to develop facial hair, deep voices, or muscle mass. People with AIS may have a female appearance as if no testosterone were present. They do not have a uterus or menstraution, but do have a vagina and labia.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, as well as irregular periods and excess androgen levels.
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) is a group of disorders that affect the endocrine glands.
- MEN is characterized by tumors in 2+ endocrine glands, which can possibly be benign or malignant.
- Type 1 MEN is characterized by tumors in the parathyroid, pancreas, and pituitary; hyperparathyroidism can cause kidney stones, bone thinning, and high HP.
- Type II MEN is characterized by tumors in the thyroid and parathyroid glands; 50% of times there are also tumors on the adrenal gland called pheochromocytoma. This tumor causes the adrenal gland to produce too much adrenaline and noradrenaline, which can cause panic attack symptoms such as high BP and rapid HR. Mucosal neuromas are noncancerous tumors that can develop in the mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, and digestive tract.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.