Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the initial position of the duodenum before it shifts during rotation?
What is the initial position of the duodenum before it shifts during rotation?
- Posterior to the pancreas
- Midline position (correct)
- Left side of the abdominal cavity
- Right side of the abdominal cavity
What is the primary blood supply to the duodenum?
What is the primary blood supply to the duodenum?
- Renal artery
- Internal thoracic artery
- Inferior mesenteric artery
- Celiac artery and branches (correct)
During which week does the liver primordium appear as an outgrowth of the endodermal epithelium?
During which week does the liver primordium appear as an outgrowth of the endodermal epithelium?
- First week
- Second week
- Third week (correct)
- Fourth week
What structure is formed by the ventral outgrowth of the bile duct?
What structure is formed by the ventral outgrowth of the bile duct?
What happens to the liver’s hematopoietic function by the end of intrauterine life?
What happens to the liver’s hematopoietic function by the end of intrauterine life?
What is the weight of the liver at approximately the 10th week of development in relation to total body weight?
What is the weight of the liver at approximately the 10th week of development in relation to total body weight?
The structures known as the lesser omentum and falciform ligament are derived from which part of the body?
The structures known as the lesser omentum and falciform ligament are derived from which part of the body?
What is the connection formed between the hepatic diverticulum and the foregut called?
What is the connection formed between the hepatic diverticulum and the foregut called?
Which part of the gut tube is primarily derived from endoderm?
Which part of the gut tube is primarily derived from endoderm?
What defines an organ as retroperitoneal?
What defines an organ as retroperitoneal?
What structure is formed from the dorsal mesentery in the region of the stomach?
What structure is formed from the dorsal mesentery in the region of the stomach?
Where does the ventral mesentery exist?
Where does the ventral mesentery exist?
What is the function of mesenteries?
What is the function of mesenteries?
What is derived from the dorsal pancreatic bud?
What is derived from the dorsal pancreatic bud?
During which developmental week does the connection of the gut tube to the mesenchyme narrow?
During which developmental week does the connection of the gut tube to the mesenchyme narrow?
What divides the ventral mesentery into the lesser omentum and falciform ligament?
What divides the ventral mesentery into the lesser omentum and falciform ligament?
What artery supplies the entire length of the midgut?
What artery supplies the entire length of the midgut?
When does insulin secretion begin during development?
When does insulin secretion begin during development?
What is the function of peritoneal ligaments?
What is the function of peritoneal ligaments?
Which structure is formed at the site of the minor papilla in the duodenum?
Which structure is formed at the site of the minor papilla in the duodenum?
Which part of the gut arises from the cephalic limb of the primary intestinal loop?
Which part of the gut arises from the cephalic limb of the primary intestinal loop?
What does the hindgut give rise to?
What does the hindgut give rise to?
What forms the pancreatic connective tissue?
What forms the pancreatic connective tissue?
At what point in fetal development does the midgut communicate with the yolk sac?
At what point in fetal development does the midgut communicate with the yolk sac?
What is formed from the ventral portion of the foregut once the respiratory diverticulum appears?
What is formed from the ventral portion of the foregut once the respiratory diverticulum appears?
How is the muscular coat of the esophagus differentiated in its upper two-thirds and lower third?
How is the muscular coat of the esophagus differentiated in its upper two-thirds and lower third?
What direction does the stomach rotate around its longitudinal axis during development?
What direction does the stomach rotate around its longitudinal axis during development?
Which structure is a derivative of the dorsal mesogastrium during stomach development?
Which structure is a derivative of the dorsal mesogastrium during stomach development?
Which part of the gut does the duodenum primarily originate from?
Which part of the gut does the duodenum primarily originate from?
What is the result of the faster growth of the posterior wall of the stomach during its rotation?
What is the result of the faster growth of the posterior wall of the stomach during its rotation?
After the rotation of the stomach, which nerve innervates the anterior wall?
After the rotation of the stomach, which nerve innervates the anterior wall?
What anatomical shape does the duodenum take as it forms during stomach rotation?
What anatomical shape does the duodenum take as it forms during stomach rotation?
Flashcards
What are the sections of the developing gut tube?
What are the sections of the developing gut tube?
The development of the primitive gut tube is divided into four sections: pharynx, foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
What germ layers contribute to the development of the digestive system?
What germ layers contribute to the development of the digestive system?
The epithelial lining of the digestive tract is derived from the endoderm. The muscle, connective tissue, and peritoneal components of the gut wall are derived from the visceral mesoderm.
What are mesenteries?
What are mesenteries?
Double layers of peritoneum that enclose an organ and connect it to the body wall. They provide pathways for vessels, nerves, and lymphatics to and from abdominal viscera.
What are intraperitoneal and retroperitoneal organs?
What are intraperitoneal and retroperitoneal organs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are peritoneal ligaments?
What are peritoneal ligaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the dorsal mesentery and what structures does it form?
What is the dorsal mesentery and what structures does it form?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the ventral mesentery?
What is the ventral mesentery?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the liver affect the ventral mesentery?
How does the liver affect the ventral mesentery?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duodenum Position Shift
Duodenum Position Shift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duodenum and Pancreas Fixation
Duodenum and Pancreas Fixation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duodenum Recanalization
Duodenum Recanalization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver Development
Liver Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Duct Formation
Bile Duct Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gallbladder Development
Gallbladder Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver Weight and Function
Liver Weight and Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver Hematopoiesis
Liver Hematopoiesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophagus Development
Esophagus Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophagus Muscle Types
Esophagus Muscle Types
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomach Development
Stomach Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomach Rotation
Stomach Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stomach Curvatures
Stomach Curvatures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Duodenum Development
Duodenum Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spleen Development
Spleen Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foregut and Midgut Junction
Foregut and Midgut Junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreas Development
Pancreas Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Bud Locations
Pancreatic Bud Locations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Bud Fusion
Pancreatic Bud Fusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Bud Contributions
Pancreatic Bud Contributions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Duct Formation
Pancreatic Duct Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Duct Entry
Pancreatic Duct Entry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midgut Development
Midgut Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midgut Loop Development
Midgut Loop Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Embryology L10: Digestive System
-
The development of the primitive gut tube and its derivatives is typically discussed in four sections:
- Foregut: Extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the respiratory diverticulum.
- Midgut: Remainder of the foregut.
- Hindgut: The remainder of the foregut.
-
Endoderm forms the epithelial lining of the digestive tract. Muscle, connective tissue, and peritoneal components of the gut wall are derived from visceral mesoderm.
Divisions of the Gut Tube
- The foregut, midgut, and hindgut initially contact the mesenchyme of the posterior abdominal wall.
- By the fifth week, these regions are suspended from the abdominal wall by the dorsal mesentery.
- The stomach develops a dorsal mesogastrium (greater omentum).
- The duodenum develops a dorsal mesoduodenum.
- The colon develops a dorsal mesocolon.
- The jejunal and ileal loops develop the mesentery proper.
Mesenteries
- Double layers of peritoneum suspend portions of the gut tube and its derivatives from the dorsal and ventral body walls.
- Organs enclosed by peritoneum are intraperitoneal; those against the posterior body wall are retroperitoneal (e.g., kidneys).
- These layers/mesenteries provide pathways for vessels, nerves, lymphatics to and from abdominal viscera.
Foregut
- Esophagus: The esophagus develops from the foregut as the respiratory diverticulum (lung bud) emerges.
- The muscular coat is striated in the upper two-thirds and innervated by the vagus nerve; the lower third is smooth muscle and innervated by splanchnic plexuses.
- Stomach: The stomach forms as a dilation of the foregut and rotates, changing position.
- The left side faces anteriorly and the right side posteriorly.
- The original posterior wall grows faster than the anterior wall to create the greater and lesser curvatures.
- During further growth, the stomach rotates, moving the pyloric part to the right and the cardiac portion to the left.
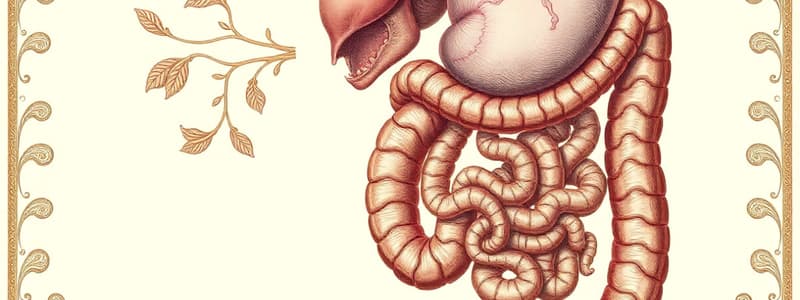
Duodenum
- Formed by the terminal part of the foregut and the cephalic portion of the midgut.
- Initially in the midline, rotation leads to a C-shape and placement on the right side of the abdominal cavity.
- The duodenum and head of the pancreas press against the dorsal body wall in a retroperitoneal position.
- The lumen is obliterated then recanalized during the second month of development.
- The duodenum is supplied by branches from both celiac and superior mesenteric arteries.
Liver and Gallbladder
- The liver primordium (liver bud) appears in the third week, extending from the foregut.
- The hepatic cells penetrate the septum transversum and connect to the foregut (duodenum), forming the bile duct.
Midgut
- Develops into the duodenum, jejunum, part of the ileum, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, and proximal two-thirds of the transverse colon.
- The midgut is suspended by the superior mesenteric artery and initially connected to the yolk sac via the vitelline duct. The gut and its mesentery elongate, forming the primary intestinal loop (first mesenteric loop).
Hindgut
- The distal third of the transverse colon, the descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and upper anal canal originate from the hindgut.
- The endoderm of the hindgut develops into the internal lining of the bladder and urethra..
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.