Podcast
Questions and Answers
From which germ layer does the epithelial lining of the digestive system originate?
From which germ layer does the epithelial lining of the digestive system originate?
- Coelom
- Endoderm (correct)
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
Which of the following structures does NOT originate from the foregut?
Which of the following structures does NOT originate from the foregut?
- Gallbladder
- Duodenum (correct)
- Liver
- Pancreas (dorsal bud)
What is the function of the mesenteries during the development of the gut?
What is the function of the mesenteries during the development of the gut?
- To provide structural support and contain blood vessels and nerves (correct)
- To filter waste products from the developing gut
- To induce rotation of the midgut
- To secrete digestive enzymes into the gut lumen
Around which axis does the primary intestinal loop rotate?
Around which axis does the primary intestinal loop rotate?
From which structure does the gallbladder originate?
From which structure does the gallbladder originate?
What structure is formed by the ventral pancreatic bud?
What structure is formed by the ventral pancreatic bud?
What is the approximate degree of counterclockwise rotation completed by the midgut during its development?
What is the approximate degree of counterclockwise rotation completed by the midgut during its development?
Which portion of the developing gut tube is characterized by herniation and subsequent return into the body cavity during rotation?
Which portion of the developing gut tube is characterized by herniation and subsequent return into the body cavity during rotation?
During which month of fetal life do the pancreatic islets develop?
During which month of fetal life do the pancreatic islets develop?
If the ventral pancreatic bud fails to properly migrate and fuse with the dorsal bud during development, what condition might this result in?
If the ventral pancreatic bud fails to properly migrate and fuse with the dorsal bud during development, what condition might this result in?
Which of the following structures originate from the gut during development?
Which of the following structures originate from the gut during development?
Which stage of gut development is characterized by the formation of the primary gut tube?
Which stage of gut development is characterized by the formation of the primary gut tube?
Which of the following structures is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption in the gut?
Which of the following structures is primarily responsible for nutrient absorption in the gut?
Flashcards
Primitive Gut Origin
Primitive Gut Origin
Originates from endoderm during cephalocaudal flexion, forming digestive and respiratory systems' lining and glands.
Endoderm Differentiation
Endoderm Differentiation
Intraembryonic endoderm forms the digestive tube, while extraembryonic endoderm lines the yolk sac.
Gut Tube Divisions
Gut Tube Divisions
Foregut, midgut, and hindgut, with the cloacal membrane persisting longer than the buccopharyngeal membrane.
Mesenteries
Mesenteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liver Primordium
Liver Primordium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gallbladder Origin
Gallbladder Origin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pancreatic Buds
Pancreatic Buds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventral Pancreatic Bud
Ventral Pancreatic Bud
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midgut Rotation Axis
Midgut Rotation Axis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midgut Rotation Result
Midgut Rotation Result
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- The primitive gut originates from the endoderm during cephalocaudal flexion of the embryo.
- The endoderm gives rise to the epithelial lining and glands of both the digestive and respiratory systems.
- Initial stages involve constriction of the yolk sac, delineating the intraembryonic endoderm (future digestive tube) and the extraembryonic endoderm (inner lining of the yolk sac).
- In sagittal section, the gut tube develops in 3 parts: foregut, midgut, and hindgut, which includes the cloaca.
- The cloacal membrane persists longer than the buccopharyngeal membrane.
- Portions of the gut tube and its derivatives are suspended from the dorsal and ventral body wall by mesenteries, which are double layers of peritoneum that enclose an organ and connect it to the body wall.
- Organs suspended by mesenteries are referred to as intraperitoneal.
- Those that lie against the posterior abdominal wall and are covered by peritoneum are retroperitoneal.
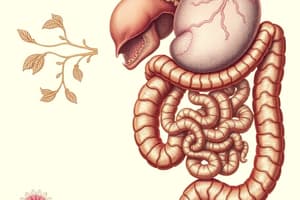
- The liver primordium appears in the middle of the 3rd week, as an outgrowth of the endodermal epithelium at the distal end of the foregut.
- The liver bud consists of rapidly proliferating cells that penetrates the septum transversum.
- The connection between the liver and the foregut narrows into the bile duct.
- A small ventral outgrowth from the bile duct gives rise to the gallbladder and cystic duct.
- The pancreas is formed by two buds (dorsal and ventral) that originate from the endodermal lining of the duodenum.
- When the duodenum rotates to the right and becomes C-shaped, the ventral bud comes to lie immediately below and behind the dorsal bud.
- The ventral bud forms the lower uncinate process of the pancreas and the remainder develops from the dorsal bud.
- Pancreatic islets develop during the 3rd month of fetal life, and insulin secretion begins during the 5th month.
- The primary intestinal loop grows in length and rotates around an axis formed by the superior mesenteric artery.
- Viewed from the front, the rotation is counterclockwise and amounts to about 270° when complete.
- During rotation, the jejunum continues to grow in length so the jejunum and ileum form a number of coiled loops.
- The large intestine (of the midgut) does not participate in rotation.
- Rotation occurs while the midgut tube is herneated out and returned into the body cavity.
- Retraction of the herniated loops occurs around the 10th week.
- The vitelline duct is a long narrow tube that joins the yolk sac to the digestive tube; it is a remnant of this connection at the end of the 4th week.
- As a rule the duct undergoes complete obliteration during the seventh week, but in about two per cent of cases its proximal part persists as a diverticulum from the small intestine (Meckel's diverticulum).
- Meckel's diverticulum is situated about two feet above the ileocecal junction, and may be attached by a fibrous cord to the abdominal wall at the umbilicus.
- Sometimes a narrowing of the lumen of the ileum is seen opposite the site of attachment of the duct.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.