Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which two bones articulate at the humeroulnar joint?
Which two bones articulate at the humeroulnar joint?
- Humerus and Radius
- Humerus and Ulna (correct)
- Radius and Ulna
- Ulna and Scapula
What is the function of the medial and lateral lips of the trochlea?
What is the function of the medial and lateral lips of the trochlea?
- They facilitate rotation of the forearm.
- They create a tight configuration of the humeroulnar joint. (correct)
- They allow for greater flexion at the elbow.
- They provide muscle attachment points.
Which structure is located on the ulna?
Which structure is located on the ulna?
- Medial Epicondyle
- Humeral Head
- Trochlear Notch (correct)
- Capitulum
Which joint is formed by the radius and ulna at the proximal end?
Which joint is formed by the radius and ulna at the proximal end?
What distinguishes the head of the ulna from the head of the radius in terms of their anatomical location?
What distinguishes the head of the ulna from the head of the radius in terms of their anatomical location?
During forearm pronation, what is the role of the pronator quadratus muscle?
During forearm pronation, what is the role of the pronator quadratus muscle?
What is a characteristic feature of the elbow joint based on its structure?
What is a characteristic feature of the elbow joint based on its structure?
Which anatomical structure articulates with the concave fovea of the radius?
Which anatomical structure articulates with the concave fovea of the radius?
In the context of the humeroulnar joint, what occurs during flexion?
In the context of the humeroulnar joint, what occurs during flexion?
What happens to the radius during pronation in a closed-chain position?
What happens to the radius during pronation in a closed-chain position?
Which joint allows for rotation without a slide during both pronation and supination?
Which joint allows for rotation without a slide during both pronation and supination?
What occurs at the humeroradial joint during forearm motion?
What occurs at the humeroradial joint during forearm motion?
During supination, how do the radius and ulna interact at the distal radio-ulnar joint?
During supination, how do the radius and ulna interact at the distal radio-ulnar joint?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
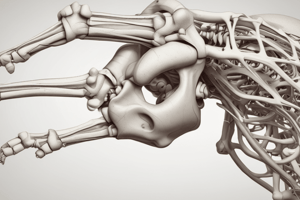
Elbow and Forearm Complex
- The elbow and forearm complex is comprised of three bones: humerus, radius, and ulna.
- There are four joints that make up the complex: humeroradial joint, humeroulnar joint, proximal radio-ulnar joint, and distal radio-ulnar joint.
- The trochlea and capitulum of the humerus are the two articulation points for the radius and ulna, respectively.
- The medial and lateral epicondyles are palpable points on the humerus.
- The olecranon process and trochlear notch are found on the ulna, but not the humerus.
- The head of the ulna is convex and articulates with the radius distally.
- The head of the radius is concave and articulates with the capitulum of the humerus.
- Pronator quadratus attaches to the radius and facilitates pronation.
- Supinator attaches to the radius and facilitates supination.
- The carpal bones of the wrist rest within the radius and become fixed in a closed-chain position.
- The elbow joint is a modified hinge joint, meaning there is slight axial rotation and side-to-side motion during flexion and extension.
- The elbow joint is comprised of the humeroulnar and humeroradial joints.
- Full extension of the elbow requires extensibility of the anterior structures (skin, biceps, anterior capsule, anterior fibers of the medial collateral ligament).
- Full flexion requires extensibility of the posterior structures (posterior capsule, triceps).
- The humeroulnar joint has a roll and slide in the same direction during flexion and extension.
- The humeroradial joint also has a roll and slide in the same direction during flexion and extension.
- Pronation and supination occur in the horizontal plane.
- Supination is when the radius and ulna are aligned, and the hand is in a supinated position.
- Pronation is when the radius rotates over the ulna.
- The proximal radio-ulnar joint has a rotation without a slide because of the annular ligament.
- The distal radio-ulnar joint has a traditional roll and slide during supination.
- During closed-chain pronation, the ulna rotates around the fixed radius.
- During closed-chain pronation, the humerus also rotates (external rotation) due to its connection to the ulna.
- During closed-chain supination, the humerus rotates internally.
- The humeroradial joint has a spin motion due to the concave favea of the radius against the convex capitulum of the humerus.
- The humeroradial joint is prone to degeneration due to the compression torque from supinator and pronator muscles.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.