Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which characteristic describes the body plan of echinoderms?
Which characteristic describes the body plan of echinoderms?
- Bilateral symmetry
- Asymmetrical
- Radial symmetry (correct)
- Cephalization present
What is the primary function of the water vascular system in sea stars?
What is the primary function of the water vascular system in sea stars?
- Respiration
- Reproduction
- Feeding
- Movement (correct)
Which of the following echinoderms are known to have feathery arms for feeding?
Which of the following echinoderms are known to have feathery arms for feeding?
- Sea lilies (correct)
- Brittle stars
- Sea urchins
- Sea cucumbers
What type of feeders are most brittle stars categorized as?
What type of feeders are most brittle stars categorized as?
What unique feature do sea cucumbers have compared to other echinoderms?
What unique feature do sea cucumbers have compared to other echinoderms?
Which class of echinoderms does not possess arms?
Which class of echinoderms does not possess arms?
What structure is the starting point of the water vascular system in sea stars?
What structure is the starting point of the water vascular system in sea stars?
Which of the following invertebrate systems is responsible for movement and support in organisms?
Which of the following invertebrate systems is responsible for movement and support in organisms?
Which of the following statements correctly describes characteristics of centipedes?
Which of the following statements correctly describes characteristics of centipedes?
What distinguishes millipedes from centipedes?
What distinguishes millipedes from centipedes?
In which subphylum do you find organisms that have three pairs of legs and could undergo metamorphosis?
In which subphylum do you find organisms that have three pairs of legs and could undergo metamorphosis?
How does the respiratory system of grasshoppers function?
How does the respiratory system of grasshoppers function?
Which type of symbiotic relationship is demonstrated when ants protect aphids in exchange for food?
Which type of symbiotic relationship is demonstrated when ants protect aphids in exchange for food?
Which of the following phyla includes creatures known as sponges?
Which of the following phyla includes creatures known as sponges?
Which feature is characteristic of all members of the Kingdom Animalia?
Which feature is characteristic of all members of the Kingdom Animalia?
What type of symmetry is characterized by having no plane of symmetry?
What type of symmetry is characterized by having no plane of symmetry?
In which evolutionary development does the blastopore become the mouth?
In which evolutionary development does the blastopore become the mouth?
What is the name given to the body plan that includes a fluid-filled body cavity containing internal organs?
What is the name given to the body plan that includes a fluid-filled body cavity containing internal organs?
Which of the following best describes bilateral symmetry?
Which of the following best describes bilateral symmetry?
What is the correct order of the stages in the evolution of a body cavity?
What is the correct order of the stages in the evolution of a body cavity?
Cephalization refers to an evolutionary trend where...
Cephalization refers to an evolutionary trend where...
What characteristic is unique to tapeworms in comparison to other worms?
What characteristic is unique to tapeworms in comparison to other worms?
How does Trichinella infection occur?
How does Trichinella infection occur?
What defines the nematode digestive system?
What defines the nematode digestive system?
Which of the following is an example of a segmented worm?
Which of the following is an example of a segmented worm?
What is the primary feature of class Polychaeta within the Annelida phylum?
What is the primary feature of class Polychaeta within the Annelida phylum?
What is an important trait of roundworms in terms of body structure?
What is an important trait of roundworms in terms of body structure?
What is the method of transmission for the eye worm?
What is the method of transmission for the eye worm?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the circulatory system of segmented worms?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the circulatory system of segmented worms?
What structure in mollusks is responsible for their primary movement?
What structure in mollusks is responsible for their primary movement?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with the Class Cephalopoda?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with the Class Cephalopoda?
Which type of excretion system is found in earthworms?
Which type of excretion system is found in earthworms?
Which of the following best describes the body symmetry of arthropods?
Which of the following best describes the body symmetry of arthropods?
What is a unique characteristic of leeches in the Class Hirudinea?
What is a unique characteristic of leeches in the Class Hirudinea?
Which class of mollusks includes species like clams and oysters?
Which class of mollusks includes species like clams and oysters?
What is the primary function of the mantle in mollusks?
What is the primary function of the mantle in mollusks?
Which characteristic is typical for the subphylum Chelicerata?
Which characteristic is typical for the subphylum Chelicerata?
What type of circulatory system do arthropods have?
What type of circulatory system do arthropods have?
Which of the following groups are considered mollusks?
Which of the following groups are considered mollusks?
What defines a pseudocoelom?
What defines a pseudocoelom?
Which organism is an example of a coelomate?
Which organism is an example of a coelomate?
What is a key characteristic of Phylum Porifera?
What is a key characteristic of Phylum Porifera?
Which type of body symmetry is found in Cnidarians?
Which type of body symmetry is found in Cnidarians?
What form does a medusa take in Cnidarians?
What form does a medusa take in Cnidarians?
Which class of flatworms is known for being free-living and carnivorous?
Which class of flatworms is known for being free-living and carnivorous?
What is the primary characteristic of Class Trematoda?
What is the primary characteristic of Class Trematoda?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of flatworms?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of flatworms?
What function do nematocysts serve in cnidarians?
What function do nematocysts serve in cnidarians?
Which term accurately describes the body structure of a sponge?
Which term accurately describes the body structure of a sponge?
Flashcards
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that lack cell walls. They are heterotrophic, meaning they get their nutrients from other organisms.
Invertebrates
Invertebrates
Invertebrates are animals without a backbone. They make up the majority of the animal kingdom.
Invertebrate Body Plans
Invertebrate Body Plans
Invertebrates have a wide variety of body plans, including those with radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and no symmetry, all of which evolved independently.
What are tapeworms?
What are tapeworms?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are tapeworms transmitted?
How are tapeworms transmitted?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What defines a roundworm?
What defines a roundworm?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do ascarids infect a host?
How do ascarids infect a host?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe key characteristics of segmented worms.
Describe key characteristics of segmented worms.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the characteristics of Polychaetes?
What are the characteristics of Polychaetes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the characteristics of Oligochaetes.
Describe the characteristics of Oligochaetes.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Subphylum Uniramia?
What is the Subphylum Uniramia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the characteristics of a centipede?
What are the characteristics of a centipede?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the characteristics of a millipede?
What are the characteristics of a millipede?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the characteristics of insects.
Describe the characteristics of insects.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is symbiosis and what are the types?
What is symbiosis and what are the types?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a pseudocoelom?
What is a pseudocoelom?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a coelom?
What is a coelom?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Phylum Porifera?
What is Phylum Porifera?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the sponge body plan.
Describe the sponge body plan.
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does water flow through a sponge?
How does water flow through a sponge?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Phylum Cnidaria?
What is Phylum Cnidaria?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compare and contrast the polyp and medusa body forms.
Compare and contrast the polyp and medusa body forms.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cnidocytes?
What are cnidocytes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Class Hydrozoa?
What is Class Hydrozoa?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Class Scyphozoa?
What is Class Scyphozoa?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nephridia
Nephridia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Earthworm Digestive System
Earthworm Digestive System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Class Hirudinea (Leeches)
Class Hirudinea (Leeches)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phylum Mollusca (Mollusks)
Phylum Mollusca (Mollusks)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mollusk body plan
Mollusk body plan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Class Bivalvia
Class Bivalvia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Class Gastropoda (Gastropods)
Class Gastropoda (Gastropods)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Class Cephalopoda (Cephalopods)
Class Cephalopoda (Cephalopods)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phylum Arthropoda (Arthropods)
Phylum Arthropoda (Arthropods)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subphylum Trilobita (Trilobites)
Subphylum Trilobita (Trilobites)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Phylum Echinodermata?
What is Phylum Echinodermata?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the water vascular system?
What is the water vascular system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are sea stars?
What are sea stars?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are brittle stars?
What are brittle stars?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are sea urchins and sand dollars?
What are sea urchins and sand dollars?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are sea cucumbers?
What are sea cucumbers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are exoskeletons and endoskeletons?
What are exoskeletons and endoskeletons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a hydrostatic skeleton?
What is a hydrostatic skeleton?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Invertebrates
- Kingdom Animalia includes invertebrates and vertebrates
- Invertebrates lack a backbone
- Invertebrates are a diverse group of animals, including sponges (Porifera), cnidarians (Cnidaria), flatworms (Platyhelminthes), roundworms (Nematoda), segmented worms (Annelida), mollusks (Mollusca), arthropods (Arthropoda), and echinoderms (Echinodermata)
- All animals (including invertebrates) are eukaryotes, multicellular, and heterotrophs
- They lack cell walls
Invertebrate Phyla
- There are 8 invertebrate phyla:
- Phylum Porifera (sponges)
- Phylum Cnidaria (cnidarians)
- Phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
- Phylum Nematoda (roundworms)
- Phylum Annelida (segmented worms)
- Phylum Mollusca (mollusks)
- Phylum Arthropoda (arthropods)
- Phylum Echinodermata (echinoderms)
Trends in Animal Evolution
- Cell Specialization: different organs and tissues with a specialized function
- Early Development: Protostomes and Deuterostomes; protostomes mouth forms first, in deuterostomes, the anus forms first
- Body Symmetry: asymmetry (no symmetry), radial symmetry (multiple planes of symmetry), or bilateral symmetry (one plane of symmetry)
- Cephalization: concentration of nerve and sensory organs in the head
- Body Cavity (coelom): acoelomates (no body cavity), pseudocoelomates (partially lined body cavity), and coelomates (completely lined body cavity).
Phylum Porifera (Sponges)
- Latin "poros" meaning passage
- Filter feeders using collar cells
- Endoskeleton made of spongin and/or spicules of calcium carbonate or silica, amoeboid cells help digest food
- Body plan is asymmetric, no germ layers, no body cavity, no cephalization
Phylum Cnidaria (Cnidarians)
- Latin "cnidaria" meaning nettles, mostly carnivores
- Tentacles bear stinging nematocysts, alternate between polyp and medusa body forms, have a gastrovascular cavity (GVC), and have a hydrostatic skeleton
- Body plan has two germ layers and radial symmetry and no cephalization
Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
- Latin "platy" = flat, "helminth" = worm
- Unsegmented
- Free-living or parasitic
- Hydrostatic skeleton
- Three germ layers, acoelomate, bilateral symmetry, cephalization is present
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms)
- Latin "nemato" = thread
- Unsegmented
- Digestive system has two openings (a mouth and an anus)
- Hydrostatic skeleton
- Free-living or parasitic
- Three germ layers, pseudocoelomate, and bilateral symmetry, cephalization is present
Phylum Annelida (Segmented Worms)
- Latin "annellus" = little ring, body composed of segments separated by internal partitions
- Digestive system with two openings
- Closed circulatory system
- Respiration by diffusion across skin
- Hydrostatic skeleton
- Three germ layers, coelomates, and bilateral symmetry, cephalization is present
Phylum Mollusca (Mollusks)
- Latin "molluscus" = soft
- Four body parts:
- Foot
- Shell (endo- or exoskeleton)
- Mantle
- Visceral mass
- Digestive system with two openings
- Three germ layers, coelomate, and bilateral symmetry, cephalization is present
Phylum Arthropoda (Arthropods)
- Latin "arthro" = jointed, "poda" = foot
- Exoskeleton of chitin
- Jointed appendages
- Segmented body
- Many undergo metamorphosis during development
- Open circulatory system
- Three germ layers, coelomate, and bilateral symmetry, cephalization is present
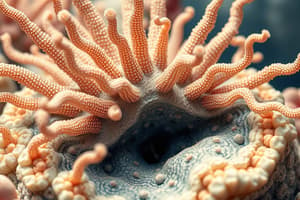
Phylum Echinodermata (Echinoderms)
- Latin "echino" = spiny, "dermata" = skin
- Deuterostomes
- Water vascular system
- Respiration across skin, gills
- Endoskeleton
- Three germ layers, coelomate, radial symmetry, no cephalization is present
Invertebrate Systems
- Six major invertebrate systems:
- Skeletal system
- Digestive system
- Circulatory system
- Respiratory system
- Excretory system
- Nervous system
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.