Podcast
Questions and Answers
What characterizes simple diffusion?
What characterizes simple diffusion?
- Requires energy for transport.
- Moves from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. (correct)
- Transports large and hydrophilic molecules.
- Involves transporter proteins.
What is the primary role of facilitated diffusion?
What is the primary role of facilitated diffusion?
- It requires ATP for transport.
- It transports materials against their concentration gradient.
- It transports water across a selectively permeable membrane.
- It uses channel or carrier proteins to transport molecules. (correct)
In which solution does water move into a cell, causing it to swell?
In which solution does water move into a cell, causing it to swell?
- Hypotonic solution (correct)
- Hypertonic solution
- Concentrated solution
- Isotonic solution
What happens in a hypertonic solution regarding cell volume?
What happens in a hypertonic solution regarding cell volume?
What process involves the diffusion of water across a membrane?
What process involves the diffusion of water across a membrane?
What energy source is used in the process of filtration?
What energy source is used in the process of filtration?
Which of the following describes an isotonic solution?
Which of the following describes an isotonic solution?
Which type of molecules primarily undergoes simple diffusion?
Which type of molecules primarily undergoes simple diffusion?
What is the main property of the plasma membrane that is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis?
What is the main property of the plasma membrane that is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis?
In the fluid-mosaic model, what structure primarily composes the plasma membrane?
In the fluid-mosaic model, what structure primarily composes the plasma membrane?
Which type of protein spans the entire width of the plasma membrane?
Which type of protein spans the entire width of the plasma membrane?
What role does cholesterol play in the plasma membrane?
What role does cholesterol play in the plasma membrane?
Which function of the plasma membrane involves regulating the flow of nutrients and waste products?
Which function of the plasma membrane involves regulating the flow of nutrients and waste products?
How do membrane proteins assist in cell communication?
How do membrane proteins assist in cell communication?
What are peripheral proteins primarily involved in regarding the plasma membrane?
What are peripheral proteins primarily involved in regarding the plasma membrane?
What characteristic of phospholipids allows the plasma membrane to maintain its structure?
What characteristic of phospholipids allows the plasma membrane to maintain its structure?
What is the primary driving force behind the filtration process in capillaries?
What is the primary driving force behind the filtration process in capillaries?
Which of the following molecules utilizes the active transport mechanism to move across the plasma membrane?
Which of the following molecules utilizes the active transport mechanism to move across the plasma membrane?
What sets phagocytosis apart from pinocytosis?
What sets phagocytosis apart from pinocytosis?
What is the function of carrier proteins in active transport?
What is the function of carrier proteins in active transport?
What type of endocytosis involves the binding of a specific molecule to a receptor prior to being engulfed by the cell?
What type of endocytosis involves the binding of a specific molecule to a receptor prior to being engulfed by the cell?
How do neurons utilize exocytosis in their function?
How do neurons utilize exocytosis in their function?
Which of the following statements about active transport is NOT true?
Which of the following statements about active transport is NOT true?
What distinguishes pinocytosis from other forms of endocytosis?
What distinguishes pinocytosis from other forms of endocytosis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
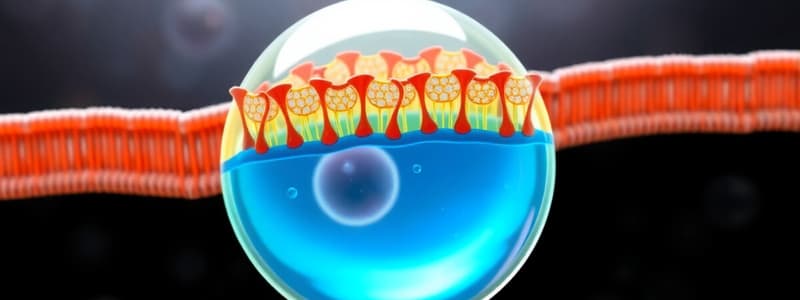
Plasma Membrane Overview
- The plasma membrane surrounds cells, exhibiting selective permeability to maintain cellular homeostasis.
- The fluid-mosaic model proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 1972 describes the plasma membrane as a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins.
Phospholipid Structure
- Each phospholipid has one hydrophilic (polar) head and two hydrophobic (nonpolar) tails.
- Hydrophobic tails repel water, while hydrophilic heads attract water, contributing to membrane structure.
Role of Cholesterol
- Cholesterol molecules are situated within the membrane to decrease permeability to water-soluble substances.
- They help stabilize membrane fluidity, ensuring structural integrity.
Types of Membrane Proteins
- Peripheral proteins are located on the membrane's inner or outer surface, while intrinsic (integral) proteins span the membrane completely.
- Membrane proteins have critical functions including:
- Facilitating material transport across the membrane.
- Participating in cell recognition as antigens.
- Serving as hormone receptors.
- Connecting to the cytoskeleton for structural support.
Functions of the Plasma Membrane
- Acts as a selective barrier, regulating substance flow.
- Maintains the internal environment and cell shape.
- Facilitates cell signaling and communication with the external environment.
- Enables the transport of essential molecules.
Movement Across Membrane
-
Simple Diffusion:
- Movement from high to low concentration without energy.
- Transports small, lipophilic molecules (e.g., O2 and CO2).
-
Facilitated Diffusion:
- Also moves substances from high to low concentration without energy.
- Involves specific proteins for transporting larger, hydrophilic molecules (e.g., glucose and amino acids).
-
Osmosis:
- The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
- Water moves from areas of higher water concentration (lower solute) to lower water concentration (higher solute).
- Solution types:
- Isotonic: Equal solute concentration, no net water movement.
- Hypotonic: Lower solute concentration than cells, water enters cells, potentially causing swelling.
- Hypertonic: Higher solute concentration than cells, water exits cells, leading to shrinkage.
-
Filtration:
- Involves the movement of water and solutes due to hydrostatic pressure from high to low pressure.
- Nutrients are delivered to cells through capillary membranes.
-
Active Transport:
- Moves substances against their concentration gradient from low to high concentration.
- Requires carrier proteins and ATP energy.
- Examples: Calcium pump and sodium-potassium pump
Endocytosis Processes
- Involves bulk uptake of materials from the external environment.
- Pinocytosis: Non-specific absorption of small droplets of extracellular fluid.
- Phagocytosis: Engulfing solid material, such as bacteria by white blood cells.
- Receptor-mediated Endocytosis: Specific receptors bind to extracellular molecules for uptake.
Exocytosis
- The process of expelling materials from the cell into the extracellular space using vesicles.
- Essential for secretion, such as neurotransmitter release by neurons.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.