Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of modifications can histones undergo to alter chromatin structure?
What type of modifications can histones undergo to alter chromatin structure?
- Hydrolysis and condensation
- Polymerization and demethylation
- Addition and removal of acetyl, phosphate, or methyl groups (correct)
- Phosphorylation and oxidation
What is the source of energy for ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes to reposition DNA?
What is the source of energy for ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes to reposition DNA?
- NADH oxidation
- ADP phosphorylation
- GTP synthesis
- ATP hydrolysis (correct)
Which of the following statements about the chromatin-remodeling complex is accurate?
Which of the following statements about the chromatin-remodeling complex is accurate?
- It is involved in exposing or hiding sequences of DNA. (correct)
- It consists of only one subunit that hydrolyzes ATP.
- It contains no recognition components for modified histones.
- It cannot function without DNA binding proteins.
How many subunits are reported to be part of the chromatin-remodeling complex from yeast?
How many subunits are reported to be part of the chromatin-remodeling complex from yeast?
What is the primary action performed by the chromatin-remodeling complex on DNA?
What is the primary action performed by the chromatin-remodeling complex on DNA?
What is the primary function of specialized proteins associated with DNA packaging?
What is the primary function of specialized proteins associated with DNA packaging?
What is the main characteristic that differentiates eukaryotic chromosomes from bacterial chromosomes?
What is the main characteristic that differentiates eukaryotic chromosomes from bacterial chromosomes?
Which of the following statements about gene expression is true?
Which of the following statements about gene expression is true?
What occurs during cell division in relation to chromosomes?
What occurs during cell division in relation to chromosomes?
What are the components of a nucleotide in DNA?
What are the components of a nucleotide in DNA?
What type of molecules do protein-coding genes produce?
What type of molecules do protein-coding genes produce?
Which of the following best describes the function of the coils and loops formed during DNA packaging?
Which of the following best describes the function of the coils and loops formed during DNA packaging?
Which bases are found in DNA nucleotides?
Which bases are found in DNA nucleotides?
In eukaryotic cells, what happens after DNA has been transcribed into RNA?
In eukaryotic cells, what happens after DNA has been transcribed into RNA?
What type of bond holds the two strands of DNA together?
What type of bond holds the two strands of DNA together?
What sugar is found in the nucleotides of DNA?
What sugar is found in the nucleotides of DNA?
What role do histone tails play in chromatin structure?
What role do histone tails play in chromatin structure?
Which is a characteristic of prokaryotic DNA compared to eukaryotic DNA?
Which is a characteristic of prokaryotic DNA compared to eukaryotic DNA?
Which of the following is true about the structure of DNA?
Which of the following is true about the structure of DNA?
Why are histones considered highly conserved proteins?
Why are histones considered highly conserved proteins?
What determines the hereditary information stored in DNA?
What determines the hereditary information stored in DNA?
How does the packing of nucleosomes in chromatin differ in living cells from what is typically illustrated?
How does the packing of nucleosomes in chromatin differ in living cells from what is typically illustrated?
What is the approximate size of the nucleosome core particle?
What is the approximate size of the nucleosome core particle?
Which statement correctly describes the directionality of DNA strands?
Which statement correctly describes the directionality of DNA strands?
What is the significance of the complementary nature of DNA strands?
What is the significance of the complementary nature of DNA strands?
Which of the following statements about DNA-histone interactions is true?
Which of the following statements about DNA-histone interactions is true?
What is a significant characteristic of the amino acid sequence of histone H4?
What is a significant characteristic of the amino acid sequence of histone H4?
Which mechanism allows for the control of chromatin structure?
Which mechanism allows for the control of chromatin structure?
What is the primary function of histones in eukaryotic cells?
What is the primary function of histones in eukaryotic cells?
What is the diameter of the chromatin fiber formed from packed nucleosomes?
What is the diameter of the chromatin fiber formed from packed nucleosomes?
Which structure is formed after the chromatin fiber is further folded into loops?
Which structure is formed after the chromatin fiber is further folded into loops?
What is the final packaging ratio of a DNA molecule when it is transformed into a mitotic chromosome?
What is the final packaging ratio of a DNA molecule when it is transformed into a mitotic chromosome?
What types of proteins assist in driving the condensation of chromatin?
What types of proteins assist in driving the condensation of chromatin?
What is the diameter of the entire mitotic chromosome structure?
What is the diameter of the entire mitotic chromosome structure?
Which type of proteins are known to be abundant and assist in chromosome condensation?
Which type of proteins are known to be abundant and assist in chromosome condensation?
What enables rapid access to the underlying DNA during chromatin packaging?
What enables rapid access to the underlying DNA during chromatin packaging?
What is currently uncertain regarding the structures involved in chromatin condensation?
What is currently uncertain regarding the structures involved in chromatin condensation?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
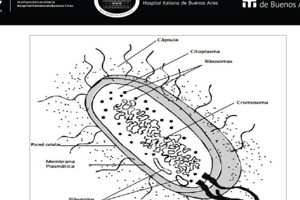
Structure of DNA
- DNA is a double-stranded helix with two polynucleotide chains.
- Each strand consists of four types of nucleotides: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
- Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogen-containing base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group.
- The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases.
- A pairs with T, and C pairs with G.
Packaging of DNA
- DNA is packaged into chromosomes to fit within the nucleus.
- Proteins bind to and fold DNA, generating coils and loops to prevent tangling.
- These folded structures allow access for enzymes and proteins involved in replication, repair, and gene expression.
Genes and Proteins
- Most genes contain instructions for protein production.
- Genes are transcribed into RNA molecules, which then direct protein synthesis.
- Some genes produce RNA molecules as their final product.
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
- Eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into compact structures.
- They are composed of DNA and proteins, primarily histones.
- Histones form nucleosomes, which are the basic units of chromatin.
Nucleosomes
- A nucleosome consists of a histone octamer (two each of H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) with DNA wrapped around it.
- Histones have unstructured N-terminal tails that are subject to reversible modifications, controlling chromatin structure.
Chromosome Organization
- Nucleosomes are further packed together to form a 30 nm chromatin fiber.
- The chromatin fiber is then folded into loops, creating higher levels of organization.
- This packaging allows DNA to be condensed and folded into mitotic chromosomes.
Regulation of Chromosome Structure
- Chromatin structure is dynamic and can be adjusted to regulate gene expression.
- ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes can reposition DNA around nucleosomes.
- These complexes use ATP hydrolysis to loosen or tighten the DNA, making it accessible or unavailable to other proteins.
- Modifications to histone tails, such as acetylation, phosphorylation, and methylation, also influence chromatin structure.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.