Podcast
Questions and Answers
What percentage of diabetic patients will undergo amputation following an ulcer?
What percentage of diabetic patients will undergo amputation following an ulcer?
- 15%
- 50%
- 85% (correct)
- 2-3%
Which of the following complications is LEAST likely to be associated with a high-risk diabetic foot?
Which of the following complications is LEAST likely to be associated with a high-risk diabetic foot?
- Retinopathy
- Macroangiopathy
- Acute sinusitis (correct)
- Nephropathy
What factor significantly contributes to the development of neuropathic ulcers in diabetic patients?
What factor significantly contributes to the development of neuropathic ulcers in diabetic patients?
- Loss of protective sensation (correct)
- Excessive exercise
- Prolonged standing
- Tight footwear
Which of the following best describes the primary goal of distal sensitivity testing in patients with diabetes?
Which of the following best describes the primary goal of distal sensitivity testing in patients with diabetes?
What percentage of diabetic patients with a history of ulcer or amputation experience a recurrence?
What percentage of diabetic patients with a history of ulcer or amputation experience a recurrence?
If a diabetic patient has some loss of sensation when tested with a monofilament, and has reduced pulses in his feet, which grade is this according to the presented gradation scale?
If a diabetic patient has some loss of sensation when tested with a monofilament, and has reduced pulses in his feet, which grade is this according to the presented gradation scale?
Which of the following is the MOST important aspect of foot care education for patients with diabetes?
Which of the following is the MOST important aspect of foot care education for patients with diabetes?
What is the recommended water temperature and duration of foot washing for a diabetic patient?
What is the recommended water temperature and duration of foot washing for a diabetic patient?
What key feature differentiates a neuropathic ulcer from an arterial ulcer in a diabetic patient?
What key feature differentiates a neuropathic ulcer from an arterial ulcer in a diabetic patient?
In the context of diabetic foot care, what does 'décharge' refer to?
In the context of diabetic foot care, what does 'décharge' refer to?
Which factor contributes significantly to the economic burden associated with diabetic foot complications?
Which factor contributes significantly to the economic burden associated with diabetic foot complications?
Which recommendation is MOST appropriate for a diabetic patient regarding shoe selection?
Which recommendation is MOST appropriate for a diabetic patient regarding shoe selection?
What is the MOST immediate risk associated with a fissure (crack) on the foot of a diabetic patient?
What is the MOST immediate risk associated with a fissure (crack) on the foot of a diabetic patient?
What is the MOST appropriate action (CAT) for an intertrigo (fungal infection) found between the toes of a diabetic patient?
What is the MOST appropriate action (CAT) for an intertrigo (fungal infection) found between the toes of a diabetic patient?
A vesicle on the foot of a diabetic patient is most indicative of what?
A vesicle on the foot of a diabetic patient is most indicative of what?
A plantar mal perforant (perforating ulcer) is MOST characteristically associated with what?
A plantar mal perforant (perforating ulcer) is MOST characteristically associated with what?
What is the MOST appropriate initial action (CAT) when encountering a patient with cellulitis of the foot?
What is the MOST appropriate initial action (CAT) when encountering a patient with cellulitis of the foot?
Which vascular condition/disease has a diagnostic differential comparable to haematoma?
Which vascular condition/disease has a diagnostic differential comparable to haematoma?
Which among the following is the role of a podologue in the care of diabetic foot?
Which among the following is the role of a podologue in the care of diabetic foot?
Which is not included in the necessary care for someone with education on diabetic foot?
Which is not included in the necessary care for someone with education on diabetic foot?
What is the relation between neuropathie sensitive and Mal Perforant Plantaire?
What is the relation between neuropathie sensitive and Mal Perforant Plantaire?
If a patient has known diabetic foot and has grade 2 based on examination. How often should patient be seeing a podologue to ensure adequate care?
If a patient has known diabetic foot and has grade 2 based on examination. How often should patient be seeing a podologue to ensure adequate care?
Which is not considered an element contributing to 'Une complication particulière (2) Le patient est souvent isolé' ?
Which is not considered an element contributing to 'Une complication particulière (2) Le patient est souvent isolé' ?
Approximately, what is the ambulance cost on patient's with diabetic foot ?
Approximately, what is the ambulance cost on patient's with diabetic foot ?
The majority of the amputated patients are diabetics with the number of risk being how many times more ?
The majority of the amputated patients are diabetics with the number of risk being how many times more ?
When is the ideal time to purchase chausettes(soquettes) or chaussures(shoes)?
When is the ideal time to purchase chausettes(soquettes) or chaussures(shoes)?
What must you palpate when considering chaussures (shoes)?
What must you palpate when considering chaussures (shoes)?
Which of the following is the most common cause of foot ulcers and amputation?
Which of the following is the most common cause of foot ulcers and amputation?
Which are the 3 categories to classify the pied(foot)?
Which are the 3 categories to classify the pied(foot)?
What stage comes after détersion with the stade de cicatrisation?
What stage comes after détersion with the stade de cicatrisation?
In an Ag clinique, what instruments are needed?
In an Ag clinique, what instruments are needed?
What are the 3 categories to determine La rôle central de la neuropathie
What are the 3 categories to determine La rôle central de la neuropathie
Based on the studies with (Mayfield, DiabetesCare 1998), what is the risk of 'ulcère and amputation' after a diabetic education?
Based on the studies with (Mayfield, DiabetesCare 1998), what is the risk of 'ulcère and amputation' after a diabetic education?
Which is more effective after and intervention after after role of chaussage?
Which is more effective after and intervention after after role of chaussage?
Flashcards
Diabetic Foot Frequency
Diabetic Foot Frequency
A frequent complication, affecting 15% of diabetics.
Complications with Diabetic Foot
Complications with Diabetic Foot
Patients at high risk often have other complications affecting eyes, kidneys, and blood vessels.
Neuropathy in Diabetic Foot
Neuropathy in Diabetic Foot
Impaired nerve function that increases risk of foot ulcers due to reduced sensation.
Role of Diabetes Imbalance
Role of Diabetes Imbalance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Classifying Diabetic Foot
Classifying Diabetic Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Characteristics of Neurogenic Ulcer
Characteristics of Neurogenic Ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arterial Ulcer
Arterial Ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment for Arterial Ulcer
Treatment for Arterial Ulcer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infections Ulcers
Infections Ulcers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment for Infected Ulcers
Treatment for Infected Ulcers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Evaluation
Local Evaluation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Healing Stages
Wound Healing Stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment for Diabetic Foot
Treatment for Diabetic Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diabetic Foot Education
Diabetic Foot Education
Signup and view all the flashcards
Education about Patient Sensitivity
Education about Patient Sensitivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Trauma
Foot Trauma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Annual Foot Exams
Annual Foot Exams
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Health Screening
Foot Health Screening
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuropathy Assessment
Neuropathy Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical Grade 2
Clinical Grade 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Care for Grade 0 Diabetic Foot
Care for Grade 0 Diabetic Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Care for Grade 1 Diabetic Foot
Care for Grade 1 Diabetic Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Care for Grade 2 Diabetic Foot
Care for Grade 2 Diabetic Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Care for Grade 3 Diabetic Foot
Care for Grade 3 Diabetic Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fissure in the food
Fissure in the food
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intertrigo
Intertrigo
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vésicule
Vésicule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hematoma - feet
Hematoma - feet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mal Perforant
Mal Perforant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Care Tips for Diabetics
Foot Care Tips for Diabetics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Diabetes and Foot Complications
- UE 2.7 covers organic failures and degenerative processes.
- Capsule 3 specifically addresses diabetes-related foot issues.
- The presentation was prepared by Professor Vincent Rigalleau from CHU Bordeaux in 2023.
Clinical Case 1
- Patient E is a 65-year-old man living alone, consuming 5 glasses of wine daily.
- He has a 10-year history of neglected diabetes.
- He stepped on a dog bone while wearing clogs and noticed it 2 days later.
- The foot is swollen with intermittent discharge, and the patient reports no pain.
- The case requires diagnostic and management considerations.
Diabetic Foot Epidemiology
- 15% of diabetics experience foot complications.
- There are 60,000 cases annually in France.
- The incidence is 2.5% of diabetics per year.
- Amputations are a severe outcome.
- The majority of amputees are diabetic.
- Diabetics have a 15-fold increased amputation risk.
- 2-3% of diabetics will undergo amputation.
- 85% of amputations occur after an ulcer.
- About half of amputations are in the foot, and half are above.
Complications of Diabetic Foot
- Foot issues rarely present in isolation.
- High-risk patients often have other complications such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and macroangiopathy.
- The mortality rate after amputation is 40% within 5 years.
- Isolation is a common issue among patients, especially men, occurring twice as often.
- Those aged 45-65 are also twice as likely to be affected.
- Alcohol and tobacco use are related factors.
- Vitamin deficiencies and social isolation also contribute.
- Access to prevention, care, and offloading possibilities is important.
- Hospitalizations for foot complications are often prolonged
- Average stays are 21 days based on Halimi's 1993 data and 17 days per Girod in 2003.
- The average length of stay for diabetology is 6 days.
- Ambulatory treatment costs 700€ per month for nursing care.
- Hospital treatment costs 2200€ per month, involving specialists and potential amputations.
Central Role of Neuropathy
- Disease duration and imbalance can lead to neuropathy.
- Motor neuropathy leads to amyotrophy, abnormal pressures, and deformities.
- Sensitive neuropathy results in loss of adaptation to walking traumas.
- Vegetative neuropathy causes dry skin.
- A precipitating event can lead to ulceration.
Deformations
- Neuropathy can cause deformities like claw or hammer toes.
- It is a primary cause of hyperpressure.
- Hyperpression leads to erythema, heat, callosities, and hematomas.
- The combination of deformities and neuropathy leads to ulcers.
- Hyperpression is made worse by obesity.
- Reduced joint mobility is a sign of future problems.
Clinical Assessment of the Foot
- Neurogenic foot (3/6 cases): indolent, possibly deformed.
- MPP is present in high-risk areas due to compression and friction.
- It will heal but will likely recur; debridement is necessary.
- Arterial foot (1/6 cases; mixed 2/6): painful, necrotic, and not budding.
- Distal pulses are absent.
- It will not heal without vascular treatment or debridement. -Infected foot
- Open with discharge and local inflammatory signs.
- Antibiotic treatment is necessary.
- Local Evaluation in Clinical Assessment:
- Size: Length and width and depth, noting involvement of bone or joints.
- Stage of healing includes debridement, budding, and epidermalization.
- Instruments: use of probes, swabs, and scissors. -Assessment value that guides prognosis and therapy.
Diabetic Foot Treatment
- Local treatment involves offloading and dressings.
- General treatment focuses on diabetes control through insulin.
- Vaccinations should be updated if necessary.
- Antibiotics are required for infection management.
- Surgical intervention may include anti-infectious procedures such as debridement and drainage.
- Vascular procedures may also be considered.
- Amputation is can also be a consideration
Education in Foot Care
- Education encompasses diet, self-monitoring, insulin therapy, hypoglycemia management, physical activity, and foot care
- Early detection and screening for complications like retinopathy, nephropathy, and cardiopathy are important.
- Regular foot examinations and patient education can reduce ulcer risk by 60% and amputation risk by 85%.
- Many ulcer patients cannot recall education within the last 10 years.
- It can be difficult to make risk-bearing patients aware of their low-level pain symptoms.
Preventative Education
- Precipitating events are often identifiable.
- 20% of ulcers are linked to trauma.
- There can be trauma from footwear, accidental cuts, nail pathologies, and decubitus ulcers.
- Edema plays a role.
Foot Risk Identification
- Includes annual foot exams, which happen 50% of the time.
- Evaluation includes ulcers and amputations
- This is the first step in education and can result in referrals for podology.
- Screening includes ulcers, amputations, neuropathies, deformities, and arteritis.
- 73% are normal at the time of screening and require education.
Identify Risk Factors
- For prior ulcers or amputations, 5% of all diabetics need to be treated for 20 years.
- There can be spontaneous recurrence of up to 30%.
- Treatment and education is very helpful
Testing and Identifying Neuropathies and Deformations
- Includes 50% of patients
- There is an 8-18x higher risk of ulcers.
- Test for sensitivity
- Use monofilament
- Use a 128 Hz diapasom
Identifying Arteritis
- Includes rare triggering
- Retardance in healing
- Test pulses
- Test for claudications
Diabetic Foot Grading
- Uses a simple clinical grading system to assess severity.
- Grade 0: No neuropathy, no arteritis, and non-specific deformities.
- Grade 1: Neuropathy (monofilament not perceived in two of three points), but no arteritis or deformity.
- Grade 2: Neuropathy with arteritis and/or deformity.
- Grade 3: History of ulceration lasting over 4 weeks or amputation.
Patient Management
- Grade 0: Should have annual foot exams.
- Grade 1: Should have foot and shoe exams, and education for diabetes on a regular schedule.
- Grade 2: Requires routine foot exams and visits to the podiatrist every three months. Orthoses should be addressed.
- Grade 3: Requires reinforcement and surveillance by a specializing center. Podiatrist visits should occur every two months.
Foot Care Education
- Education involves understanding sensitivity to pain, temperature, and touch.
- It also includes security such as protective footwear.
- Education also includes daily cleaning the feet and keeping them dry
- A daily examination of the foot also happens
Footwear Guidance
- Emphasis is placed on wearing the correct socks
- Footwear should be progressive and comfortable
Complications of Ulcers
- Ulcers often need to be treated by a professional
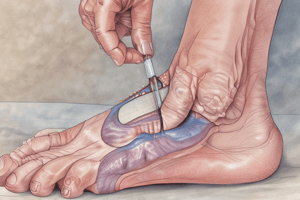
Foot Problems
- Feet have a tendency to develop problems.
- These include intertrigo, fissures, vesicularity, hematomas, plantar perforations, and cellulitis.
- Fissure Diagnostic Value:
- Dry skin and hyperkeratosis with hypertension.
- Major risk is Cellulite
- Patients must moisturize and soften
Foot Problems of Intertrigo
- Not diagnostic
- Poor hygiene
- Risk of Cellulitis
- Patients must keep feet dry
Foot Problems of Vesicules
- From hypertension
- Caused by neuropathy
- Have openings that are dangerous when closed or ruptured
Foot Problems of Hematoma
- Very similar to a foot gangrene infection
- Vascularized
- Major risk of foot gangrene
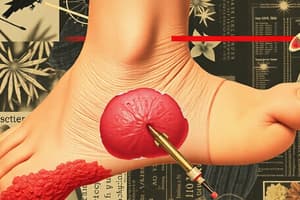
Foot Problems of Plantar Perforations
- Is a sensitive neuropathy
- Deep extension causing Osteitis
- Must have local care
Foot Problems of Cellulite
- Comes with an infection
- Can turn into Necrosis
- Requires a medical doctor
Conclusion
- Is a clinical diagnosis
- Can be catastrophic for patients
- Focuses on treatments
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.