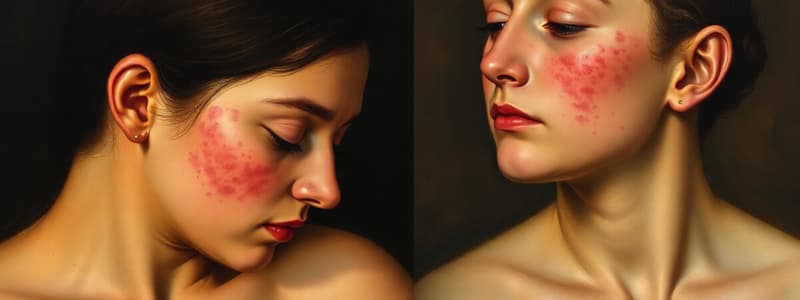Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of nevus is first in the natural progression of a mole?
What type of nevus is first in the natural progression of a mole?
- Junctional nevus (correct)
- Compound nevus
- Dermal nevus
- Atypical nevus
Which type of nevus is characterized by being flat and brown?
Which type of nevus is characterized by being flat and brown?
- Dermal nevus
- Compound nevus
- Junctional nevus (correct)
- Atypical nevus
What distinct feature differentiates atypical nevi from typical nevi?
What distinct feature differentiates atypical nevi from typical nevi?
- They have irregular borders and shapes. (correct)
- They contain only one color.
- They are round and have smooth borders.
- They are always skin-colored.
What is the term for moles that are raised and skin-colored?
What is the term for moles that are raised and skin-colored?
How many major types of moles are described?
How many major types of moles are described?
Which feature is NOT characteristic of a typical nevus?
Which feature is NOT characteristic of a typical nevus?
What common feature do junctional and compound nevi share?
What common feature do junctional and compound nevi share?
Which feature indicates that a nevus is atypical?
Which feature indicates that a nevus is atypical?
What is a characteristic appearance of atypical nevi?
What is a characteristic appearance of atypical nevi?
Which area does acne involvement typically indicate more severe disease?
Which area does acne involvement typically indicate more severe disease?
What is the size of a nodule in acne?
What is the size of a nodule in acne?
Which type of lesion is characterized by a small (1-2 mm) flesh-colored papule?
Which type of lesion is characterized by a small (1-2 mm) flesh-colored papule?
What is a primary pathogenesis factor in the development of acne?
What is a primary pathogenesis factor in the development of acne?
Which lesion is NOT classified as one of the six distinct types of acne lesions?
Which lesion is NOT classified as one of the six distinct types of acne lesions?
What does the presence of chin and/or jawline lesions in women generally indicate?
What does the presence of chin and/or jawline lesions in women generally indicate?
Which type of acne scar is characterized by a narrow, deep depression?
Which type of acne scar is characterized by a narrow, deep depression?
What is the primary theory regarding the cause of darkening and thickening associated with acanthosis nigricans?
What is the primary theory regarding the cause of darkening and thickening associated with acanthosis nigricans?
What is considered the most effective treatment for acanthosis nigricans in obese individuals?
What is considered the most effective treatment for acanthosis nigricans in obese individuals?
In evaluating a patient with acanthosis nigricans, what aspect is crucial to investigate for underlying causes?
In evaluating a patient with acanthosis nigricans, what aspect is crucial to investigate for underlying causes?
Which underlying malignancy is classically associated with acanthosis nigricans?
Which underlying malignancy is classically associated with acanthosis nigricans?
When should a patient with rapidly developing acanthosis nigricans be evaluated for malignancies?
When should a patient with rapidly developing acanthosis nigricans be evaluated for malignancies?
What is the term used for the lesion that is not visible to the naked eye and occurs due to the accumulation of sebaceous secretions within the follicle?
What is the term used for the lesion that is not visible to the naked eye and occurs due to the accumulation of sebaceous secretions within the follicle?
What is the main reason for the dark color of an open comedone (blackhead)?
What is the main reason for the dark color of an open comedone (blackhead)?
What type of lesion forms from inflammation in the superficial portion of the hair follicle?
What type of lesion forms from inflammation in the superficial portion of the hair follicle?
Which bacterial species is identified as a source of inflammatory stimuli in acne?
Which bacterial species is identified as a source of inflammatory stimuli in acne?
What consequence occurs when a papule ruptures and releases its contents into the dermis?
What consequence occurs when a papule ruptures and releases its contents into the dermis?
In what manner do androgenic hormones contribute to the development of acne?
In what manner do androgenic hormones contribute to the development of acne?
The treatment of acne aimed at patients with predominantly open and closed comedones focuses on which of the following?
The treatment of acne aimed at patients with predominantly open and closed comedones focuses on which of the following?
What happens to sebaceous production when the follicle is compressed by the accumulation of material?
What happens to sebaceous production when the follicle is compressed by the accumulation of material?
What is the typical initial manifestation of Pityriasis Rosea in over half of the cases?
What is the typical initial manifestation of Pityriasis Rosea in over half of the cases?
Which of the following describes the appearance of the plaques in Pityriasis Rosea?
Which of the following describes the appearance of the plaques in Pityriasis Rosea?
What is a common cause of Keratosis Pilaris?
What is a common cause of Keratosis Pilaris?
What skincare treatments are typically recommended for Keratosis Pilaris?
What skincare treatments are typically recommended for Keratosis Pilaris?
What is a characteristic presentation of Acanthosis Nigricans?
What is a characteristic presentation of Acanthosis Nigricans?
What is typically effective for treating associated pruritus in Pityriasis Rosea?
What is typically effective for treating associated pruritus in Pityriasis Rosea?
Which populations are most commonly affected by Pityriasis Rosea?
Which populations are most commonly affected by Pityriasis Rosea?
What is the typical duration for spontaneous resolution of Pityriasis Rosea?
What is the typical duration for spontaneous resolution of Pityriasis Rosea?
What is the primary effect of isotretinoin in acne treatment?
What is the primary effect of isotretinoin in acne treatment?
What should be considered when choosing oral contraceptives for acne treatment?
What should be considered when choosing oral contraceptives for acne treatment?
Which medication is known for its non-specific anti-inflammatory activity and for reducing P.acnes counts?
Which medication is known for its non-specific anti-inflammatory activity and for reducing P.acnes counts?
What percentage of patients is expected to be 'cured' of their acne after a course of isotretinoin?
What percentage of patients is expected to be 'cured' of their acne after a course of isotretinoin?
Why is compliance considered a critical factor in acne treatment?
Why is compliance considered a critical factor in acne treatment?
Which treatment is specifically designed to reduce P.acnes populations?
Which treatment is specifically designed to reduce P.acnes populations?
What is one of the common side effects of topical regimens that include retinoids?
What is one of the common side effects of topical regimens that include retinoids?
How long is the typical treatment course for isotretinoin?
How long is the typical treatment course for isotretinoin?
Flashcards
Mole (Nevus)
Mole (Nevus)
A common skin growth caused by a cluster of melanocytes.
Junctional Nevus
Junctional Nevus
A type of mole where melanocytes are located mainly at the junction between the epidermis and dermis.
Compound Nevus
Compound Nevus
A type of mole characterized by melanocyte growth both at the junction and within the dermis.
Dermal Nevus
Dermal Nevus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dermal Nevi Characteristics
Dermal Nevi Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Junctional Nevi Characteristics
Junctional Nevi Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atypical Nevus
Atypical Nevus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atypical Nevus Characteristics
Atypical Nevus Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open comedone (Blackhead)
Open comedone (Blackhead)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Closed comedone (Whitehead)
Closed comedone (Whitehead)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Papule
Papule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pustule
Pustule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nodule
Nodule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Raised scar
Raised scar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ice pick scar
Ice pick scar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microcomedone
Microcomedone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open and Closed Comedones
Open and Closed Comedones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes)
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Androgenic Hormones in Acne
Androgenic Hormones in Acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acne Treatment
Acne Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are retinoids used for in acne treatment?
What are retinoids used for in acne treatment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is salicylic acid used for in acne treatment?
What is salicylic acid used for in acne treatment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do topical antibiotics work in acne treatment?
How do topical antibiotics work in acne treatment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a key benefit of oral antibiotics for acne?
What is a key benefit of oral antibiotics for acne?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which treatment can permanently reduce sebaceous gland activity?
Which treatment can permanently reduce sebaceous gland activity?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Besides reducing sebaceous gland activity, what is another long-term effect of isotretinoin?
Besides reducing sebaceous gland activity, what is another long-term effect of isotretinoin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What treatments are used for acne with a hormonal component?
What treatments are used for acne with a hormonal component?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a major factor in determining the success of acne treatment?
What is a major factor in determining the success of acne treatment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acanthosis Nigricans (AN)
Acanthosis Nigricans (AN)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment for Acanthosis Nigricans (AN)
Treatment for Acanthosis Nigricans (AN)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Evaluating AN for Underlying Causes
Evaluating AN for Underlying Causes
Signup and view all the flashcards
AN Associated with Malignancies
AN Associated with Malignancies
Signup and view all the flashcards
AN and Diabetes
AN and Diabetes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratosis Pilaris (KP)
Keratosis Pilaris (KP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pityriasis Rosea (PR)
Pityriasis Rosea (PR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Herald Patch
Herald Patch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Christmas Tree Distribution
Christmas Tree Distribution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pruritus
Pruritus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Topical Steroids
Topical Steroids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratolytic Moisturizers
Keratolytic Moisturizers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Moles (Melanocytic Nevi)
- Moles are common, with most people having at least one.
- Moles can be junctional, compound, dermal, or atypical.
- Junctional nevi are flat and brown, located at the epidermis-dermis junction.
- Compound nevi are raised and brown, with melanocytes at the epidermis-dermis junction and in the dermis.
- Dermal nevi are raised and skin-colored, with melanocytes only in the dermis.
- Atypical nevi are different from compound nevi clinically and histologically; they often have irregular boundaries, irregular shape, mixed colors, and a larger size (>6mm).
Other Nevi
- Halo Nevus: A mole with a white rim around it, potentially linked to an immune response, melanoma, or vitiligo. Full body exam is recommended.
- Nevus Spilus: Congenital light tan macule with dark speckles; often removed for cosmetic reasons.
- Blue Nevus: Homogenous blue macule; typically flat, small, and symmetrical. Evaluation and removal if atypical features (e.g., irregular borders, non-homogenous color) are present.
- Ephelides (Freckles): Small brown macules on sun-exposed areas, decreasing in presence with decreased sun exposure.
- Lentigines (Liver Spots): Larger, darker spots than freckles; do not fade with decreased sun exposure.
Acne
- Acne is common, affecting over 50% of the population without impacting health.
- Acne primarily begins with puberty but can emerge earlier.
- It typically affects the face, chest, and back, with the chin/jawline in women indicative of hormonal involvement.
- Acne has different lesion types: open comedones (blackheads), closed comedones (whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules, and scars.
Pityriasis Rosea (PR)
- Common in teens and young adults, typically starts with a herald patch (oval, red-brown plaque).
- Within days to weeks, more similar-shaped plaques appear across the trunk.
- The distribution of plaques is often in a "Christmas Tree" pattern.
- Self-resolves in 6-8 weeks, but occasionally persists longer.
Keratosis Pilaris (KP)
- Common, characterized by rough, red papules at hair follicle openings.
- Usually on the upper arms and anterior thighs.
- Treated with keratolytic moisturizers or retinoids.
Acanthosis Nigricans (AN)
- Characterized by darkening and thickening of skin folds.
- Often linked to obesity, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance.
- May be associated with underlying malignancies.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.