Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of tungsten carbide burs in fixed prosthodontics?
What is the primary function of tungsten carbide burs in fixed prosthodontics?
- Creating friction for enhanced cutting efficiency
- Cutting and reducing tooth structure (correct)
- Polishing tooth surfaces
- Measuring preparation depth
Why should diamond burs be used with caution?
Why should diamond burs be used with caution?
- They do not create any friction during use.
- They are less efficient for crown preparations.
- They can lead to overheating of both the bur and the tooth. (correct)
- They have a longer cutting lifespan than carbide burs.
What does a three-number code before the period in a bur's item code indicate?
What does a three-number code before the period in a bur's item code indicate?
- Shape and taper of the bur (correct)
- Cutting diameter of the bur
- Maximum cutting length of the bur
- Grit and width of the bur
When preparing a shoulder margin, which bur design is most appropriate?
When preparing a shoulder margin, which bur design is most appropriate?
How is the cutting diameter of a bur indicated in its identification code?
How is the cutting diameter of a bur indicated in its identification code?
What happens to diamond burs with excessive use?
What happens to diamond burs with excessive use?
What are wheel burs primarily used for in dental procedures?
What are wheel burs primarily used for in dental procedures?
What does the two-digit number between the periods in a bur's item code denote?
What does the two-digit number between the periods in a bur's item code denote?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
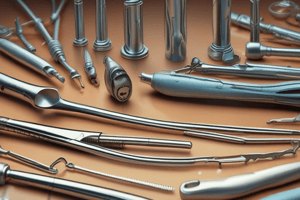
Bur Types
- Carbide vs. Diamond: Carbide burs are made of tungsten carbide with a set number of blades that slice away tooth structure. Diamond burs are constructed with stainless steel bonded with diamond particles, which grind away hard tissue.
- Bur Features: Burs have various shapes, head angles, blade geometry, grit, and cutting diameters.
- Bur Identification: Carbide burs are identified by a numerical code (e.g., 330, 557). Diamond burs are identified by a numerical code on their packaging.
- Shape: The three numbers before the period in the code indicate the bur's shape and taper.
- Grit: Grit influences how much material is removed, a finer grit is used for finishing and a coarser grit is used for rough cuts.
- Cutting Diameter: The last numbers in the code refer to the bur's maximum cutting diameter in millimeters (mm).
- Cutting Length: The two-digit number between the periods in the code denotes the bur's length.
- Bur Selection: The appropriate bur selection depends on the desired application, for example, a shoulder bur (flat end taper) is commonly used for creating a shoulder margin. Barrel burs are used for reducing occlusal surfaces on molars, wheel burs for incisal edges, and egg burs for reducing lingual surfaces on anteriors.
Reduction Matrices
- Lab Putty Properties: Lab putty is a material used to create custom reduction matrices which are used for facilitating even reduction of tooth structure.
- Mixing, Placement, Sectioning, and Usage: Lab putty is mixed according to manufacturer's instructions, placed around the tooth, allowed to set, and then sectioned to create a mold that guides the preparation.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.