Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary cause of corneal edema?
What is the primary cause of corneal edema?
The primary cause of corneal edema is excess fluid accumulating within the corneal stroma and forcing the collagen lamellae apart.
Corneal edema is always a result of age-related endothelial cell loss.
Corneal edema is always a result of age-related endothelial cell loss.
False (B)
How does the endothelium play a role in preventing corneal edema and maintaining transparency?
How does the endothelium play a role in preventing corneal edema and maintaining transparency?
The endothelium helps pump solutes from the stroma to the aqueous humor. This maintains a proper fluid balance in the cornea, preventing tears from entering the stroma and keeping the cornea clear.
What are two types of corneal edema?
What are two types of corneal edema?
Corneal epithelial cell loss leads to more opaque edema compared to endothelial cell loss.
Corneal epithelial cell loss leads to more opaque edema compared to endothelial cell loss.
Endothelial cells regenerate faster than epithelial cells.
Endothelial cells regenerate faster than epithelial cells.
What are the two categories of corneal edema based on fluorescein staining?
What are the two categories of corneal edema based on fluorescein staining?
What is the significance of fluorescein staining in determining corneal edema?
What is the significance of fluorescein staining in determining corneal edema?
When should a thorough intraocular exam be performed for corneal edema?
When should a thorough intraocular exam be performed for corneal edema?
What is the suggested approach to address corneal ulceration related to corneal edema?
What is the suggested approach to address corneal ulceration related to corneal edema?
What is the diagnostic algorithm used for patients with corneal edema?
What is the diagnostic algorithm used for patients with corneal edema?
Topical antibiotics are always indicated for corneal edema.
Topical antibiotics are always indicated for corneal edema.
Topical fluroscein should be applied when corneal bullas rupture.
Topical fluroscein should be applied when corneal bullas rupture.
What is the purpose of hyperosmotic 5% sodium chloride ointment in managing corneal edema?
What is the purpose of hyperosmotic 5% sodium chloride ointment in managing corneal edema?
Flashcards
What is corneal edema?
What is corneal edema?
Corneal edema is a condition where excessive fluid accumulates in the cornea, causing a loss of transparency due to collagen lamellae being forced apart.
How does the endothelium maintain corneal transparency?
How does the endothelium maintain corneal transparency?
The endothelium regulates stromal fluid balance by pumping out solutes (and water) from the stroma to the aqueous humor.
What role does the epithelium play in corneal transparency?
What role does the epithelium play in corneal transparency?
The epithelium prevents tears from entering the stroma.
What are the characteristics of diffuse corneal edema?
What are the characteristics of diffuse corneal edema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the characteristics of focal corneal edema?
What are the characteristics of focal corneal edema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What can cause diffuse corneal edema?
What can cause diffuse corneal edema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What can cause focal corneal edema?
What can cause focal corneal edema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does aging affect corneal edema?
How does aging affect corneal edema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Can corneal edema be reversed?
Can corneal edema be reversed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do deep blood vessels appear in the cornea?
How do deep blood vessels appear in the cornea?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do superficial blood vessels appear in the cornea?
How do superficial blood vessels appear in the cornea?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the clinical significance of corneal vascularization?
What is the clinical significance of corneal vascularization?
Signup and view all the flashcards
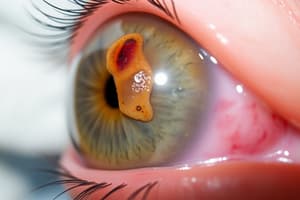
What are corneal bullae?
What are corneal bullae?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is bullous keratopathy?
What is bullous keratopathy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What treatment is necessary if corneal bullae rupture?
What treatment is necessary if corneal bullae rupture?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is corneal malacia?
What is corneal malacia?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the visual appearance of corneal edema?
What is the visual appearance of corneal edema?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the visual appearance of corneal vascularization?
What is the visual appearance of corneal vascularization?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the visual appearance of corneal fibrosis?
What is the visual appearance of corneal fibrosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is corneal melanosis?
What is corneal melanosis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the visual appearance of stromal infiltration with white blood cells?
What is the visual appearance of stromal infiltration with white blood cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the visual appearance of anterior stromal deposition of lipid and/or mineral?
What is the visual appearance of anterior stromal deposition of lipid and/or mineral?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the cornea receive nutrition?
How does the cornea receive nutrition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are visual indicators of keratitis?
What are visual indicators of keratitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the effects of topical corticosteroids on corneal healing?
What are the effects of topical corticosteroids on corneal healing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When is the use of topical corticosteroids justified?
When is the use of topical corticosteroids justified?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Corneal Edema
- Corneal edema is a critical factor in corneal transparency
- Control of relative water is essential
- The corneal stroma and endothelium make the balance
- The aqueous humor plays a role in preventing tears entering the stroma
- Different degrees of transparency affect the stroma
- Severe edema may result in formation of small vesicles
- Fluorescein usually does not remain in diffused marked edema.
Corneal Blood Vessels
- Superficial vessels are called "trees"
- Insufficient corneal protection rule out lagotphalmos, macrophthalmos fissure, CN V or VII dysfunction, ectropion, and kcs
- Excessive corneal irritation rule out entropion, distichiasis, ectropic cilia, trichiasis, foreign body, blepharitis, eyelid mass, "pannus" (UV light), and herpesvirus
- Deep blood vessels are called "hedges"
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.