Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the cerebellum control?
What does the cerebellum control?
Bodily coordination, balance, muscle tone, and some aspects of memory involving procedure-related movements.
What structures make up the convolutions of the cerebral cortex?
What structures make up the convolutions of the cerebral cortex?
- Sulci
- Fissures
- Gyri
- All of the above (correct)
The left hemisphere specializes in spatial visualization.
The left hemisphere specializes in spatial visualization.
False (B)
What is the primary function of the primary motor cortex?
What is the primary function of the primary motor cortex?
Which lobe is primarily responsible for auditory processing?
Which lobe is primarily responsible for auditory processing?
The corpus callosum connects both _____ of the brain.
The corpus callosum connects both _____ of the brain.
What type of stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain suddenly breaks?
What type of stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain suddenly breaks?
What is the role of neurotransmitters?
What is the role of neurotransmitters?
What technique uses a thin electrode to record changes in electrical activity of a single neuron?
What technique uses a thin electrode to record changes in electrical activity of a single neuron?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is less invasive than other imaging techniques.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is less invasive than other imaging techniques.
What do PET scans measure?
What do PET scans measure?
Which type of brain injuries involve an intact skull but damage to the brain?
Which type of brain injuries involve an intact skull but damage to the brain?
_____ refers to the back part of the brain.
_____ refers to the back part of the brain.
What is defined as the study of the brain structures and functions postmortem?
What is defined as the study of the brain structures and functions postmortem?
What are cones?
What are cones?
What is the function of photo pigments?
What is the function of photo pigments?
What forms the optic nerve?
What forms the optic nerve?
What is the role of the lateral geniculate nucleus?
What is the role of the lateral geniculate nucleus?
What does the dorsal pathway process?
What does the dorsal pathway process?
Which pathway is referred to as the ventral pathway?
Which pathway is referred to as the ventral pathway?
What is bottom-up perception?
What is bottom-up perception?
What is direct perception according to Gibson's theory?
What is direct perception according to Gibson's theory?
What is the purpose of feature-matching theories?
What is the purpose of feature-matching theories?
What are geons in recognition-by-components theory?
What are geons in recognition-by-components theory?
What does the law of Prägnanz state?
What does the law of Prägnanz state?
The ability to perceive an object as stable despite changes in the proximal stimulus is known as _____ constancy.
The ability to perceive an object as stable despite changes in the proximal stimulus is known as _____ constancy.
What is simultaneous agnosia?
What is simultaneous agnosia?
What is prosopagnosia?
What is prosopagnosia?
Which theory emphasizes that perception is constructed using prior knowledge and sensory data?
Which theory emphasizes that perception is constructed using prior knowledge and sensory data?
What are the main bottom-up theoretical approaches to pattern perception?
What are the main bottom-up theoretical approaches to pattern perception?
What are agnosias?
What are agnosias?
What is the definition of attention?
What is the definition of attention?
Signal-detection theory (SDT) explains how people pick out important stimuli embedded in a wealth of __________ stimuli.
Signal-detection theory (SDT) explains how people pick out important stimuli embedded in a wealth of __________ stimuli.
Consciousness has no overlap with attention.
Consciousness has no overlap with attention.
Match the attentional models with their characteristics:
Match the attentional models with their characteristics:
What are the three primary symptoms of ADHD?
What are the three primary symptoms of ADHD?
Change blindness refers to the inability to detect changes in objects or scenes.
Change blindness refers to the inability to detect changes in objects or scenes.
What does the term 'automatic processes' refer to?
What does the term 'automatic processes' refer to?
What is the primary neurotransmitter involved in the alerting function of attention?
What is the primary neurotransmitter involved in the alerting function of attention?
Which factor can influence our ability to pay attention?
Which factor can influence our ability to pay attention?
What is a 'slip' in the context of automatic processes?
What is a 'slip' in the context of automatic processes?
What does priming in psychology refer to?
What does priming in psychology refer to?
What is a good predictor of academic success?
What is a good predictor of academic success?
Which areas are involved in the visuospatial sketchpad? (Select all that apply)
Which areas are involved in the visuospatial sketchpad? (Select all that apply)
What type of memory does Endel Tulving distinguish between?
What type of memory does Endel Tulving distinguish between?
Lesions in the frontal lobe affect recollection of when a stimulus was presented.
Lesions in the frontal lobe affect recollection of when a stimulus was presented.
What is the phenomenon called when memory retrieval of seemingly forgotten memories is achieved?
What is the phenomenon called when memory retrieval of seemingly forgotten memories is achieved?
What kind of amnesia is characterized by the inability to recall events prior to a traumatic event?
What kind of amnesia is characterized by the inability to recall events prior to a traumatic event?
What is the main effect of Alzheimer's disease on memory?
What is the main effect of Alzheimer's disease on memory?
What is Amnesia?
What is Amnesia?
The model called HERA demonstrates greater activation in the left prefrontal hemisphere for tasks requiring retrieval from ______ memory.
The model called HERA demonstrates greater activation in the left prefrontal hemisphere for tasks requiring retrieval from ______ memory.
The neural connections among nodes in connectionist models are essential for the representation of knowledge and ______.
The neural connections among nodes in connectionist models are essential for the representation of knowledge and ______.
What is the dyad of triads task?
What is the dyad of triads task?
What does the tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon refer to?
What does the tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon refer to?
Blindsight occurs when someone has no conscious awareness of visual sensations.
Blindsight occurs when someone has no conscious awareness of visual sensations.
What is one of the main functions of attention?
What is one of the main functions of attention?
What distinguishes controlled from automatic processing?
What distinguishes controlled from automatic processing?
What technique do researchers use to measure sensitivity to targets?
What technique do researchers use to measure sensitivity to targets?
What is the difference between recall and recognition tasks?
What is the difference between recall and recognition tasks?
The traditional model of memory includes three stores: sensory store, short-term store, and __________.
The traditional model of memory includes three stores: sensory store, short-term store, and __________.
What is the capacity of the sensory memory according to research?
What is the capacity of the sensory memory according to research?
What is procedural knowledge?
What is procedural knowledge?
Which phenomenon reflects facilitation of the ability to utilize missing information?
Which phenomenon reflects facilitation of the ability to utilize missing information?
The higher the level of processing, the lower the probability of remembering the item.
The higher the level of processing, the lower the probability of remembering the item.
In which model of memory is working memory a central focus?
In which model of memory is working memory a central focus?
What is cognitive psychology?
What is cognitive psychology?
Which philosophical perspective emphasizes knowledge through logical analysis?
Which philosophical perspective emphasizes knowledge through logical analysis?
Who is considered the father of structuralism?
Who is considered the father of structuralism?
Behaviourism focuses on observable behaviour and not on mental states.
Behaviourism focuses on observable behaviour and not on mental states.
What is the law of effect according to Edward Lee Thorndike?
What is the law of effect according to Edward Lee Thorndike?
What did Ivan Pavlov study?
What did Ivan Pavlov study?
Who proposed the concept of cell assemblies?
Who proposed the concept of cell assemblies?
Which of the following methods is used in cognitive psychology research?
Which of the following methods is used in cognitive psychology research?
What is the main criticism of behaviourism?
What is the main criticism of behaviourism?
Neuroscientific research looks at the relationship between cognitive performance and cerebral events.
Neuroscientific research looks at the relationship between cognitive performance and cerebral events.
The ________ is essential for thinking and other mental processes.
The ________ is essential for thinking and other mental processes.
What is the upper limit with which an observer can match a response to information given called?
What is the upper limit with which an observer can match a response to information given called?
Which research method involves individuals describing aloud all their thoughts during a task?
Which research method involves individuals describing aloud all their thoughts during a task?
What concept did Noam Chomsky criticize in regards to language acquisition?
What concept did Noam Chomsky criticize in regards to language acquisition?
What is the name of the network of neurons essential for regulating consciousness and attention?
What is the name of the network of neurons essential for regulating consciousness and attention?
Flashcards
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive Psychology
Study of how people perceive, learn, remember, and think about information.
Heuristic
Heuristic
Mental shortcut for information processing.
Dialectic Development
Dialectic Development
Thesis, antithesis, synthesis stages of idea progression
Structuralism
Structuralism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functionalism
Functionalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Associationism
Associationism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Behaviorism
Behaviorism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt Psychology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short-term memory
Short-term memory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rationalism
Rationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Empiricism
Empiricism
Signup and view all the flashcards
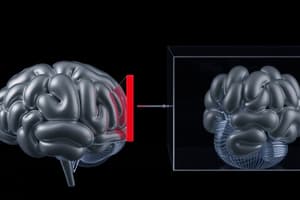
Cortex
Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hippocampus
Hippocampus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amygdala
Amygdala
Signup and view all the flashcards
Frontal Lobe
Frontal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuron
Neuron
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perception
Perception
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
-
ory memory storage prior to filtering relevant informCognitive Psychology Overview
- Cognitive psychology studies how people perceive, learn, remember, and think about information.
- Heuristic methods serve as mental shortcuts for information processing.
- Dialectic development includes thesis, antithesis, and synthesis stages.
- Cultural influences impact cognitive processes, including concepts of intelligence.
Philosophical Foundations
- Cognitive psychology originates from rationalism (logical knowledge, Plato, Descartes) and empiricism (knowledge from observation, Aristotle, Locke).
- Immanuel Kant synthesized these views, while Hegel described dialectical progression of ideas.
Historical Development of Psychology
- Structuralism, founded by Wilhelm Wundt, analyzes the structure of the mind through introspection.
- Functionalism, led by William James, emphasizes the functions and processes of thought.
- Associationism links learning with mental associations, highlighting contiguity, similarity, and contrast.
- Behaviorism, championed by John Watson and B.F. Skinner, focuses solely on observable behaviors and their environmental contingencies.
Theoretical Evolution
- Edward Tolman introduced goal-directed behavior into behaviorism.
- Gestalt psychology promotes understanding phenomena as organized wholes.
- Cognitive psychology arose through a synthesis of behaviorism and Gestaltism in the 1950s, emphasizing internal mental processes.
Key Figures in Cognitive Psychology
- Karl Spencer Lashley emphasized the brain's organization of behavior.
- Noam Chomsky critiqued behaviorism's approach to language acquisition, advocating for innate cognitive structures.
- George Miller introduced concepts like the "Magic Number Seven" related to short-term memory.
Research Methodologies
- Cognitive psychologists employ various research methods:
- Laboratory experiments with independent and dependent variables.
- Neuroscientific studies linking cognitive processes to brain function.
- Self-reports and case studies for insight into cognitive processes.
- Computer simulations and artificial intelligence to model cognition.
Current Issues and Focus Areas
- Cognitive psychology addresses ongoing debates between rationalism and empiricism, and the importance of cognitive structures and processes.
- Major research topics include attention, memory, language, problem-solving, intelligence, and the effects of culture on cognition.
Brain Anatomy and Function
- Brain divided into forebrain (cerebral cortex, limbic system), midbrain (eye movement, arousal), and hindbrain (basic life functions).
- The cerebral cortex is vital for higher-level thinking, emotional regulation, and memory.
- Key structures include the basal ganglia for motion, hippocampus for memory formation, and thalamus for sensory information processing.
Hemispheric Specialization
- The brain has two hemispheres with distinct functions, connected by the corpus callosum.
- The left hemisphere is specialized for language and analytical functions, while the right hemisphere excels in spatial and holistic processes.
- Split-brain patients illustrate functional asymmetries between hemispheres.
Practical Implications
- Cognitive psychology’s integration with AI and neuroscience fosters advancements in understanding human cognition.
- The discipline continues to explore fundamental cognitive processes and their applications in real-world scenarios.### Frontal Lobe
- Involved in motor processing and higher thought processes, such as abstract reasoning, problem-solving, planning, and judgment.
- Crucial for speech production; damage can lead to speech difficulties.
- Prefrontal cortex integrates information over time, facilitating complex motor control tasks.
- Primary motor cortex is responsible for planning, controlling, and executing movements, with a contralateral organization for body control (homunculi maps).
Parietal Lobe
- Located at the upper back of the brain; plays a role in somatosensory processing and spatial awareness.
- Primary somatosensory cortex receives sensory information related to pressure, texture, temperature, and pain.
Temporal Lobe
- Situated below the parietal lobe; primarily handles auditory processing and language comprehension.
- Retains visual memories, aiding in the recognition of objects and events.
Occipital Lobe
- Located at the back of the brain; specialized in visual processing with various areas analyzing color, motion, and form.
- Contains the primary visual cortex, critical for interpreting visual stimuli.
Brain Orientation Terms
- Rostral: Refers to the anterior part of the brain.
- Ventral: Indicates the inferior surface of the brain.
- Caudal: Means posterior, resembling the tail region.
- Dorsal: Signifies the superior part of the brain.
Neuronal Structure and Function
- Neurons consist of four main parts: soma (cell body), dendrites, axon, and terminal buttons.
- Soma contains the nucleus and connects dendrites to the axon.
- Dendrites collect information from other neurons while axons send electrochemical signals to other neurons.
- Myelin sheaths around axons speed up signal transmission; nodes of Ranvier enhance conduction.
- Terminal buttons release neurotransmitters across the synapse to relay information.
Neurotransmitters
- Chemical messengers allow communication across synapses; categories include:
- Monoamines, amino-acid neurotransmitters, and neuropeptides.
- Key neurotransmitters include:
- Acetylcholine: Associated with memory, sleep, and arousal.
- Dopamine: Linked to attention, learning, movement control, and motivation.
- Serotonin: Regulates eating behaviors, body weight, aggression, and impulsivity.
Brain Research Methods
- Postmortem Studies: Connecting behaviors to brain anomalies, e.g., Broca's patient Tan.
- Nonhuman Animal Studies: Techniques like single-cell recordings, lesioning, and genetic knockout procedures.
- Live Human Studies: Include:
- Electrical Recordings: EEGs track brain wave activity; ERPs measure changes in response to stimuli.
- Static Imaging: CT and MRI scans assess structural and functional aspects of the brain.
- Metabolic Imaging: PET scans and fMRI examine brain activity based on glucose and oxygen use.
Brain Disorders
- Stroke: Sudden blood flow disruption, leading to cognitive function loss. Two types: ischemic (blockage) and hemorrhagic (bleeding).
- Brain Tumors: Can be primary (originating in brain) or secondary (spread from elsewhere). Symptoms may include severe headaches, nausea, and cognitive changes.
- Head Injuries: Classified as closed (intact skull) or open (breached skull). Symptoms include abnormal breathing, speech disturbances, and cognitive issues.
Perception Concepts
- Sensation to Perception: Recognizing and organizing sensory information.
- Basic Perception Terms: Distal object (external), informational medium (stimuli), proximal stimulation (sensory receptor interaction), perceptual object (mental representation).
- Sensory adaptation can affect perception, e.g., the Ganzfeld effect where constant stimuli lead to perceived disappearance.
Visual System Function
- Vision begins with light entering through the cornea and passes through the pupil, lens, and vitreous humor, ultimately focusing on the retina.
- Contains photoreceptors: rods (night vision, peripheral sensitivity) and cones (color perception, concentrated in the fovea).
- Signals travel via bipolar and ganglion cells to form the optic nerve and transmit visual information to the primary visual cortex.
Visual Processing Pathways
- What-Where Hypothesis: Dorsal pathway processes spatial information while the ventral pathway identifies objects.
- What-How Hypothesis: Focuses on object identification and interaction pathways.
Bottom-Up Perception Theories
- Four primary theories:
- Direct Perception: Emphasizes the sufficiency of sensory information for perception.
- Template Theories: Suggest recognition occurs by matching stimuli to stored templates.
- Feature-Matching Theories: Compare stimulus features to stored memory features.
- Pandemonium Model: Illustrates the hierarchical processing of stimulus features through metaphorical "demons" with specific responsibilities.### Feature Matching Theories
- Feature demons detect matches between stimuli and specific features, calling out relevant information.
- Cognitive demons identify stored patterns in memory corresponding to features noted by feature demons.
- Decision demons evaluate input based on the frequency of cognitive demons' outputs.
- Global features provide the overall shape, while local features concern detailed aspects of patterns.
- Global precedence effect: Slowed identification when recognizing small 'S's forming a large 'H' compared to small 'H's forming a large 'H.'
- Local precedence effect: Faster recognition of widely spaced local features than global forms, especially with contradictory stimuli.
Neuroscientific Evidence
- Visual cortex neurons respond to specific stimuli types, such as orientation.
- Each neuron corresponds to a specific retinal receptive field, illustrating a hierarchical complexity in responses.
- Gnostic units or “grandmother cells” are neurons linked to recognizing complex objects.
Recognition-by-Components (RBC) Theory
- Recognition of 3-D objects involves decomposing them into simpler geometric shapes known as geons.
- Geons possess viewpoint invariance, aiding general recognition but struggling with specific instances.
- Neurons in the inferior temporal cortex are sensitive to viewpoint invariance and may show varying responses based on object rotation.
Top-Down Theories
- Perception is influenced by high-level cognitive processes, prior knowledge, and expectations, forming a constructive approach.
- Constructive perception combines sensory data with cognitive understanding.
- Color constancy maintains the perception of color despite lighting changes.
- Hypotheses about percepts are formed from sensory data, memory knowledge, and inferences.
- Context effects demonstrate how surroundings influence perception; complex configurations improve recognition efficiency.
Gestalt Laws of Perception
- Gestalt principles explain perception through holistic approaches, emphasizing the organization of visual arrays into coherent forms.
- The law of Prägnanz favors simple organization of visual elements.
- Principles include figure-ground perception, proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, and symmetry.
- Human children utilize Gestalt principles, differing notably from other primates.
Recognition of Patterns and Faces
- Two systems for pattern recognition: feature analysis focuses on parts, while configurational analysis emphasizes whole configurations.
- Face recognition is primarily managed in the fusiform gyrus, with a distinct response to faces compared to other objects.
- The "face positivity" effect indicates older adults prefer happy faces.
- Amygdala activation connects emotional responses with face processing.
- Prosopagnosia illustrates severe difficulties in recognizing faces, linked to damage in the configurational system.
Perceptual Constancies
- Perceptual constancy ensures stable perception despite changing sensory conditions; includes size and shape constancy.
- Size constancy involves perceiving an object's size as constant, irrespective of proximal stimulus changes.
- Shape constancy retains perceived shape despite changes in proximal stimuli.
Depth Perception
- Depth is understood as the distance from surfaces, driven by binocular and monocular cues.
- Monocular cues include texture gradients, relative size, interposition, linear perspective, aerial perspective, and motion parallax.
- Binocular depth cues rely on the disparity and convergence of images from both eyes, interpreted by the brain to gauge distance.
Deficits in Perception
- Agnosias are deficits caused by brain lesions affecting the ability to recognize objects.
- Visual-object agnosia permits seeing parts without recognizing objects; simultagnosia limits attention to one object.
- Prosopagnosia severely impairs face recognition capabilities.
- (Optic) ataxia disrupts visual guidance of movements linked to the dorsal pathway.
Anomalies in Color Perception
- Color perception anomalies, more common in men, include rod monochromacy (no color vision) and various types of dichromacy.
- Types of color blindness vary by which color perception mechanisms fail: protanopia (red-green), deuteranopia (green), tritanopia (blue-yellow).
The Nature of Attention and Consciousness
- Attention actively selects information from environmental stimuli, enhancing reaction speed and accuracy toward salient stimuli.
- Consciousness encompasses awareness and linking past memories with present sensations.
- Functions of attention include signal detection, vigilance, search, selective attention, and divided attention.
- Signal-detection theory assesses effectiveness in identifying targeted stimuli among distractions.
Search Mechanisms
- Search involves scanning the environment for specific features, distinguishing between feature and conjunction searches.
- Feature search targets one characteristic unaffected by distractors, while conjunction search combines multiple features; complexity increases with the number of distractors.
- Feature-integration theory suggests a two-stage process in object perception, first recognizing features and then linking them.
Selective Attention
- The cocktail party problem illustrates the ability to focus on one conversation amidst distractions.
- Dichotic presentation reveals how individuals can notice sensory changes in unattended messages but miss semantic ones.
- The early filter model posits sensation.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.