Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the circulatory system?
What is the primary function of the circulatory system?
- To initiate the inflammatory response
- To deliver oxygen and nutrients to all cells (correct)
- To regulate body temperature through sweat
- To manage the respiratory gases in the body
Which components make up the blood vessels in the circulatory system?
Which components make up the blood vessels in the circulatory system?
- Muscles and nerves
- Lymphatic vessels and arteries
- Arteries, veins, and capillaries (correct)
- Only arteries and capillaries
How do arteries differ from veins?
How do arteries differ from veins?
- Arteries carry oxygen-poor blood back to the heart
- Arteries have thicker walls to withstand high pressure (correct)
- Veins carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart
- Veins branch into smaller vessels called arterioles
What characterizes Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)?
What characterizes Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)?
Which of the following statements about lung cancer is correct?
Which of the following statements about lung cancer is correct?
Which sequence correctly describes the steps involved in breathing?
Which sequence correctly describes the steps involved in breathing?
What is the primary role of water vapor in exhaled air?
What is the primary role of water vapor in exhaled air?
What percentage of oxygen is typically exhaled after breathing?
What percentage of oxygen is typically exhaled after breathing?
What is the primary function of pulmonary circulation?
What is the primary function of pulmonary circulation?
Which component carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs?
Which component carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs?
What role do systemic capillaries play in systemic circulation?
What role do systemic capillaries play in systemic circulation?
What major artery is responsible for distributing oxygen-rich blood throughout the body?
What major artery is responsible for distributing oxygen-rich blood throughout the body?
How do arterioles function within systemic circulation?
How do arterioles function within systemic circulation?
What differentiates pulmonary circulation from systemic circulation regarding its pathway?
What differentiates pulmonary circulation from systemic circulation regarding its pathway?
What is the function of pulmonary veins in the circulatory system?
What is the function of pulmonary veins in the circulatory system?
What is the primary function of red blood cells?
What is the primary function of red blood cells?
During systemic circulation, which part of the heart pumps oxygenated blood?
During systemic circulation, which part of the heart pumps oxygenated blood?
Which type of blood cell is crucial for the immune response?
Which type of blood cell is crucial for the immune response?
What condition is characterized by high blood pressure against artery walls?
What condition is characterized by high blood pressure against artery walls?
What is the role of platelets in the circulatory system?
What is the role of platelets in the circulatory system?
Atherosclerosis leads to what main consequence in the arteries?
Atherosclerosis leads to what main consequence in the arteries?
What component of blood serves as a transport medium for various elements?
What component of blood serves as a transport medium for various elements?
What best describes the condition of heart failure?
What best describes the condition of heart failure?
What does pulmonary circulation refer to?
What does pulmonary circulation refer to?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
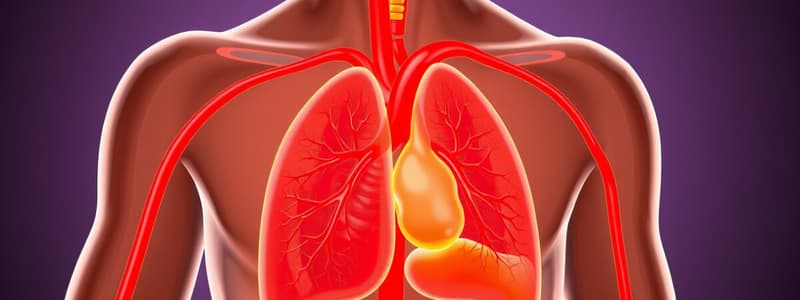
Pulmonary Circulation
- Facilitates oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange between lungs and blood.
- Main components include pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and capillaries.
- Pulmonary arteries transport deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
- Gas exchange occurs in the pulmonary capillaries surrounding the alveoli.
Systemic Circulation
- Delivers oxygenated blood to organs, tissues, and removes waste products.
- Key components include aorta, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins.
- Oxygenated blood is pumped through the left ventricle to systemic circulation.
- Systemic capillaries facilitate gas, nutrient, and waste exchange between blood and tissues.
Components of the Circulatory System
- Aorta: Largest artery, distributing oxygen-rich blood to the entire body.
- Arteries: Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
- Arterioles: Regulate blood flow and blood pressure in the circulation.
Differences Between Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation
- Pulmonary circulation connects the heart and lungs.
- Systemic circulation serves all body organs, ensuring continuous nutrient and oxygen delivery.
Blood Composition
- Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): Most abundant cells, transporting oxygen using hemoglobin.
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): Key in immune defense against infections and diseases.
- Platelets: Crucial for blood clotting; they form plugs at injury sites and release clotting-promoting chemicals.
- Plasma: Liquid portion of blood, transporting cells, nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Circulatory System Disorders
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can lead to heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems.
- Atherosclerosis: Fatty plaques in arteries reduce blood flow, increasing cardiovascular risks.
- Heart Failure: Heart's inability to pump enough blood to meet bodily needs.
Changes in Breathed Air Composition
- Oxygen: Inhaled (21%), Exhaled (16%).
- Carbon Dioxide: Inhaled (0.04%), Exhaled (4%).
- Nitrogen: Remains constant (79%).
- Water Vapor: Less in inhaled, more in exhaled air.
Common Respiratory Disorders
- Asthma: Characterized by airway inflammation and narrowing, causing breathing difficulties.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Encompasses conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema, leading to reduced lung function.
- Pneumonia: Infection inflaming air sacs in the lungs, presenting with fever and difficulty breathing.
- Lung Cancer: Uncontrolled growth of abnormal lung cells.
Breathing Process
- Stimulated by the brain's breathing center.
- Diaphragm and rib muscles contract.
- Ribcage expands, increasing chest cavity size.
- Pressure inside the lungs decreases, causing air to flow in from higher to lower pressure.
Circulatory System Overview
- Comprises blood vessels, heart, and blood for delivery of oxygen and nutrients.
- Blood vessels include arteries, veins, and capillaries, forming an extensive network.
- Arteries have thick, elastic walls to handle high pressure from heart pumping; they branch into arterioles.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.