Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the chambers of the heart?
What are the chambers of the heart?
- Two upper ventricles and two lower atria
- Two upper atria and two lower ventricles (correct)
- One chamber for blood reception and one for ejection
- Three upper chambers and one lower chamber
What are the top two chambers of the heart called?
What are the top two chambers of the heart called?
Atria
What are the larger two chambers on the bottom of the heart called?
What are the larger two chambers on the bottom of the heart called?
Ventricles
The paired atria receive blood from blood vessels returning to the heart.
The paired atria receive blood from blood vessels returning to the heart.
What is the structure called on the anterior surface of each atrium?
What is the structure called on the anterior surface of each atrium?
What do sulci in the heart contain?
What do sulci in the heart contain?
What marks the external boundary between the superior atria and inferior ventricles?
What marks the external boundary between the superior atria and inferior ventricles?
What does the anterior interventricular sulcus mark?
What does the anterior interventricular sulcus mark?
What continues around to the posterior of the heart from the anterior interventricular sulcus?
What continues around to the posterior of the heart from the anterior interventricular sulcus?
What forms the right surface of the heart and receives blood from three veins?
What forms the right surface of the heart and receives blood from three veins?
Veins always carry blood away from the heart.
Veins always carry blood away from the heart.
What separates the right atrium from the left atrium internally?
What separates the right atrium from the left atrium internally?
What groove marks the border between atria and ventricles?
What groove marks the border between atria and ventricles?
What valve does blood pass through from the right atrium into the right ventricle?
What valve does blood pass through from the right atrium into the right ventricle?
What is the tricuspid valve also known as?
What is the tricuspid valve also known as?
How is the wall of the left ventricle compared to that of the right ventricle?
How is the wall of the left ventricle compared to that of the right ventricle?
What are the valves of the heart composed of?
What are the valves of the heart composed of?
From which veins does the right atrium receive blood?
From which veins does the right atrium receive blood?
What forms most of the anterior surface of the heart?
What forms most of the anterior surface of the heart?
What partitions the right ventricle from the left ventricle?
What partitions the right ventricle from the left ventricle?
Where does the right ventricle send blood?
Where does the right ventricle send blood?
What valve does blood pass through in the right ventricle?
What valve does blood pass through in the right ventricle?
What forms the base of the heart?
What forms the base of the heart?
How many pulmonary veins does the left atrium receive blood from?
How many pulmonary veins does the left atrium receive blood from?
What is considered the thickest chamber of the heart?
What is considered the thickest chamber of the heart?
What valve does blood pass from the left atrium into the left ventricle?
What valve does blood pass from the left atrium into the left ventricle?
What valve does blood pass through the left ventricle?
What valve does blood pass through the left ventricle?
Arteries always take blood towards the heart.
Arteries always take blood towards the heart.
What does the word 'artery' signify?
What does the word 'artery' signify?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
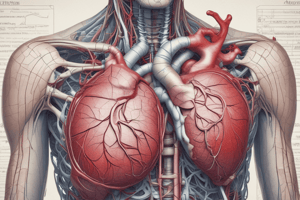
Chambers of the Heart
- Heart consists of four chambers: two atria (upper) and two ventricles (lower).
- Atria receive blood from returning blood vessels; ventricles eject blood into arteries.
Atria
- The top two chambers are known as atria, which includes the right atrium and left atrium.
- Each atrium has an auricle, a wrinkled structure that increases its capacity.
Ventricles
- The ventricles are larger and referred to as "little bellies." The left ventricle has a thicker wall than the right ventricle.
- The right ventricle forms much of the anterior surface of the heart and sends blood to the lungs.
Blood Flow
- Blood enters the right atrium from three sources: superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus.
- Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve (or right atrioventricular valve).
- Blood passes from the right ventricle through the pulmonary valve to the lungs for oxygenation.
- The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via four pulmonary veins.
- Blood moves from the left atrium into the left ventricle through the bicuspid (mitral) valve and then ejected through the aortic valve into the aorta.
Septum and Valves
- The interatrial septum separates the right and left atria and features the fossa ovalis.
- The interventricular septum separates the right and left ventricles.
- Heart valves (tricuspid, pulmonary, bicuspid, aortic) are made of dense connective tissue covered by endocardium.
Coronary Sulcus and Sulci
- Coronary sulcus grooves mark the boundary between atria and ventricles.
- Deep coronary sulcus encircles the heart, while the anterior and posterior interventricular sulci mark boundaries between ventricles.
Blood Vessel Functions
- Veins carry blood towards the heart, while arteries carry blood away from the heart, indicated by the term "artery" meaning "away."
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.