Podcast
Questions and Answers
How many NADH are produced by glycolysis?
How many NADH are produced by glycolysis?
2
In glycolysis, ATP molecules are produced by _____.
In glycolysis, ATP molecules are produced by _____.
substrate-level phosphorylation
Which of these is NOT a product of glycolysis?
Which of these is NOT a product of glycolysis?
- ATP
- NADH + H+
- FADH2 (correct)
- Pyruvate
In glycolysis, what starts the process of glucose breakdown?
In glycolysis, what starts the process of glucose breakdown?
In glycolysis there is a net gain of _____ ATP.
In glycolysis there is a net gain of _____ ATP.
For each glucose that enters glycolysis, _____ NADH enter the electron transport chain.
For each glucose that enters glycolysis, _____ NADH enter the electron transport chain.
In cellular respiration, most ATP molecules are produced by _____
In cellular respiration, most ATP molecules are produced by _____
The final electron acceptor of cellular respiration is _____
The final electron acceptor of cellular respiration is _____
During electron transport, energy from _____ is used to pump hydrogen ions into the _____.
During electron transport, energy from _____ is used to pump hydrogen ions into the _____.
The proximate (immediate) source of energy for oxidative phosphorylation is _____
The proximate (immediate) source of energy for oxidative phosphorylation is _____
Which of the following molecules is broken down in cellular respiration, providing fuel for the cell?
Which of the following molecules is broken down in cellular respiration, providing fuel for the cell?
Which energy-rich molecule produced by cellular respiration directly powers cell work?
Which energy-rich molecule produced by cellular respiration directly powers cell work?
Select the correct sequence of steps as energy is extracted from glucose during cellular respiration.
Select the correct sequence of steps as energy is extracted from glucose during cellular respiration.
What is the correct general equation for cellular respiration?
What is the correct general equation for cellular respiration?
Which of the following processes takes place in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell?
Which of the following processes takes place in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell?
In what organelle would you find acetyl CoA formation, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain?
In what organelle would you find acetyl CoA formation, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain?
Which statement describes glycolysis?
Which statement describes glycolysis?
Which statement describes the citric acid cycle?
Which statement describes the citric acid cycle?
Which statement describes the electron transport chain?
Which statement describes the electron transport chain?
The transfer of _____ from one molecule to another is an oxidation-reduction reaction, or redox reaction.
The transfer of _____ from one molecule to another is an oxidation-reduction reaction, or redox reaction.
In cellular respiration, glucose becomes _____ to carbon dioxide (CO2) as it loses electrons.
In cellular respiration, glucose becomes _____ to carbon dioxide (CO2) as it loses electrons.
In cellular respiration, oxygen becomes _____ to water (H2O) as it gains electrons.
In cellular respiration, oxygen becomes _____ to water (H2O) as it gains electrons.
In cellular respiration, organic molecules become oxidized as _____ picks up electrons and H+ and becomes reduced to NADH.
In cellular respiration, organic molecules become oxidized as _____ picks up electrons and H+ and becomes reduced to NADH.
NADH delivers electrons to an electron transport chain, which passes the electrons through carrier molecules in a series of redox reactions to the final electron acceptor, _____.
NADH delivers electrons to an electron transport chain, which passes the electrons through carrier molecules in a series of redox reactions to the final electron acceptor, _____.
The energy released from the redox reactions in the electron transport chain is used by the cell to make _____.
The energy released from the redox reactions in the electron transport chain is used by the cell to make _____.
In muscle cells, fermentation produces _____.
In muscle cells, fermentation produces _____.
When proteins are used as a source of energy for the body, the proteins are converted mainly into intermediates of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle.
When proteins are used as a source of energy for the body, the proteins are converted mainly into intermediates of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle.
Which of the following statements about the energy yield of aerobic respiration is false?
Which of the following statements about the energy yield of aerobic respiration is false?
Most NADH molecules generated during cellular respiration are produced during __________.
Most NADH molecules generated during cellular respiration are produced during __________.
Describe how food molecules reach the body's cells and fuel cellular respiration. Start with the ingestion of food on the left.
Describe how food molecules reach the body's cells and fuel cellular respiration. Start with the ingestion of food on the left.
As electrons move through the mitochondrial space, what happens?
As electrons move through the mitochondrial space, what happens?
Which of the following statements about the energy yields from cellular respiration is true?
Which of the following statements about the energy yields from cellular respiration is true?
During cellular respiration, NADH delivers its electron load to which molecule?
During cellular respiration, NADH delivers its electron load to which molecule?
NADH is also used by cells when making certain molecules. Based on your knowledge of the role of NADH in cellular respiration, what do you think NADH's role is in biosynthesis of molecules?
NADH is also used by cells when making certain molecules. Based on your knowledge of the role of NADH in cellular respiration, what do you think NADH's role is in biosynthesis of molecules?
In cellular respiration, which of the following outcomes is the result of electrons moving through the electron transport chain?
In cellular respiration, which of the following outcomes is the result of electrons moving through the electron transport chain?
In an experiment, mice were fed glucose (C6H12O6) containing a small amount of radioactive carbon. The mice were closely monitored, and in a few minutes, radioactive carbon atoms showed up in __________.
In an experiment, mice were fed glucose (C6H12O6) containing a small amount of radioactive carbon. The mice were closely monitored, and in a few minutes, radioactive carbon atoms showed up in __________.
The electron transport chain is, in essence, a series of redox reactions that conclude cellular respiration. During these redox reactions, __________.
The electron transport chain is, in essence, a series of redox reactions that conclude cellular respiration. During these redox reactions, __________.
Inputs of cellular respiration
Inputs of cellular respiration
Outputs of cellular respiration
Outputs of cellular respiration
Sunlight is essential for the varied life on Earth because it provides __________.
Sunlight is essential for the varied life on Earth because it provides __________.
Which of the following is the role of cellular respiration?
Which of the following is the role of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that harvest energy in the form of ______ from ______ and other organic molecules.______ and ______ are also released.
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that harvest energy in the form of ______ from ______ and other organic molecules.______ and ______ are also released.
A person's basal metabolic rate (BMR) is equal to about __________.
A person's basal metabolic rate (BMR) is equal to about __________.
Given the relatively modest number of calories burned by any but the most vigorous activities, why can most people consume more than 2,000 kilocalories per day yet maintain a healthy body weight?
Given the relatively modest number of calories burned by any but the most vigorous activities, why can most people consume more than 2,000 kilocalories per day yet maintain a healthy body weight?
A molecule that functions as the electron donor in a redox reaction __________.
A molecule that functions as the electron donor in a redox reaction __________.
In cellular respiration, ______ is oxidized when it loses electrons in hydrogen atoms, and ______ is reduced as it gains electrons in hydrogen atoms.
In cellular respiration, ______ is oxidized when it loses electrons in hydrogen atoms, and ______ is reduced as it gains electrons in hydrogen atoms.
In cellular respiration, glucose __________ electrons and oxygen __________ electrons.
In cellular respiration, glucose __________ electrons and oxygen __________ electrons.
What is the role of the dehydrogenase enzyme at the beginning of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
What is the role of the dehydrogenase enzyme at the beginning of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
How does the electron transport chain run?
How does the electron transport chain run?
Oxidative phosphorylation could not occur without glycolysis and the citric acid cycle because __________.
Oxidative phosphorylation could not occur without glycolysis and the citric acid cycle because __________.
The main function of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle is...
The main function of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle is...
Which of the following statements about glycolysis is correct?
Which of the following statements about glycolysis is correct?
In glycolysis, how many ATP are invested? How many ATP are produced?
In glycolysis, how many ATP are invested? How many ATP are produced?
Glycolysis begins with __________ and ends with __________.
Glycolysis begins with __________ and ends with __________.
How many carbon atoms are in glucose?
How many carbon atoms are in glucose?
How many carbon atoms are in pyruvate?
How many carbon atoms are in pyruvate?
At what point in cellular respiration is the first molecule of CO2 produced?
At what point in cellular respiration is the first molecule of CO2 produced?
Each glucose molecule yields __________ molecule(s) of ATP during the citric acid cycle.
Each glucose molecule yields __________ molecule(s) of ATP during the citric acid cycle.
Each turn of the citric acid cycle generates one ATP molecule as well as which energy-rich molecules?
Each turn of the citric acid cycle generates one ATP molecule as well as which energy-rich molecules?
In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are passed from one electron carrier to another. The energy released is used to __________.
In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are passed from one electron carrier to another. The energy released is used to __________.
What does the proton pump do?
What does the proton pump do?
What 'powers' ATP synthase, allowing it to catalyze the conversion of ADP to ATP in the presence of phosphate?
What 'powers' ATP synthase, allowing it to catalyze the conversion of ADP to ATP in the presence of phosphate?
Evidence suggests that heat-generating brown fat is most active in __________.
Evidence suggests that heat-generating brown fat is most active in __________.
About how much ATP is produced by the metabolism of one molecule of glucose in cellular respiration?
About how much ATP is produced by the metabolism of one molecule of glucose in cellular respiration?
During fermentation, __________ that was produced during glycolysis is converted back to __________.
During fermentation, __________ that was produced during glycolysis is converted back to __________.
Why are wine barrels and beer fermentation vats designed to keep air out?
Why are wine barrels and beer fermentation vats designed to keep air out?
Which of the following statements about glycolysis is INCORRECT?
Which of the following statements about glycolysis is INCORRECT?
Fat is the most efficient fuel molecule because __________.
Fat is the most efficient fuel molecule because __________.
Let's look at the big picture here: Fueled by the ATP generated during cellular respiration, the intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, such as pyruvate and acetyl CoA, are siphoned off and used to __________.
Let's look at the big picture here: Fueled by the ATP generated during cellular respiration, the intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, such as pyruvate and acetyl CoA, are siphoned off and used to __________.
What process regulates the rate of cellular respiration?
What process regulates the rate of cellular respiration?
Flashcards
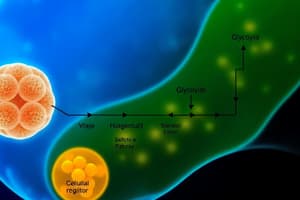
Glycolysis
Glycolysis
The first step in cellular respiration, breaking down glucose into 2 pyruvate molecules.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation
ATP production where a phosphate group is directly transferred to ADP from a substrate.
ATP investment in glycolysis
ATP investment in glycolysis
2 ATP are used to initiate glucose breakdown, yielding a net gain of 2 ATP.
NADH
NADH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyruvate
Pyruvate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electron Transport Chain
Electron Transport Chain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Citric Acid Cycle
Citric Acid Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acetyl CoA
Acetyl CoA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fermentation
Fermentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lactate
Lactate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
FADH2
FADH2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feedback Inhibition
Feedback Inhibition
Signup and view all the flashcards
ATP
ATP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen
Oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
NAD+
NAD+
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose
Glucose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytosol
Cytosol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat
Fat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Energy Transformation
Energy Transformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metabolism
Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Glycolysis Overview
- Glycolysis produces 2 NADH per glucose molecule.
- ATP is generated via substrate-level phosphorylation; a phosphate is transferred from glyceraldehyde phosphate to ADP.
- ATP investment in glycolysis: 2 ATP are used, producing a total of 4 ATP; net gain is 2 ATP.
- Initiation of glucose breakdown requires ATP.
- Glycolysis is the first step, yielding 2 pyruvate molecules from one glucose (6 carbon atoms).
- It takes place in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells, outside the mitochondria.
Cell Respiration Processes
- The primary stages of cellular respiration: glycolysis → acetyl CoA formation → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain.
- Cellular respiration's overall equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP energy.
- Glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide, while oxygen is reduced to water.
- NAD+ is reduced to NADH during these processes, which then delivers electrons to the electron transport chain.
Citric Acid Cycle Insights
- Each glucose molecule enters two turns of the citric acid cycle, yielding 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2.
- Carbon dioxide is released during the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, marking the first carbon dioxide release in cellular respiration.
- The cycle captures energy-rich molecules that transport electrons to the electron transport chain.
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Most ATP in cellular respiration comes from oxidative phosphorylation, utilizing energy released by electron transport.
- The final electron acceptor is oxygen, which combines with electrons and protons to form water.
- Energy from NADH and FADH2 drives hydrogen ion pumping into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient.
- ATP synthesis occurs as protons flow back down their gradient through ATP synthase.
Anaerobic Processes and Fermentation
- In muscle cells, fermentation produces lactate and regenerates NAD+ from NADH.
- The preference of facultative anaerobes for aerobic pathways explains the design of fermentation vessels to keep air out, ensuring alcohol production.
Energy and Metabolism Insights
- A person's basal metabolic rate (BMR) is approximately 1,300-1,500 Calories/day, supporting essential functions.
- Fat is a highly efficient fuel due to its high hydrogen content, which provides abundant high-energy electrons.
- Metabolism in cells involves utilizing ATP and other intermediates for building proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Regulatory Mechanisms
- Feedback inhibition regulates the rate of cellular respiration, ensuring that metabolic pathways respond to the energy needs of the cell.
- Signals from reactive products control enzymatic activities and energy usage efficiency.
General Highlights
- Cellular respiration's efficiency surpasses that of car engines in harnessing energy from fuels.
- A glucose molecule generally produces approximately 32 ATP through various stages.
- Understanding energy transformation and regulation is key in biology, impacting health and metabolism.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.