Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is the primary aim of cellular respiration?
Which of the following is the primary aim of cellular respiration?
- To produce glucose from inorganic molecules.
- To synthesize ATP and NADH from organic molecules. (correct)
- To break down carbon dioxide into simpler molecules.
- To convert water into energy.
During aerobic respiration, what happens to oxygen and carbon dioxide?
During aerobic respiration, what happens to oxygen and carbon dioxide?
- Both oxygen and carbon dioxide are consumed.
- Oxygen is released, and carbon dioxide is consumed.
- Oxygen is consumed, and carbon dioxide is released. (correct)
- Both oxygen and carbon dioxide are released.
What is the correct summary equation for aerobic respiration?
What is the correct summary equation for aerobic respiration?
- $C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 \rightarrow 6CO_2 + 6H_2O + \text{energy}$ (correct)
- $6O_2 + \text{energy} \rightarrow C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6CO_2 + 6H_2O $
- $C_6H_{12}O_6 \rightarrow 6CO_2 + 6H_2O + 6O_2 + \text{energy}$
- $6CO_2 + 6H_2O \rightarrow C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 + \text{energy}$
Where does glycolysis take place in a cell?
Where does glycolysis take place in a cell?
Which statement accurately describes the requirement of oxygen in Glycolysis?
Which statement accurately describes the requirement of oxygen in Glycolysis?
During glycolysis, how many phases are involved, and what is the net production molecules of ATP?
During glycolysis, how many phases are involved, and what is the net production molecules of ATP?
What is produced when 6 carbon molecules are broken down during the cleavage phase of glycolysis?
What is produced when 6 carbon molecules are broken down during the cleavage phase of glycolysis?
During cellular respiration, what molecule is formed when pyruvate is broken down?
During cellular respiration, what molecule is formed when pyruvate is broken down?
What two products are the result break down of pyruvate?
What two products are the result break down of pyruvate?
What is the main purpose of the citric acid cycle?
What is the main purpose of the citric acid cycle?
What molecule must be present to initiate the citric acid cycle?
What molecule must be present to initiate the citric acid cycle?
What is the final stage of cellular respiration?
What is the final stage of cellular respiration?
What is the primary role of NADH and FADH2 in oxidative phosphorylation?
What is the primary role of NADH and FADH2 in oxidative phosphorylation?
How is energy released during the electron transport chain (ETC)?
How is energy released during the electron transport chain (ETC)?
Besides glucose, which type of organic molecule can be used as an energy source?
Besides glucose, which type of organic molecule can be used as an energy source?
Which of the following describes fermentation?
Which of the following describes fermentation?
What is the role of NADH in the reduction of pyruvate during fermentation?
What is the role of NADH in the reduction of pyruvate during fermentation?
In the context of muscle cells, what causes muscle fatigue during intense activity?
In the context of muscle cells, what causes muscle fatigue during intense activity?
What response do animals exhibit when there is a lack of oxygen?
What response do animals exhibit when there is a lack of oxygen?
What is the net ATP production during anaerobic metabolism, compared to aerobic?
What is the net ATP production during anaerobic metabolism, compared to aerobic?
Flashcards
Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration
Process where cells obtain energy from organic molecules.
Glucose
Glucose
Aerobic respiration primarily uses this molecule.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis
Breaks down glucose, producing ATP and pyruvate.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cleavage Phase
Cleavage Phase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acetyl Group
Acetyl Group
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organic Molecules
Organic Molecules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Photosynthesis and Respiration
Photosynthesis and Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Used for energy
Used for energy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yeasts
Yeasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lactate or Alcohol & Carbon Dioxide
Lactate or Alcohol & Carbon Dioxide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fermentation
Fermentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Cellular respiration is a process where living cells obtain energy from organic molecules.
- The primary goal of cellular respiration is to produce ATP and NADH.
- Aerobic respiration uses oxygen: O2 is consumed and CO2 is released.
- Glucose is primarily used, but other organic molecules can also be used.
- The overall equation for aerobic respiration is C6H12O6 + 6O2 yields 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (36 or 38 ATP).
- Glucose is oxidized, and oxygen is reduced during aerobic respiration.
Metabolic Pathways
- Glycolysis.
- Breakdown of pyruvate to an acetyl group.
- Citric acid cycle.
- Oxidative phosphorylation.
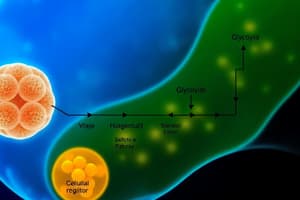
Glycolysis
- Glycolysis, the first stage of cellular respiration, occurs within the cytoplasm (outside the mitochondria).
- Glucose is broken down into 2 pyruvate molecules.
- This process does not require oxygen.
- Glycolysis involves 10 steps, divided into 3 phases.
- The steps in glycolysis are nearly identical in all living species.
- The three phases are: energy investment, cleavage, and energy liberation.
- Two ATP molecules are hydrolyzed to create fructose-1,6 bisphosphate.
- A 6-carbon molecule breaks down into two 3-carbon molecules of glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate.
- Two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate molecules are broken down into two pyruvate molecules, producing 2 NADH and 4 ATP.
- The net ATP yield in glycolysis is 2.
Breakdown of Pyruvate to Acetyl Group
- In eukaryotes, pyruvate is transported to the mitochondrial matrix.
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase breaks down pyruvate.
- A molecule of CO2 is removed from each pyruvate.
- The remaining acetyl group attaches to CoA (coenzyme A) to make acetyl CoA.
- One NADH is produced for each pyruvate molecule.
Citric Acid Cycle
- Acetyl CoA is formed from acetyl and removes it to form citrate, starting the citric acid cycle.
- The process releases 2 CO2, 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2
- Oxaloacetate is regenerated to start the cycle again.
- The cycle begins when the acetyl group from acetyl CoA attaches to oxaloacetate to form citrate.
- Citrate is rearranged to isocitrate
- Isocitrate is oxidized to α-ketoglutarate and CO2 is released, NADH is formed
- α-Ketoglutarate is oxidized as it combines with CoA to form succinyl CoA, once again, CO2 is released and NADH, is formed.
- Succinyl CoA is broken down to CoA and succinate.
- Succinate can be oxidized to fumarate and FADH2 is made
- Fumarate then combines with water to make malate
- Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate and NADH is made,
Oxidative Phosphorylation
- High-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 used to make ATP.
- This process typically requires oxygen.
- The oxidative process involves the electron transport chain (ETC).
- Phosphorylation occurs by ATP synthase.
- FADH2 produces ~2 ATPs per molecule.
- NADH produces ~3 ATPs per molecule.
Electron Transport Chain
- Both photosynthesis and respiration use an electron transport system with membrane-bound carriers.
- These carriers pass electrons from one to another.
- High-energy electrons enter the system, and low-energy electrons exit.
- Each transfer of electrons releases energy, ultimately producing ATP.
- Protein complexes and small organic molecules are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane
- Molecules acceot and donate electrons in a linear manner in a series of redox reactions.
- Movement of electrons generates a H+ electrochemical gradient/proton-motive force with excess positive charge outside of the matrix.
Other Organic Molecules
- Besides glucose, other molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can be used for energy.
- These molecules enter glycolysis or the citric acid cycle at different points.
- Using the same pathways for breakdown increases efficiency.
- Metabolism can also be used to create molecules (anabolism).
Anaerobic Metabolism
- Anaerobic metabolism does not require oxygen.
- Anaerobic bacteria (like those in cheese) use fermentation.
- Yeast uses this pathway to produce alcohol and CO2 (which makes bread rise).
- Glycolysis is followed by the reduction of pyruvate by NADH to either lactate or alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- Animal cells (e.g., humans) use fermentation.
- This is common in muscle cells.
- Fermentation provides a rapid burst of ATP.
- Lactate produces and blood carries away
- Lactate buildup causes muscles fatigue
- When stop running and heavy breathing to restore
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.