Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main role of the glycocalyx in cellular function?
What is the main role of the glycocalyx in cellular function?
- Cell recognition and attachment to other cells (correct)
- Insulation of the cell membrane
- Storage of genetic material
- Facilitation of nutrient absorption
Which of the following processes is considered a nonselective form of endocytosis?
Which of the following processes is considered a nonselective form of endocytosis?
- Pinocytosis
- Active transport
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis
- Phagocytosis (correct)
What differentiates exocytosis from endocytosis at the molecular level?
What differentiates exocytosis from endocytosis at the molecular level?
- The energy requirements of the processes
- The protein molecules utilized (correct)
- The membrane potential changes
- The type of molecules transported
Which type of transport includes both active and passive mechanisms?
Which type of transport includes both active and passive mechanisms?
What structural components contribute to the formation of the glycocalyx?
What structural components contribute to the formation of the glycocalyx?
What is the primary structural feature that distinguishes phospholipids from triglycerides?
What is the primary structural feature that distinguishes phospholipids from triglycerides?
How do phospholipids achieve their amphipathic nature?
How do phospholipids achieve their amphipathic nature?
What characteristic does the fluid mosaic model attribute to the cell membrane?
What characteristic does the fluid mosaic model attribute to the cell membrane?
Which type of bond connects fatty acids to the glycerol backbone in glycerophospholipids?
Which type of bond connects fatty acids to the glycerol backbone in glycerophospholipids?
What key functional feature differentiates sphingophospholipids from glycerophospholipids?
What key functional feature differentiates sphingophospholipids from glycerophospholipids?
What role do coated pits play in the process of endocytosis?
What role do coated pits play in the process of endocytosis?
What happens to the clathrin coat after the coated vesicle fuses with early endosomes?
What happens to the clathrin coat after the coated vesicle fuses with early endosomes?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the fate of ligands in early endosomes?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the fate of ligands in early endosomes?
How do ATP-linked H+ pumps affect the endosomal environment?
How do ATP-linked H+ pumps affect the endosomal environment?
What occurs when both the receptor and ligand are transported to the late endosome?
What occurs when both the receptor and ligand are transported to the late endosome?
What causes respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants?
What causes respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants?
Which component is primarily responsible for the formation of sphingomyelin?
Which component is primarily responsible for the formation of sphingomyelin?
Which phospholipid serves as a major blood clotting factor?
Which phospholipid serves as a major blood clotting factor?
What is the role of the hydrophilic head of phospholipids in membranes?
What is the role of the hydrophilic head of phospholipids in membranes?
What substance is produced when lecithin is split by lecithinase enzyme?
What substance is produced when lecithin is split by lecithinase enzyme?
Flashcards
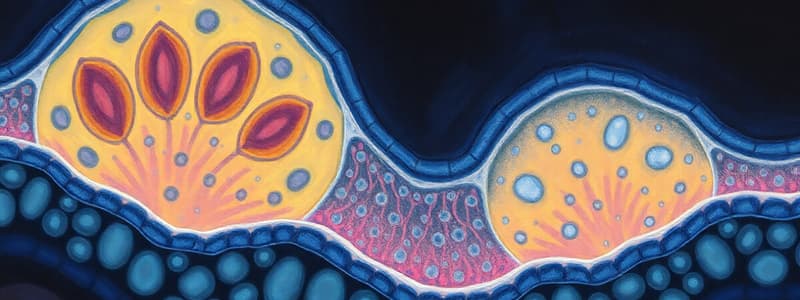
Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx
The fuzzy carbohydrate-rich region on the external surface of a cell, composed of carbohydrate chains linked to membrane proteins and lipids, and cell-secreted glycoproteins and proteoglycans.
Endocytosis
Endocytosis
The process by which a cell ingests substances from the extracellular environment.
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis
A non-selective type of endocytosis where cells engulf larger particles like microorganisms or cell debris.
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a ligand?
What is a ligand?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are coated pits?
What are coated pits?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens to clathrin after vesicle formation?
What happens to clathrin after vesicle formation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the fate of endocytosed material?
What is the fate of endocytosed material?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do endosomes become acidic?
How do endosomes become acidic?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phosphatidic Acid
Phosphatidic Acid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lecithin (Phosphatidylcholine)
Lecithin (Phosphatidylcholine)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cephalin (Phosphatidyl Ethanolamine)
Cephalin (Phosphatidyl Ethanolamine)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sphingomyelin
Sphingomyelin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structure-Function Relationship of phospholipids
Structure-Function Relationship of phospholipids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Mosaic Model
Fluid Mosaic Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Asymmetric Cell Membrane
Asymmetric Cell Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phospholipid Structure
Phospholipid Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glycerophospholipids
Glycerophospholipids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sphingophospholipids
Sphingophospholipids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cell Membrane and Vesicular Transport
- Cell membranes have diverse functions, relating to molecular structure of membrane lipids and integral/peripheral molecules.
- The fluid mosaic model describes membrane structure.
- Endocytosis and exocytosis are vital processes for transport across the cell membrane.
- Different types of endocytosis exist under normal and pathological conditions.
Cell Components
- Cells are composed of cytoplasm and nucleus.
- Cytoplasmic components are typically not easily distinguished in standard staining.
- The nucleus stains dark blue/black.
- Plasma membrane (plasmalemma) separates cytoplasm from external environment.
- Cytoplasm contains cytosol, organelles, cytoskeleton, and deposits of carbohydrates, lipids, and pigments.
- Cells organize into tissues, organs, and systems.
Plasma Membrane Structure
- Composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and oligosaccharides.
- Functions as a selective barrier.
- Membranes are thin (7.5-10nm) and only visible under electron microscopes.
Membrane Phospholipids
- Two nonpolar hydrocarbon tails linked to a hydrophilic head group.
- Tails are hydrophobic; heads are hydrophilic.
- Cholesterol is also a constituent.
Membrane Proteins
- Integral proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer.
- Peripheral proteins are loosely associated with membrane surfaces.
- Organelle-specific proteins confer unique functions to organelles.
Carbohydrates (Glycocalyx)
- Carbohydrate-rich layer lining the cell exterior (glycocalyx).
- Linked to membrane proteins and lipids, and cell-secreted components.
- Involved in cell recognition and attachments.
Membrane Transport
- Passive transport (simple and facilitated diffusion).
- Active transport (pump and cotransport carrier).
- Bulk transport (endocytosis and exocytosis).
Endocytosis
- Nonselective processes: phagocytosis (cell eating) and pinocytosis (cell drinking).
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a selectively endocytotic process.
- Involves receptors binding with cargo molecules.
- Cargo receptors are transmembrane proteins and molecules such as LDLs or protein hormones bind to these receptors.
Endosome Fate
- Early endosomes may recycle receptors to the cell surface or transfer them to late endosomes for degradation.
- Late endosomes fuse with lysosomes.
- Contents of endosomes are broken down; this includes cargo molecules, receptors, and sometimes the whole vesicle.
- Receptor-ligand complexes are also returned to cell membrane for reuse.
Lipid Structure & Functions in Bio-Membranes
- Membranes are "fluid mosaic model", meaning they are flexible to allow cell motion of components.
Phospholipids
- Ionic compounds with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
- Two main classes: glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides) and sphingophospholipids.
- Glycerophospholipids have a glycerol backbone attached to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
Cholesterol
- A steroid with four interconnected rings.
- Amphipathic.
- Controls membrane fluidity; increases fluidity at low temperatures and decreases fluidity at high temperatures.
- Helps secure proteins.
Lipid Rafts
- Specialized microdomains in the plasma membrane enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids.
- Involved in signal transduction and other cellular processes.
- Example of microdomains include caveolae
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.