Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the phrase 'form follows function' imply in architecture?
What does the phrase 'form follows function' imply in architecture?
- Buildings should be built as inexpensively as possible.
- Construction materials should prioritize aesthetics over usability.
- Buildings should have a decorative design.
- The design of buildings should support their intended use. (correct)
Which of the following are characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
Which of the following are characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
- Single circular chromosome
- Lack of organelles
- Membrane-bound nucleus (correct)
- Multiple membrane-bound organelles (correct)
What can be inferred about organelles in eukaryotic cells?
What can be inferred about organelles in eukaryotic cells?
- They perform identical functions within the cell.
- They lack a structural role in the cell.
- They compartmentalize different cellular functions. (correct)
- They are only present in plant cells.
Why do eukaryotic cells have a 'true nucleus'?
Why do eukaryotic cells have a 'true nucleus'?
What is the role of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells?
What is the role of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells?
How do eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells?
How do eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells?
What specialized cellular functions do organelles in eukaryotic cells resemble?
What specialized cellular functions do organelles in eukaryotic cells resemble?
Which of the following describes chromosomes in eukaryotic cells?
Which of the following describes chromosomes in eukaryotic cells?
What is a primary reason for eukaryotic cells having a membrane-bound nucleus?
What is a primary reason for eukaryotic cells having a membrane-bound nucleus?
Which of the following is an example of a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells?
Which of the following is an example of a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells?
How do eukaryotic cells ensure that various cellular functions are efficiently organized?
How do eukaryotic cells ensure that various cellular functions are efficiently organized?
What is a characteristic feature of the chromosomes found in eukaryotic cells?
What is a characteristic feature of the chromosomes found in eukaryotic cells?
What role does the plasma membrane play in eukaryotic cells?
What role does the plasma membrane play in eukaryotic cells?
Why might a hospital need to follow the principle of 'form follows function' in its architectural design?
Why might a hospital need to follow the principle of 'form follows function' in its architectural design?
What distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells in terms of organelles?
What distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells in terms of organelles?
In what way do the functions of organelles in eukaryotic cells compare to organs in the human body?
In what way do the functions of organelles in eukaryotic cells compare to organs in the human body?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Concept of "Form Follows Function"
- Philosophy emphasizes that the design of structures should support their intended activities.
- In architecture, this principle manifests in practical designs, such as elevators in skyscrapers and accessible emergency rooms in hospitals.
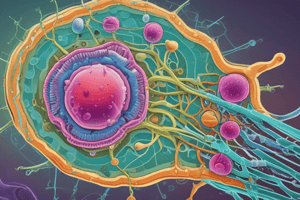
Eukaryotic Cells vs. Prokaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells possess a membrane-bound nucleus, distinguishing them from prokaryotic cells.
- They contain numerous membrane-bound organelles, including:
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Eukaryotic cells house rod-shaped chromosomes, contributing to genetic material organization.
Importance of Membrane-Bound Structures
- The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is described as a "true nucleus" due to its surrounding membrane.
- Organelles are likened to "little organs" with specialized functions within the cell.
Structural Complexity
- Eukaryotic cells exhibit greater complexity compared to prokaryotic cells.
- The presence of organelles allows for compartmentalization of different cellular functions, enhancing efficiency and organization within the cell.
Key Components of the Cell
- Before studying organelles, it is essential to understand the two fundamental components of the cell:
- Plasma membrane
- Cytoplasm
Concept of "Form Follows Function"
- Philosophy emphasizes that the design of structures should support their intended activities.
- In architecture, this principle manifests in practical designs, such as elevators in skyscrapers and accessible emergency rooms in hospitals.
Eukaryotic Cells vs. Prokaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells possess a membrane-bound nucleus, distinguishing them from prokaryotic cells.
- They contain numerous membrane-bound organelles, including:
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Eukaryotic cells house rod-shaped chromosomes, contributing to genetic material organization.
Importance of Membrane-Bound Structures
- The nucleus of eukaryotic cells is described as a "true nucleus" due to its surrounding membrane.
- Organelles are likened to "little organs" with specialized functions within the cell.
Structural Complexity
- Eukaryotic cells exhibit greater complexity compared to prokaryotic cells.
- The presence of organelles allows for compartmentalization of different cellular functions, enhancing efficiency and organization within the cell.
Key Components of the Cell
- Before studying organelles, it is essential to understand the two fundamental components of the cell:
- Plasma membrane
- Cytoplasm
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.