Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the cardiovascular system?
What is the main function of the cardiovascular system?
- To produce hormones that regulate metabolism
- To filter waste and excess fluids from the blood
- To regulate body temperature
- To transport oxygen and nutrients to cells and remove waste products (correct)
What is the outermost layer of the blood vessel wall composed of?
What is the outermost layer of the blood vessel wall composed of?
- Endothelium
- Tunica media
- Tunica externa
- Adventitia (correct)
What is the term for the sequence of electrical events that occurs in the heart during each heartbeat?
What is the term for the sequence of electrical events that occurs in the heart during each heartbeat?
- Electrocardiogram
- Electrical conduction
- Cardiac cycle (correct)
- Cardiac contraction
Which of the following blood vessels has the thickest tunica media?
Which of the following blood vessels has the thickest tunica media?
What is the primary function of the endothelium in blood vessels?
What is the primary function of the endothelium in blood vessels?
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of mechanical events that occurs in the heart during each heartbeat.
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of mechanical events that occurs in the heart during each heartbeat.
The tunica intima is the middle layer of the blood vessel wall.
The tunica intima is the middle layer of the blood vessel wall.
The tunica media is the outermost layer of the blood vessel wall.
The tunica media is the outermost layer of the blood vessel wall.
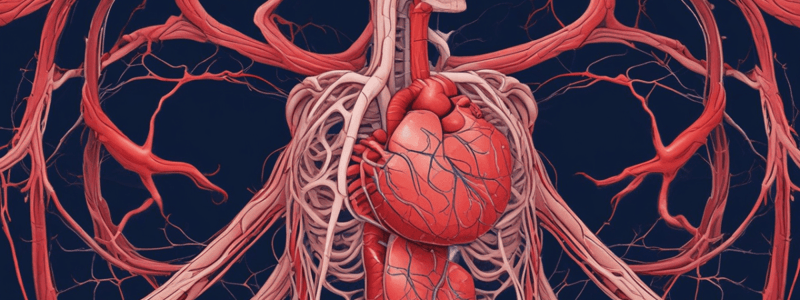
The cardiovascular system is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body's cells and removing waste products.
The cardiovascular system is responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body's cells and removing waste products.
The cardiac cycle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
The cardiac cycle is controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
In the cardiovascular system, blood is carried through a network of ______
In the cardiovascular system, blood is carried through a network of ______
The structure of the blood vessel wall consists of tunica intima, tunica media, and ______
The structure of the blood vessel wall consists of tunica intima, tunica media, and ______
The cardiac cycle involves the electrical conduction through the ______
The cardiac cycle involves the electrical conduction through the ______
The thickest layer of the blood vessel wall is the ______
The thickest layer of the blood vessel wall is the ______
Blood vessels play a crucial role in the circulation of ______
Blood vessels play a crucial role in the circulation of ______
Tachycardia is characterized by a ______ heart rate
Tachycardia is characterized by a ______ heart rate
Bradycardia is characterized by a ______ heart rate
Bradycardia is characterized by a ______ heart rate
Asystole results in no ______ contraction
Asystole results in no ______ contraction
The lumen is the space within the blood vessel where the ______ flows
The lumen is the space within the blood vessel where the ______ flows
Vaso- is a prefix relating to a ______
Vaso- is a prefix relating to a ______
What is the term for a heart rate that is slower than normal?
What is the term for a heart rate that is slower than normal?
What is the term for the membrane or layer of tissue that envelops a blood vessel?
What is the term for the membrane or layer of tissue that envelops a blood vessel?
What is the term for a heart rate that is faster than normal?
What is the term for a heart rate that is faster than normal?
What is the term for the cavity or channel within a tube or tubular organ such as a blood vessel?
What is the term for the cavity or channel within a tube or tubular organ such as a blood vessel?
What is the prefix that relates to a vessel?
What is the prefix that relates to a vessel?
What is the term for the absence of ventricular contraction in the heart?
What is the term for the absence of ventricular contraction in the heart?
What is the function of the lumen in a blood vessel?
What is the function of the lumen in a blood vessel?
What is the prefix that means 'relating to a vessel'?
What is the prefix that means 'relating to a vessel'?
What is the term for the layer of tissue that envelops a blood vessel?
What is the term for the layer of tissue that envelops a blood vessel?
What is the term for a heart rate that is faster than normal?
What is the term for a heart rate that is faster than normal?
The lumen is the outermost layer of the blood vessel wall.
The lumen is the outermost layer of the blood vessel wall.
Tachycardia is a condition characterized by a slow heart rate.
Tachycardia is a condition characterized by a slow heart rate.
Vaso- is a prefix that means 'relating to the heart'.
Vaso- is a prefix that means 'relating to the heart'.
Asystole is a condition characterized by a normal heart rate.
Asystole is a condition characterized by a normal heart rate.
The tunica is the innermost layer of the blood vessel wall.
The tunica is the innermost layer of the blood vessel wall.
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Match the following cardiovascular terms with their meanings:
Match the following cardiovascular terms with their meanings:
Pair the terms with their cardiovascular descriptions:
Pair the terms with their cardiovascular descriptions:
Match the terminology with their vessel-related associations:
Match the terminology with their vessel-related associations:
Connect the terms with their cardiovascular meanings:
Connect the terms with their cardiovascular meanings:
____ is a fast heart rate
____ is a fast heart rate
The absence of ventricular contraction is known as ______
The absence of ventricular contraction is known as ______
The ______ is the cavity within a tubular organ such as a blood vessel
The ______ is the cavity within a tubular organ such as a blood vessel
Tunica is the enveloping membrane or layer of tissue of a ______
Tunica is the enveloping membrane or layer of tissue of a ______
____ is pertaining to a vessel
____ is pertaining to a vessel
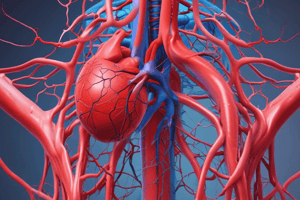
What is the main function of the oxygenated blood leaving the heart through the aorta?
What is the main function of the oxygenated blood leaving the heart through the aorta?
What is the location of gas and nutrient exchange in the cardiovascular system?
What is the location of gas and nutrient exchange in the cardiovascular system?
What is the direction of blood flow in the arteries?
What is the direction of blood flow in the arteries?
What happens to the blood vessels after the capillaries?
What happens to the blood vessels after the capillaries?
Which type of blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood, apart from the pulmonary veins?
Which type of blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood, apart from the pulmonary veins?
Arteries carry deoxygenated blood away from the heart.
Arteries carry deoxygenated blood away from the heart.
Veins carry oxygenated blood towards the heart.
Veins carry oxygenated blood towards the heart.
Gas and nutrient exchange occurs in the arteries through passive diffusion.
Gas and nutrient exchange occurs in the arteries through passive diffusion.
The cranial and caudal vena cavae are arteries that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
The cranial and caudal vena cavae are arteries that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
The aorta is the largest vein that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.
The aorta is the largest vein that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the ______
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the ______
Carry oxygenated blood apart from the ______ arteries
Carry oxygenated blood apart from the ______ arteries
Oxygenated blood leaves the heart through the ______ – divides into smaller and smaller arteries
Oxygenated blood leaves the heart through the ______ – divides into smaller and smaller arteries
The vessels converge and get larger and larger until the deoxygenated blood enters the ______ and ______ vena cavae
The vessels converge and get larger and larger until the deoxygenated blood enters the ______ and ______ vena cavae
Gas and nutrient exchange occurs in the ______ by passive diffusion
Gas and nutrient exchange occurs in the ______ by passive diffusion