Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the average size of the heart?
What is the average size of the heart?
- 9cm X 6cm
- 12cm X 9cm (correct)
- 15cm X 10cm
- 10cm X 7cm
What are the two functional components of the cardiovascular system?
What are the two functional components of the cardiovascular system?
Heart and Vascular System
The pericardium is the inner layer of the heart wall.
The pericardium is the inner layer of the heart wall.
False (B)
What are the three layers of the heart wall?
What are the three layers of the heart wall?
The heart weighs approximately ______.
The heart weighs approximately ______.
What is known as the epicardium?
What is known as the epicardium?
What is the function of the pericardium?
What is the function of the pericardium?
What does the pericardial cavity contain?
What does the pericardial cavity contain?
What lies between the two layers of the pericardium?
What lies between the two layers of the pericardium?
Match the components of the heart with their functions:
Match the components of the heart with their functions:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Overview of the Cardiovascular System
- Central components: heart (pump) and vasculature (blood vessels) for blood distribution.
- Core functions include collection and distribution of blood, transporting oxygen and nutrients, and removing waste products.
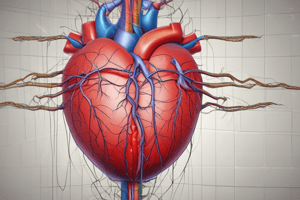
The Functional Anatomy of the Heart
- Muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the circulatory system.
- Dimensions: approximately 12 cm in length and 9 cm in breadth, resembling a closed fist.
- Average weight is around 250 grams.
- Located between the lungs in the mediastinum, resting on the diaphragm, positioned ⅔ to the left of the midline.
The Wall of the Heart
- Composed of three main layers: pericardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
Pericardium
-
Outer Parietal Pericardium:
- Strong protective sac that anchors the heart in the mediastinum.
- Composed of two layers: outer fibrous layer and inner serous layer.
-
Inner Viscera Pericardium (Epicardium):
- Lines the surface of the myocardium, composed of flattened epithelial cells.
Outer Fibrous Layer
- Made of thick fibrous connective tissue with inelastic fibers.
- Protects the heart from overstretching and is continuous with the outer wall (tunica adventitia) of entering and exiting blood vessels.
Inner Serous Layer
- Composed of mesothelium with squamous epithelial cells.
- Secretes a small amount of fluid to reduce friction during heart movement.
Functions of the Pericardium
- Protects and anchors the heart.
- Prevents overfilling of the heart with blood.
- Allows for friction-free movement of the heart during contraction and relaxation.
Chambers of the Heart
-
Left Side:
- Comprises the left atrium (LA) and left ventricle (LV).
-
Right Side:
- Comprises the right atrium (RA) and right ventricle (RV).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.