Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of glycolysis in glucose metabolism?
What is the primary purpose of glycolysis in glucose metabolism?
Which of the following accurately describes the glycolytic pathway?
Which of the following accurately describes the glycolytic pathway?
How many pyruvic acid molecules are formed from one glucose molecule during glycolysis?
How many pyruvic acid molecules are formed from one glucose molecule during glycolysis?
What compound is formed directly from glucose before it is split in glycolysis?
What compound is formed directly from glucose before it is split in glycolysis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most significant advantage of the enzymatic breakdown of glucose?
What is the most significant advantage of the enzymatic breakdown of glucose?
Signup and view all the answers
In how many steps is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate converted into pyruvic acid during glycolysis?
In how many steps is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate converted into pyruvic acid during glycolysis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of cytochrome A3 in the electron transport chain?
What is the primary role of cytochrome A3 in the electron transport chain?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens during the transport of electrons through the electron transport chain?
What happens during the transport of electrons through the electron transport chain?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the outcome of high concentrations of H+ ions in the outer chamber of mitochondria?
What is the outcome of high concentrations of H+ ions in the outer chamber of mitochondria?
Signup and view all the answers
Which protein molecule is primarily responsible for converting ADP into ATP?
Which protein molecule is primarily responsible for converting ADP into ATP?
Signup and view all the answers
What is formed when ionic oxygen combines with hydrogen during the electron transport process?
What is formed when ionic oxygen combines with hydrogen during the electron transport process?
Signup and view all the answers
What effect does the electron transport chain have on the inner matrix of the mitochondrion?
What effect does the electron transport chain have on the inner matrix of the mitochondrion?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of protein carrier molecules in glucose transport?
What is the primary role of protein carrier molecules in glucose transport?
Signup and view all the answers
What mechanism allows glucose to be absorbed against its concentration gradient?
What mechanism allows glucose to be absorbed against its concentration gradient?
Signup and view all the answers
What effect does insulin have during the process of facilitated diffusion of glucose?
What effect does insulin have during the process of facilitated diffusion of glucose?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements about phosphorylation of glucose is true?
Which of the following statements about phosphorylation of glucose is true?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main function of glucose phosphatase in certain cells?
What is the main function of glucose phosphatase in certain cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the result of glucose combining with a phosphate radical upon entering the cell cytoplasm?
What is the result of glucose combining with a phosphate radical upon entering the cell cytoplasm?
Signup and view all the answers
During which process does glucose concentration change from high to low?
During which process does glucose concentration change from high to low?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of transport mechanism does not require energy?
Which type of transport mechanism does not require energy?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of carbohydrate metabolism in the body?
What is the primary role of carbohydrate metabolism in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What is one of the main metabolic pathways compared in carbohydrate metabolism?
What is one of the main metabolic pathways compared in carbohydrate metabolism?
Signup and view all the answers
Which molecules primarily control the process of glycolysis in the body?
Which molecules primarily control the process of glycolysis in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What is glycogenesis?
What is glycogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following describes gluconeogenesis?
Which of the following describes gluconeogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is primarily oxidized to release energy during carbohydrate metabolism?
What is primarily oxidized to release energy during carbohydrate metabolism?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the net gain of ATP from glycolysis?
What is the net gain of ATP from glycolysis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is primarily produced during the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)?
What is primarily produced during the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP)?
Signup and view all the answers
Which molecule does the hydrogen atom combine with in the pentose phosphate pathway?
Which molecule does the hydrogen atom combine with in the pentose phosphate pathway?
Signup and view all the answers
How many molecules of glucose can be resynthesized for every 6 molecules of glucose broken down in the cycle?
How many molecules of glucose can be resynthesized for every 6 molecules of glucose broken down in the cycle?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to glucose when the glycolytic pathway slows due to cellular inactivity?
What happens to glucose when the glycolytic pathway slows due to cellular inactivity?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the pentose phosphate pathway provide independently of the Krebs cycle?
What does the pentose phosphate pathway provide independently of the Krebs cycle?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the end product of glucose breakdown in the pentose phosphate pathway?
What is the end product of glucose breakdown in the pentose phosphate pathway?
Signup and view all the answers
How many revolutions of the cycle are needed to resynthesize one molecule of glucose?
How many revolutions of the cycle are needed to resynthesize one molecule of glucose?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Carbohydrate Metabolism Overview
- Central role of glucose in providing energy for physiological functions such as muscle activity and nerve transmission.
- Energy is released from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins via chemical reactions.
- Cellular enzymes and energy transfer systems facilitate the coupling of reactions to physiological functions.
Glucose Transport
- Glucose moves from areas of high concentration to low concentration across cell membranes.
- Proteins act as carriers for glucose through facilitated diffusion, supported by sodium-glucose co-transport which requires ATP for the active transport of sodium.
- Insulin enhances the facilitated diffusion of glucose.
Glycogen Formation and Storage
- Upon entering the cytoplasm, glucose is phosphorylated by glucokinase (in the liver) or hexokinase (in other cells), trapping it inside the cell.
- The phosphorylation process is irreversible except in specific cells (liver, renal, intestinal) where glucose phosphatase allows reversibility.
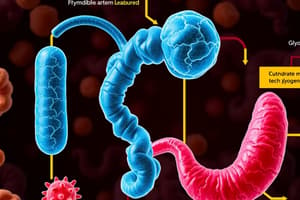
Glycolysis and Metabolic Pathways
- Glycolysis is the initial step of glucose metabolism, splitting glucose to form two molecules of pyruvic acid and generating ATP.
- Ten specific enzyme-catalyzed reactions occur during glycolysis, starting from glucose to pyruvate.
- The Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation follow glycolysis, maximizing ATP production (up to 38 moles of ATP from 1 mole of glucose).
Krebs Cycle and ATP Production
- Electrons produced in glycolysis are transported via cytochromes in the electron transport chain to reduce oxygen and form water while releasing energy.
- Energy released from the electron transport chain generates an H+ ion gradient, enabling ATP synthesis by ATP synthetase.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP)
- Alternative pathway for glucose metabolism, particularly in liver and fat cells, that metabolizes glucose independently of the Krebs cycle.
- Produces D-ribulose from glucose, which can be converted into various carbon sugars, allowing for glucose resynthesis.
- High efficiency in resynthesizing glucose, requiring 6 glucose molecules to form 5 glucose molecules overall in the cycle.
Regulation of Gluconeogenesis
- H atoms generated during the PPP, combining with NADP+ to form NADPH, are crucial for fat synthesis from carbohydrates.
- When glycolysis is slowed due to inactivity, the PPP continues to function, breaking down excess glucose and maintaining metabolic balance.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the intricacies of carbohydrate metabolism, focusing on the formation and storage of glycogen, and the various metabolic pathways including glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. This quiz will also delve into the regulatory mechanisms of glycolysis and the process of gluconeogenesis. Enhance your understanding of how ATP and ADP concentrations control these vital processes.