Podcast
Questions and Answers
In the context of assessing sagittal plane mobility at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ), what clinical finding would most strongly suggest underlying generalized ligamentous laxity, potentially influencing the biomechanical approach to hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction?
In the context of assessing sagittal plane mobility at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ), what clinical finding would most strongly suggest underlying generalized ligamentous laxity, potentially influencing the biomechanical approach to hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction?
- A total excursion of 12 mm, indicative of moderate sagittal plane hypermobility.
- A total excursion of 8 mm, with 4 mm of dorsiflexion and 4 mm of plantarflexion.
- Presence of crepitus during sagittal plane range of motion testing.
- A total excursion of 16 mm or greater, suggesting substantial hypermobility. (correct)
During physical examination of a patient with hallux abducto valgus (HAV), assessment of transverse plane mobility is crucial. Which statement accurately reflects the expected findings and their clinical implications?
During physical examination of a patient with hallux abducto valgus (HAV), assessment of transverse plane mobility is crucial. Which statement accurately reflects the expected findings and their clinical implications?
- Normally, there is minimal to no transverse plane mobility at the first MTPJ. (correct)
- A significant increase in transverse plane mobility at the first MTPJ indicates severe degenerative joint disease.
- Transverse plane mobility should normally be pronounced; its absence suggests joint fusion.
- Transverse plane mobility is directly proportional to the severity of the hallux abductus angle (HAA).
When evaluating the quality of motion at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) in a patient with hallux abducto valgus (HAV), what clinical finding is most indicative of structural adaptation of the articular cartilage, which may influence surgical decision-making?
When evaluating the quality of motion at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) in a patient with hallux abducto valgus (HAV), what clinical finding is most indicative of structural adaptation of the articular cartilage, which may influence surgical decision-making?
- Hypermobility detected during sagittal plane assessment.
- Poor quality of motion, characterized by restricted or altered joint movement. (correct)
- Presence of crepitus throughout the entire range of motion.
- Pain elicited during retrograde force application across the joint.
In the evaluation of the axis of motion at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) in hallux abducto valgus (HAV), which observation during physical examination would prompt the consideration of lateral soft tissue release as an initial step?
In the evaluation of the axis of motion at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) in hallux abducto valgus (HAV), which observation during physical examination would prompt the consideration of lateral soft tissue release as an initial step?
A patient presents with a pinch callus under the second metatarsal. What specific pathomechanics is most likely influencing the formation of this pinch callus?
A patient presents with a pinch callus under the second metatarsal. What specific pathomechanics is most likely influencing the formation of this pinch callus?
What radiographic projection is critical for accurately evaluating the degree of sesamoid subluxation and crista erosion in the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity?
What radiographic projection is critical for accurately evaluating the degree of sesamoid subluxation and crista erosion in the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity?
When evaluating radiographic parameters for hallux abducto valgus (HAV), what is the clinical implication of an elevated Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA) exceeding 35 degrees?
When evaluating radiographic parameters for hallux abducto valgus (HAV), what is the clinical implication of an elevated Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA) exceeding 35 degrees?
What is the primary advantage of obtaining weightbearing radiographs when assessing hallux abducto valgus (HAV) compared to non-weightbearing radiographs?
What is the primary advantage of obtaining weightbearing radiographs when assessing hallux abducto valgus (HAV) compared to non-weightbearing radiographs?
In a patient presenting with hallux abducto valgus (HAV) and a hallux interphalangeus angle (HIAA) of 12 degrees, which of the following statements is most appropriate?
In a patient presenting with hallux abducto valgus (HAV) and a hallux interphalangeus angle (HIAA) of 12 degrees, which of the following statements is most appropriate?
Surgical correction of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) aims to restore normal anatomy and biomechanics. Which osteotomy is least likely to correct the PASA?
Surgical correction of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) aims to restore normal anatomy and biomechanics. Which osteotomy is least likely to correct the PASA?
A surgeon is planning a McBride bunionectomy for a patient with hallux abducto valgus (HAV). Which of the following steps is considered a component of the classical or 'true' McBride procedure but is now largely avoided due to increased risk of complications?
A surgeon is planning a McBride bunionectomy for a patient with hallux abducto valgus (HAV). Which of the following steps is considered a component of the classical or 'true' McBride procedure but is now largely avoided due to increased risk of complications?
What is the impact of the Silver bunionectomy on deformity correction?
What is the impact of the Silver bunionectomy on deformity correction?
In the context of understanding blood supply to the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ), which surgical approach minimizes the risk of iatrogenic avascular necrosis (AVN) to the first metatarsal head?
In the context of understanding blood supply to the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ), which surgical approach minimizes the risk of iatrogenic avascular necrosis (AVN) to the first metatarsal head?
What negative outcome can result from 'staking' the metatarsal head during a silver bunionectomy?
What negative outcome can result from 'staking' the metatarsal head during a silver bunionectomy?
A patient with a complex hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity undergoes a Lapidus procedure. Postoperatively, the patient develops persistent pain and radiographic evaluation reveals a non-union at the tarsometatarsal joint and nerve entrapment. What mechanical factor is most likely contributing to the non-union in this scenario?
A patient with a complex hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity undergoes a Lapidus procedure. Postoperatively, the patient develops persistent pain and radiographic evaluation reveals a non-union at the tarsometatarsal joint and nerve entrapment. What mechanical factor is most likely contributing to the non-union in this scenario?
Which of the following statement accurately reflects a key technical consideration during a Silver bunionectomy?
Which of the following statement accurately reflects a key technical consideration during a Silver bunionectomy?
In the context of proximal phalangeal osteotomies for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, an oblique Akin osteotomy, known for its ability to accommodate screw fixation, is described as a 'cheater' Akin. What does this term imply?
In the context of proximal phalangeal osteotomies for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, an oblique Akin osteotomy, known for its ability to accommodate screw fixation, is described as a 'cheater' Akin. What does this term imply?
What is the primary factor in determining the type of distal metatarsal osteotomy?
What is the primary factor in determining the type of distal metatarsal osteotomy?
A patient presents with hallux abducto valgus, elevated intermetatarsal angle (IMA), and radiographic evidence of metatarsus primus elevatus. Which surgical procedure addresses all three components of this deformity?
A patient presents with hallux abducto valgus, elevated intermetatarsal angle (IMA), and radiographic evidence of metatarsus primus elevatus. Which surgical procedure addresses all three components of this deformity?
When performing a medial capsulorrhaphy to tighten the medial joint capsule during hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, which statement accurately reflects a critical component for optimizing surgical outcome?
When performing a medial capsulorrhaphy to tighten the medial joint capsule during hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, which statement accurately reflects a critical component for optimizing surgical outcome?
A surgeon is considering a distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction. Which characteristic explicitly prohibits correction of the frontal plane using DMO?
A surgeon is considering a distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction. Which characteristic explicitly prohibits correction of the frontal plane using DMO?
In the context of distal metatarsal osteotomies (DMOs), what is the key distinction between a unicorrectional and a bicorrectional osteotomy?
In the context of distal metatarsal osteotomies (DMOs), what is the key distinction between a unicorrectional and a bicorrectional osteotomy?
When performing a SCARF osteotomy for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, what specific complication related to the capital fragment might arise during surgical execution?
When performing a SCARF osteotomy for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, what specific complication related to the capital fragment might arise during surgical execution?
During a Lapidus procedure, a surgeon aims to achieve multiplanar correction of hallux abducto valgus (HAV). What statement reflects the most significant advantage when compared to other HAV correction?
During a Lapidus procedure, a surgeon aims to achieve multiplanar correction of hallux abducto valgus (HAV). What statement reflects the most significant advantage when compared to other HAV correction?
Ankle Equinus influence on Bunion?
Ankle Equinus influence on Bunion?
A patient develops iatrogenic hallux varus following surgical correction of hallux abducto valgus (HAV). If revision surgery is being considered while preserving the joint, what does this indicate?
A patient develops iatrogenic hallux varus following surgical correction of hallux abducto valgus (HAV). If revision surgery is being considered while preserving the joint, what does this indicate?
What is a transverse plane instability at the first MTPJ?
What is a transverse plane instability at the first MTPJ?
A 46-year-old female presents with a left bunion. She is having difficulty finding shoes that fit, and has substantial pain. She has tried many conservative treatments, and has no remarkable PMH. PE reveals a severe HAV deformity with a hypermobile first ray, and the ROM of the hallux is track-bound without crepitus. What should be the next step?
A 46-year-old female presents with a left bunion. She is having difficulty finding shoes that fit, and has substantial pain. She has tried many conservative treatments, and has no remarkable PMH. PE reveals a severe HAV deformity with a hypermobile first ray, and the ROM of the hallux is track-bound without crepitus. What should be the next step?
A 42-year-old female presents with a right bunion with severe HAV deformity and hypermobile first ray with a history of gastric bypass surgery. Conservative measures have failed. Which step would most likely be involved in the treatment?
A 42-year-old female presents with a right bunion with severe HAV deformity and hypermobile first ray with a history of gastric bypass surgery. Conservative measures have failed. Which step would most likely be involved in the treatment?
A patient presents to your practice complaining of bunion pain with a history of having a gastric bypass. Recognizing the potential impact from the bypass, you order bloodwork. What kind of vitamin deficiency would you be most concerned in terms of its influence on both bone quality and nerve health?
A patient presents to your practice complaining of bunion pain with a history of having a gastric bypass. Recognizing the potential impact from the bypass, you order bloodwork. What kind of vitamin deficiency would you be most concerned in terms of its influence on both bone quality and nerve health?
What is a main concern with the Kalish osteotomy
What is a main concern with the Kalish osteotomy
What structural change occur in hallux varus when the hallux assumes the adducted plane?
What structural change occur in hallux varus when the hallux assumes the adducted plane?
A 68 year old female needs a bunionecotomy, what should you do?
A 68 year old female needs a bunionecotomy, what should you do?
What should be done during the first step of bunion evaluation?
What should be done during the first step of bunion evaluation?
What view do you view tibial sesamoid?
What view do you view tibial sesamoid?
When would DMO be performed?
When would DMO be performed?
A patient undergoes Keller resection, what are their potential complications?
A patient undergoes Keller resection, what are their potential complications?
After performing a bunionectomy, what complication can you expect?
After performing a bunionectomy, what complication can you expect?
What two nerves are you concerned about transection during bunion surgery?
What two nerves are you concerned about transection during bunion surgery?
What does reefing a capsule imply, during surgery?
What does reefing a capsule imply, during surgery?
A patient with a severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity exhibits radiographic evidence of an 'atavistic' medial cuneiform. Which statement best elucidates the clinical implications of this finding?
A patient with a severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity exhibits radiographic evidence of an 'atavistic' medial cuneiform. Which statement best elucidates the clinical implications of this finding?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, which of the following statements most accurately correlates the clinical relevance of the metatarsal head shape with the biomechanical function and stability of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ)?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, which of the following statements most accurately correlates the clinical relevance of the metatarsal head shape with the biomechanical function and stability of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ)?
When evaluating radiographic parameters in hallux abducto valgus (HAV), an elevated Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA) exceeding 35 degrees presents a significant challenge to comprehensive deformity correction. What surgical consideration is most appropriate?
When evaluating radiographic parameters in hallux abducto valgus (HAV), an elevated Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA) exceeding 35 degrees presents a significant challenge to comprehensive deformity correction. What surgical consideration is most appropriate?
A patient undergoing hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction exhibits a pre-operative Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) significantly outside the normal range. Which statement reflects the most critical surgical implication of this finding?
A patient undergoing hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction exhibits a pre-operative Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) significantly outside the normal range. Which statement reflects the most critical surgical implication of this finding?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) surgery, what is the most critical implication to the surgeon of overtightening the medial capsule?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) surgery, what is the most critical implication to the surgeon of overtightening the medial capsule?
In scenarios necessitating isolated medial eminence resection, like the Silver procedure, preserving the tibial sesamoid articulation is paramount to prevent a specific complication. What intraoperative error should be avoided?
In scenarios necessitating isolated medial eminence resection, like the Silver procedure, preserving the tibial sesamoid articulation is paramount to prevent a specific complication. What intraoperative error should be avoided?
A surgeon, attempting to re-establish a congruent first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) following distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV), overlooks a pre-existing lateral soft tissue contracture. What outcome is most likely?
A surgeon, attempting to re-establish a congruent first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) following distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV), overlooks a pre-existing lateral soft tissue contracture. What outcome is most likely?
A 46-year-old female presents with left bunion pain, a severe HAV deformity, a hypermobile first ray and track-bound without crepitus. Shoe-gear and custom orthotics did not help sufficiently . What is the most likely next step?
A 46-year-old female presents with left bunion pain, a severe HAV deformity, a hypermobile first ray and track-bound without crepitus. Shoe-gear and custom orthotics did not help sufficiently . What is the most likely next step?
In performing Keller resection what is the result of complete resection?
In performing Keller resection what is the result of complete resection?
In a patient with a progressive hallux abducto valgus deformity where conservative treatments have failed, and radiographic assessment reveals a significantly elevated hallux interphalangeus angle (HIAA) exceeding 20 degrees, What step should be taken?
In a patient with a progressive hallux abducto valgus deformity where conservative treatments have failed, and radiographic assessment reveals a significantly elevated hallux interphalangeus angle (HIAA) exceeding 20 degrees, What step should be taken?
During a modified McBride bunionectomy, what anatomical structure requires meticulous identification and protection to prevent iatrogenic complications?
During a modified McBride bunionectomy, what anatomical structure requires meticulous identification and protection to prevent iatrogenic complications?
During a Lapidus procedure, what is the surgeon's primary goal in correcting frontal plane rotation of the first metatarsal, and how is this achieved?
During a Lapidus procedure, what is the surgeon's primary goal in correcting frontal plane rotation of the first metatarsal, and how is this achieved?
When performing a distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus correction, which of the following is an absolute contraindication?
When performing a distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus correction, which of the following is an absolute contraindication?
In the context of performing a medial capsulorrhaphy as part of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, reefing the capsule implies what surgical maneuver, and what biomechanical principle does it aim to restore?
In the context of performing a medial capsulorrhaphy as part of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, reefing the capsule implies what surgical maneuver, and what biomechanical principle does it aim to restore?
What are the steps of a true McBride Bunionectomy?
What are the steps of a true McBride Bunionectomy?
Hallux Varus assumes what kind of position?
Hallux Varus assumes what kind of position?
What are the primary goals of a Lapidus procedure in the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, and how does it achieve multiplanar stability?
What are the primary goals of a Lapidus procedure in the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, and how does it achieve multiplanar stability?
In performing distal metatarsal osteotomies (DMOs) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, surgeons must distinguish between unicorrectional and bicorrectional techniques. At which plane does this distinction occur?
In performing distal metatarsal osteotomies (DMOs) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, surgeons must distinguish between unicorrectional and bicorrectional techniques. At which plane does this distinction occur?
What are the benefits and drawbacks of using the Kalish osteotomy?
What are the benefits and drawbacks of using the Kalish osteotomy?
Which statement best describes the primary objective of metatarsal osteotomies?
Which statement best describes the primary objective of metatarsal osteotomies?
In a patient status post bunionectomy, what are the two main nerves of concern, relative to the transection, during surgery?
In a patient status post bunionectomy, what are the two main nerves of concern, relative to the transection, during surgery?
In instances when structural adaption of the articular cartilage occurs, what can that lead to?
In instances when structural adaption of the articular cartilage occurs, what can that lead to?
How is Hallux Interphalangeus diagnosed in radiographic evaluation?
How is Hallux Interphalangeus diagnosed in radiographic evaluation?
Why must radiorgraphs be weight bearing when dealing with bunion?
Why must radiorgraphs be weight bearing when dealing with bunion?
In evaluating hallux abducto valgus, how would hypermobility be measured?
In evaluating hallux abducto valgus, how would hypermobility be measured?
When performing a SCARF osteotomy, what surgical error can be made?
When performing a SCARF osteotomy, what surgical error can be made?
With DMO which is Versatility?
With DMO which is Versatility?
What is reefing?
What is reefing?
True or False. Silver Bunionectomy has deformity correction.
True or False. Silver Bunionectomy has deformity correction.
What was part of the original procedure for Akin when it was described in 1925?
What was part of the original procedure for Akin when it was described in 1925?
What radiographic parameter should be assessed when taking the first step in bunion evaluation?
What radiographic parameter should be assessed when taking the first step in bunion evaluation?
What is the next step after seeing a severe HAV deformity with a hypermobile first ray, on a 42 year old female with a history of gastric bypass?
What is the next step after seeing a severe HAV deformity with a hypermobile first ray, on a 42 year old female with a history of gastric bypass?
If you have a long and mildly elevated 1st metatarsals, what should you perform?
If you have a long and mildly elevated 1st metatarsals, what should you perform?
What should a surgeon do to remove the medial prominence, or a Silver procedure?
What should a surgeon do to remove the medial prominence, or a Silver procedure?
Structural deformity within the hallux, are hallux is Hallus Interphalangeus or is it
Structural deformity within the hallux, are hallux is Hallus Interphalangeus or is it
Metartsal length can be adjuste with which one?
Metartsal length can be adjuste with which one?
Which vitamin deficiency is commonly seen with bypass surgery, and should be assessed when thinking about bones?
Which vitamin deficiency is commonly seen with bypass surgery, and should be assessed when thinking about bones?
The Modified McBride bunionectomy is more common how?
The Modified McBride bunionectomy is more common how?
True or False: is first MTPJ fusion appropriate even with a non-arthritic joint?
True or False: is first MTPJ fusion appropriate even with a non-arthritic joint?
Are you able to correct for the lateral plane with Scarf?
Are you able to correct for the lateral plane with Scarf?
In a complex revision case following a failed Lapidus procedure with persistent non-union, what adjuvant surgical intervention, beyond standard bone grafting and internal fixation augmentation, would most directly address compromised intrinsic vascularity at the fusion site?
In a complex revision case following a failed Lapidus procedure with persistent non-union, what adjuvant surgical intervention, beyond standard bone grafting and internal fixation augmentation, would most directly address compromised intrinsic vascularity at the fusion site?
A patient exhibiting a hallux abducto valgus (HAV) exhibits radiographic evidence of an atavistic medial cuneiform configuration. How would you evaluate this radiographic finding?
A patient exhibiting a hallux abducto valgus (HAV) exhibits radiographic evidence of an atavistic medial cuneiform configuration. How would you evaluate this radiographic finding?
During a SCARF osteotomy for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, excessive 'troughing' is observed intraoperatively. This error inadvertently causes which of the following:
During a SCARF osteotomy for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, excessive 'troughing' is observed intraoperatively. This error inadvertently causes which of the following:
A surgeon is planning a Lapidus procedure for a patient with severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV) and noted hypermobility. Considering current evidence-based practice, what adjunctive measure would best mitigate the risk of recurrent deformity and maximize long-term stability?
A surgeon is planning a Lapidus procedure for a patient with severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV) and noted hypermobility. Considering current evidence-based practice, what adjunctive measure would best mitigate the risk of recurrent deformity and maximize long-term stability?
A patient presents with a painful, recurrent hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity several years after undergoing a McBride bunionectomy with fibular sesamoidectomy. Radiographic evaluation reveals significant hallux varus, negative intermetatarsal angle, and degenerative changes at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). What revisional procedure offers the most predictable and biomechanically sound long-term solution?
A patient presents with a painful, recurrent hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity several years after undergoing a McBride bunionectomy with fibular sesamoidectomy. Radiographic evaluation reveals significant hallux varus, negative intermetatarsal angle, and degenerative changes at the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). What revisional procedure offers the most predictable and biomechanically sound long-term solution?
A 42-year-old female with a history of gastric bypass presents with severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV). Recognizing potential complications related to her prior surgery, what bloodwork would be most beneficial to assess before surgical intervention?
A 42-year-old female with a history of gastric bypass presents with severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV). Recognizing potential complications related to her prior surgery, what bloodwork would be most beneficial to assess before surgical intervention?
In the context of a Lapidus procedure, meticulous reduction and maintenance of first metatarsal alignment are paramount. Intraoperatively, how can a surgeon best ensure accurate rotational alignment of the first metatarsal in the transverse plane relative to the lesser tarsus?
In the context of a Lapidus procedure, meticulous reduction and maintenance of first metatarsal alignment are paramount. Intraoperatively, how can a surgeon best ensure accurate rotational alignment of the first metatarsal in the transverse plane relative to the lesser tarsus?
A 68-year-old female who is an avid caregiver for multiple cats presents for bunion evaluation. Considering her age and lifestyle, what modifications should be done?
A 68-year-old female who is an avid caregiver for multiple cats presents for bunion evaluation. Considering her age and lifestyle, what modifications should be done?
In a patient undergoing hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction with an elevated Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA) exceeding 35 degrees, what must be considered about performing a metatarsus adductus correction?
In a patient undergoing hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction with an elevated Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA) exceeding 35 degrees, what must be considered about performing a metatarsus adductus correction?
During surgical planning for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, a surgeon notes the patient's first metatarsal head exhibits a significantly rounded shape on radiographs. How best would you interpret this shape?
During surgical planning for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction, a surgeon notes the patient's first metatarsal head exhibits a significantly rounded shape on radiographs. How best would you interpret this shape?
A surgeon is about to perform a distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction. Which intraoperative assessment would absolutely contraindicate proceeding with a DMO?
A surgeon is about to perform a distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO) for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction. Which intraoperative assessment would absolutely contraindicate proceeding with a DMO?
A patient who underwent a hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction now demonstrates a hallux that assumes an adducted position in the transverse plane. What change in the hallux structures happened?
A patient who underwent a hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction now demonstrates a hallux that assumes an adducted position in the transverse plane. What change in the hallux structures happened?
When performing a medial capsulorrhaphy, reefing of the capsule implies
When performing a medial capsulorrhaphy, reefing of the capsule implies
Which statement is most accurate regarding the classification of distal metatarsal osteotomies (DMOs) as unicorrectional or bicorrectional?
Which statement is most accurate regarding the classification of distal metatarsal osteotomies (DMOs) as unicorrectional or bicorrectional?
During a true McBride bunionectomy what anatomical structure will be excised or resected?
During a true McBride bunionectomy what anatomical structure will be excised or resected?
A 46-year-old female presents with a painful left bunion. Physical examination reveals a severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity with a hypermobile first ray, and the hallux is track-bound without crepitus. Shoe-gear modifications and custom orthotics have provided insufficient relief. What should you consider?
A 46-year-old female presents with a painful left bunion. Physical examination reveals a severe hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformity with a hypermobile first ray, and the hallux is track-bound without crepitus. Shoe-gear modifications and custom orthotics have provided insufficient relief. What should you consider?
Which statement best articulates the overarching objective of metatarsal osteotomies performed for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction?
Which statement best articulates the overarching objective of metatarsal osteotomies performed for hallux abducto valgus (HAV) correction?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) surgery, what is the most critical implication of overtightening the medial capsule?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) surgery, what is the most critical implication of overtightening the medial capsule?
Hallux varus assumes what position?
Hallux varus assumes what position?
While performing a Silver bunionectomy, you must preserve the medial groove (tibial sesamoid articulation) because do not
While performing a Silver bunionectomy, you must preserve the medial groove (tibial sesamoid articulation) because do not
A normal sagittal plane position demonstrates 20 mm total, with 10 mm dorsiflexion & 10 mm plantarflexion.
A normal sagittal plane position demonstrates 20 mm total, with 10 mm dorsiflexion & 10 mm plantarflexion.
Hypermobility in the sagittal plane is associated with what total excursion?
Hypermobility in the sagittal plane is associated with what total excursion?
What is the first step to correcting ROM when tracking is largely dependent on lateral soft tissue contracture?
What is the first step to correcting ROM when tracking is largely dependent on lateral soft tissue contracture?
Increased HIAA is hallux ______________.
Increased HIAA is hallux ______________.
Which of the following radiographic views must always be taken weightbearing?
Which of the following radiographic views must always be taken weightbearing?
What is the normal reference value for the Hallux Abductus Angle (HAA)?
What is the normal reference value for the Hallux Abductus Angle (HAA)?
A normal Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) is 15-20 degrees.
A normal Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) is 15-20 degrees.
Which tibial sesamoid position is considered normal on radiographic evaluation?
Which tibial sesamoid position is considered normal on radiographic evaluation?
Which of the following joint positions is characterized by lines that intersect inside the joint space on radiographic evaluation?
Which of the following joint positions is characterized by lines that intersect inside the joint space on radiographic evaluation?
Which metatarsal head shape is considered the most unstable on radiographic evaluation?
Which metatarsal head shape is considered the most unstable on radiographic evaluation?
Medial cuneiform obliquity is considered stable.
Medial cuneiform obliquity is considered stable.
What term describes a modification of a biological structure whereby an ancestral genetic trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary change?
What term describes a modification of a biological structure whereby an ancestral genetic trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary change?
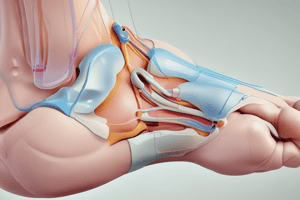
Match the following anatomical structures with their corresponding labels:
Match the following anatomical structures with their corresponding labels:
The adductor hallucis tendon inserts along the fibular sesamoid and the __________ phalanx.
The adductor hallucis tendon inserts along the fibular sesamoid and the __________ phalanx.
Which of the following is a surgical indication for bunion correction?
Which of the following is a surgical indication for bunion correction?
A Silver bunionectomy is a soft tissue procedure that includes deformity correction and reduction of the IMA.
A Silver bunionectomy is a soft tissue procedure that includes deformity correction and reduction of the IMA.
What factor makes proper orientation important during saw use while resecting the medial eminence of the Silver Bunionectomy procedure?
What factor makes proper orientation important during saw use while resecting the medial eminence of the Silver Bunionectomy procedure?
What is a potential risk associated with fibular sesamoidectomy?
What is a potential risk associated with fibular sesamoidectomy?
During medial first MTPJ capsulorrhaphy, what nautical term describes folding a sail to reduce surface area?
During medial first MTPJ capsulorrhaphy, what nautical term describes folding a sail to reduce surface area?
Which proximal phalangeal osteotomy is described as needing further correction following the initial procedure?
Which proximal phalangeal osteotomy is described as needing further correction following the initial procedure?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) surgery, what does DMO stand for?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV) surgery, what does DMO stand for?
Distal metatarsal osteotomies can correct frontal plane deformity.
Distal metatarsal osteotomies can correct frontal plane deformity.
Which of the following is a type of distal metatarsal osteotomy?
Which of the following is a type of distal metatarsal osteotomy?
Which of the following osteotomies can correct PASA?
Which of the following osteotomies can correct PASA?
The Reverdin-Laird osteotomy spares the sesamoid articulations.
The Reverdin-Laird osteotomy spares the sesamoid articulations.
Which osteotomy is useful for long and mildly elevated 1st metatarsals?
Which osteotomy is useful for long and mildly elevated 1st metatarsals?
Which of the following is a metatarsal shaft osteotomy?
Which of the following is a metatarsal shaft osteotomy?
A Kalish osteotomy can correct PASA.
A Kalish osteotomy can correct PASA.
What term describes a specific complication of the traditional scarf osteotomy that causes elevation of the capital fragment?
What term describes a specific complication of the traditional scarf osteotomy that causes elevation of the capital fragment?
Which of the following is a component of triplanar correction achieved with a Lapidus procedure?
Which of the following is a component of triplanar correction achieved with a Lapidus procedure?
After a Lapidus procedure, patients are traditionally non-weightbearing for 1-2 weeks.
After a Lapidus procedure, patients are traditionally non-weightbearing for 1-2 weeks.
In which scenario may a 1st MTPJ fusion be more appropriate?
In which scenario may a 1st MTPJ fusion be more appropriate?
Hallux assumes an adducted position in the transverse plane in hallux _________.
Hallux assumes an adducted position in the transverse plane in hallux _________.
What general principle is critical to avoid iatrogenic hallux varus?
What general principle is critical to avoid iatrogenic hallux varus?
What is a treatment aption for iatrogenic hallux varus?
What is a treatment aption for iatrogenic hallux varus?
Hypermobility of the first ray is always present in cases of severe HAV deformity.
Hypermobility of the first ray is always present in cases of severe HAV deformity.
A radiographic finding of a DASA greater than 12 may be indicative of which structural deformity within the hallux?
A radiographic finding of a DASA greater than 12 may be indicative of which structural deformity within the hallux?
Post-op course after a Silver bunionectomy is based on _______________ of the incision.
Post-op course after a Silver bunionectomy is based on _______________ of the incision.
A 42-year-old female who presents with a right bunion and a history of gastric bypass surgery poses a challenge for ideal bunion correction. Which of these factors is most likely to be the challenge?
A 42-year-old female who presents with a right bunion and a history of gastric bypass surgery poses a challenge for ideal bunion correction. Which of these factors is most likely to be the challenge?
An elderly patient presents for painful bunion deformity. She has no remarkable findings. What can you expect from exam findings?
An elderly patient presents for painful bunion deformity. She has no remarkable findings. What can you expect from exam findings?
Increased HAV mobility is generally associated with decreased transverse plane mobility
Increased HAV mobility is generally associated with decreased transverse plane mobility
What is being evaluated when assessing the quality of 1st MTPJ motion through full ROM in both the deviated and corrected positions during a physical exam?
What is being evaluated when assessing the quality of 1st MTPJ motion through full ROM in both the deviated and corrected positions during a physical exam?
What does crepitus indicate during physical examination of the 1st MTPJ?
What does crepitus indicate during physical examination of the 1st MTPJ?
Poor quality of motion during physical examination of the 1st MTPJ is typically indicative of structural _____________ of cartilage.
Poor quality of motion during physical examination of the 1st MTPJ is typically indicative of structural _____________ of cartilage.
A normal sagittal plane position allows for a total excursion of 20 mm (10 mm dorsiflexion & 10 mm plantarflexion).
A normal sagittal plane position allows for a total excursion of 20 mm (10 mm dorsiflexion & 10 mm plantarflexion).
Hypermobility in the sagittal plane is often associated with which condition?
Hypermobility in the sagittal plane is often associated with which condition?
What does crepitus during the physical examination of the 1st MTPJ suggest?
What does crepitus during the physical examination of the 1st MTPJ suggest?
Inability to adduct the hallux indicates a track-bound condition.
Inability to adduct the hallux indicates a track-bound condition.
Tracking is largely dependent on the lateral soft tissue ______.
Tracking is largely dependent on the lateral soft tissue ______.
What is often the first step to correct ROM when tracking is present?
What is often the first step to correct ROM when tracking is present?
What does a pinch callus typically indicate?
What does a pinch callus typically indicate?
What does a Sub 2nd met lesion most likely indicate?
What does a Sub 2nd met lesion most likely indicate?
Radiographs for HAV should be taken without weightbearing to accurately assess 'angles and dangles.'
Radiographs for HAV should be taken without weightbearing to accurately assess 'angles and dangles.'
What is a normal range for the Hallux Abductus Angle (HAA)?
What is a normal range for the Hallux Abductus Angle (HAA)?
An increased Hallux Interphalangeal Abductus Angle (HIAA) indicates which condition?
An increased Hallux Interphalangeal Abductus Angle (HIAA) indicates which condition?
What is the normal range (in degrees) for the Proximal Articular Set Angle (PASA)?
What is the normal range (in degrees) for the Proximal Articular Set Angle (PASA)?
The normal range for the Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) is 0-5 degrees.
The normal range for the Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) is 0-5 degrees.
What is considered a normal Metatarsal Protrusion Distance?
What is considered a normal Metatarsal Protrusion Distance?
In radiographic evaluation, a tibial sesamoid position of '1' indicates what?
In radiographic evaluation, a tibial sesamoid position of '1' indicates what?
Match the joint positions with their radiographic characteristics:
Match the joint positions with their radiographic characteristics:
Which metatarsal head shape is considered the most unstable?
Which metatarsal head shape is considered the most unstable?
An 'atavistic' cuneiform refers to an unusually stable medial cuneiform alignment.
An 'atavistic' cuneiform refers to an unusually stable medial cuneiform alignment.
What anatomical structure is represented by 'C' in the provided diagram?
What anatomical structure is represented by 'C' in the provided diagram?
The adductor hallucis tendon inserts along the fibular sesamoid and the [blank] phalanx.
The adductor hallucis tendon inserts along the fibular sesamoid and the [blank] phalanx.
Which surgical approach is typically used in the described bunion correction?
Which surgical approach is typically used in the described bunion correction?
According to the material provided, deformity is NOT a recognized surgical indication for bunion correction.
According to the material provided, deformity is NOT a recognized surgical indication for bunion correction.
Match the following surgical procedure categories with their descriptions:
Match the following surgical procedure categories with their descriptions:
Which of the following is TRUE regarding deformity correction in a Silver bunionectomy?
Which of the following is TRUE regarding deformity correction in a Silver bunionectomy?
A Silver bunionectomy is appropriate if the goal is to remove the medial ______ only.
A Silver bunionectomy is appropriate if the goal is to remove the medial ______ only.
What must be preserved when resecting the medial eminence during a Silver bunionectomy?
What must be preserved when resecting the medial eminence during a Silver bunionectomy?
A key step in a McBride bunionectomy procedure involves bone grafting at the MTPJ.
A key step in a McBride bunionectomy procedure involves bone grafting at the MTPJ.
Steps of a Modified McBride procedure includes:
Steps of a Modified McBride procedure includes:
Medial capsulorrhaphy involves reefing, which is similar to what?
Medial capsulorrhaphy involves reefing, which is similar to what?
After an Akin procedure is performed at the proximal phalanx, what deformity does it correct?
After an Akin procedure is performed at the proximal phalanx, what deformity does it correct?
What does DASA stand for?
What does DASA stand for?
Oblique Akin is popular because it's easy to correct the PASA.
Oblique Akin is popular because it's easy to correct the PASA.
Which of the following DMO procedures can correct intermetatarsal angle?
Which of the following DMO procedures can correct intermetatarsal angle?
The Reverdin osteotomy corrects the ______ but violates the sesamoid articulation.
The Reverdin osteotomy corrects the ______ but violates the sesamoid articulation.
Reverdin-Laird spares sesamoid articulation
Reverdin-Laird spares sesamoid articulation
Which osteotomy is useful for a long and mildly elevated first metatarsal?
Which osteotomy is useful for a long and mildly elevated first metatarsal?
Which of the following is a triplanar correction?
Which of the following is a triplanar correction?
Positioning during MTPJ fusion is not critical and can be adjusted during the procedure.
Positioning during MTPJ fusion is not critical and can be adjusted during the procedure.
What is a common complication of HAV correction, resulting in an adducted position of the hallux?
What is a common complication of HAV correction, resulting in an adducted position of the hallux?
Excessive medial ______ can lead to iatrogenic hallux varus.
Excessive medial ______ can lead to iatrogenic hallux varus.
Overcorrection of a bunion always results in a successful outcome; true of false?
Overcorrection of a bunion always results in a successful outcome; true of false?
What is the normal total sagittal plane position excursion during a physical examination for HAV?
What is the normal total sagittal plane position excursion during a physical examination for HAV?
Hypermobility in the sagittal plane during physical examination is defined as greater than 15 mm total excursion and is often associated with generalized ligamentous laxity.
Hypermobility in the sagittal plane during physical examination is defined as greater than 15 mm total excursion and is often associated with generalized ligamentous laxity.
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV), what does 'tracking' refer to during a physical examination?
In the context of hallux abducto valgus (HAV), what does 'tracking' refer to during a physical examination?
During the physical examination of a patient with a suspected bunion, the entirety of the 1st ______ should be palpated for symptoms.
During the physical examination of a patient with a suspected bunion, the entirety of the 1st ______ should be palpated for symptoms.
A pinch callus on the foot indicates what?
A pinch callus on the foot indicates what?
Radiographs for evaluating hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformities should always be non-weightbearing to accurately assess the angles and alignment.
Radiographs for evaluating hallux abducto valgus (HAV) deformities should always be non-weightbearing to accurately assess the angles and alignment.
What range defines a normal Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA)?
What range defines a normal Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA)?
Match the Intermetatarsal Angle (IMA) ranges with the correct classification.
Match the Intermetatarsal Angle (IMA) ranges with the correct classification.
What is the reference value for a normal hallux abductus angle (HAA)?
What is the reference value for a normal hallux abductus angle (HAA)?
What is the normal range for the Proximal Articular Set Angle (PASA)?
What is the normal range for the Proximal Articular Set Angle (PASA)?
A Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) of 15 degrees is considered within normal limits.
A Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) of 15 degrees is considered within normal limits.
In radiographic evaluation, a tibial sesamoid position value of ______ is considered normal.
In radiographic evaluation, a tibial sesamoid position value of ______ is considered normal.
What type of joint position is defined by lines that intersect inside the joint space on radiographic evaluation?
What type of joint position is defined by lines that intersect inside the joint space on radiographic evaluation?
According to the information provided, what type of blood supply can be found within the safe zone for osteotomy.
According to the information provided, what type of blood supply can be found within the safe zone for osteotomy.
The Silver bunionectomy is an isolated procedure that corrects deformity and reduces IMA.
The Silver bunionectomy is an isolated procedure that corrects deformity and reduces IMA.
What is the primary goal when performing a Silver bunionectomy?
What is the primary goal when performing a Silver bunionectomy?
What complication is associated with fibular sesamoidectomy?
What complication is associated with fibular sesamoidectomy?
Reefing during a medial first MTPJ capsulorrhaphy is a ______ term referring to folding a sail to reduce surface area.
Reefing during a medial first MTPJ capsulorrhaphy is a ______ term referring to folding a sail to reduce surface area.
Which of the following Distal Metatarsal Osteotomies (DMO) spares the sesamoid articulations, corrects PASA, and keeps the lateral cortex intact?
Which of the following Distal Metatarsal Osteotomies (DMO) spares the sesamoid articulations, corrects PASA, and keeps the lateral cortex intact?
Flashcards
Sagittal Plane Position
Sagittal Plane Position
Sagittal plane position in the first MTPJ.
Hypermobility Definition
Hypermobility Definition
Hypermobility in sagittal plane position
Transverse Plane Mobility
Transverse Plane Mobility
Mobility in the transverse plane
1st MTPJ Motion Quality
1st MTPJ Motion Quality
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crepitus
Crepitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Poor Quality of Motion
Poor Quality of Motion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tracking
Tracking
Signup and view all the flashcards
Track-bound
Track-bound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tracking's Dependence
Tracking's Dependence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Interphalangeal Joint
Hallux Interphalangeal Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain Location Elucidation
Pain Location Elucidation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pinch callus
Pinch callus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sub met 1
Sub met 1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sub 2nd met
Sub 2nd met
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Position
Hallux Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weightbearing Radiographs
Weightbearing Radiographs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiographic Angles Distortion
Radiographic Angles Distortion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA)
Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsus Adductus Constraint
Metatarsus Adductus Constraint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermetatarsal Angle (IMA)
Intermetatarsal Angle (IMA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
IMA reference values
IMA reference values
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Abductus Angle (HAA)
Hallux Abductus Angle (HAA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal HAA Value
Normal HAA Value
Signup and view all the flashcards
HAIA
HAIA
Signup and view all the flashcards
PASA
PASA
Signup and view all the flashcards
DASA
DASA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Protrusion Distance
Metatarsal Protrusion Distance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibial Sesamoid Position
Tibial Sesamoid Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Congruous Joints
Congruous Joints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deviated Joint
Deviated Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subluxed Joint
Subluxed Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Head Shape- Round
Metatarsal Head Shape- Round
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Head Shape- Square
Metatarsal Head Shape- Square
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Head Shape- Square w/ ridge
Metatarsal Head Shape- Square w/ ridge
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial cuneiform obliquity
Medial cuneiform obliquity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sesamoid Axial View- Radiographic
Sesamoid Axial View- Radiographic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral View
Lateral View
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Supply
Blood Supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surgical Approach
Surgical Approach
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surgical indications for bunion correction
Surgical indications for bunion correction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soft Tissue Procedures
Soft Tissue Procedures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Silver Bunionectomy
Silver Bunionectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Silver Bunionectomy Goal
Silver Bunionectomy Goal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Groove
Medial Groove
Signup and view all the flashcards
Staking the head.
Staking the head.
Signup and view all the flashcards
McBride Bunionectomy
McBride Bunionectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial first MTPJ capsulorrhaphy
Medial first MTPJ capsulorrhaphy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Akin Procedures
Akin Procedures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Akin Procedures
Akin Procedures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal Sagittal plane position
Normal Sagittal plane position
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Interphalangeal Joint Evaluation
Hallux Interphalangeal Joint Evaluation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soft tissue procedure definition
Soft tissue procedure definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Abducto Valgus surgery
Hallux Abducto Valgus surgery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Silver bunionectomy definition
Silver bunionectomy definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Steps of a Modified McBride bunionectomy
Steps of a Modified McBride bunionectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the akin procedures
What are the akin procedures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Akin definition
Akin definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Akin use case
Akin use case
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oblique akin popularity definition
Oblique akin popularity definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Akin Function
Proximal Akin Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Metatarsal Osteotomies (DMO)
Distal Metatarsal Osteotomies (DMO)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dependence of DMOs metatarsal width
Dependence of DMOs metatarsal width
Signup and view all the flashcards
Versatility of distal metatarsal osteotomies.
Versatility of distal metatarsal osteotomies.
Signup and view all the flashcards
DMOs limitation
DMOs limitation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal length can be adjust definition
Metatarsal length can be adjust definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reverdin Osteotomy
Reverdin Osteotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reverdin-Green
Reverdin-Green
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reverdin-Laird Osteotomy
Reverdin-Laird Osteotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Austin (Chevron) Osteotomy
Austin (Chevron) Osteotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biplanar Austin
Biplanar Austin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bicorrectional Austin
Bicorrectional Austin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Youngswick-Austin
Youngswick-Austin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal fixations
Metatarsal fixations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kalish osteotomy definion
Kalish osteotomy definion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kalish osteotomy actions
Kalish osteotomy actions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Fixations Controversies
Metatarsal Fixations Controversies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lapidus procedure definition
Lapidus procedure definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
lapidus actions
lapidus actions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lapidus - Complications & Risks
Lapidus - Complications & Risks
Signup and view all the flashcards
1st MTPJ fusion key points
1st MTPJ fusion key points
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux Varus definition
Hallux Varus definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Learning Objectives
- Physical examination of bunion deformities
- Radiographic evaluation of Hallux Abducto Valgus (HAV) deformities
- Functional anatomy of the medial column
- Soft tissue procedures at the 1st Metatarsophalangeal Joint (MTPJ)
- Proximal phalangeal base osteotomies of the hallux for bunion correction
- First metatarsal head osteotomies for bunion correction
- First metatarsal shaft osteotomies for bunion correction
- The Lapidus procedure
- First MTPJ fusion procedure
- Hallux Abducto Valgus (HAV) correction complications
Physical Examination
- Sagittal plane position should be assessed
- Normal sagittal plane position is 10 mm total, including 5 mm dorsiflexion and 5 mm plantarflexion
- Hypermobility is greater than 15 mm total excursion and usually associated with generalized ligamentous laxity
- Transverse plane mobility is also assessed
- Normally, there is little to no mobility in the transverse plane
- Hallux Abducto Valgus - mobility increases
- Quality of motion is evaluated at the 1st MTPJ with a retrograde force across the joint.
- The joint is taken through full ROM in the deviated and corrected positions.
- Crepitus signifies articular damage
- Poor quality of motion signifies structural adaptation of cartilage
- Axis of motion should be evaluated by looking at the dorsiflexion and plantarflexion in the corrected position
- Tendency to deviate into abnormal position constitutes tracking
- Inability to adduct the hallux indicates track-bound
- Correcting this requires lateral release, which is the first step to correct ROM
- Hallux interphalangeal joint should be evaluated for sagittal and transverse plane deformity
- Pain location: the entirety of the 1st MTPJ should be palpated for symptoms
- Presence of hyperkeratotic lesions -Pinch callus indicates abnormal pronatory roll off -Sub met 1 indicates plantarflexed first ray/hypertrophic sesamoid -Sub 2nd met indicates first ray insufficiency/met primus elevatus/2nd toe pathology
- Hallux position includes: no contact, abutting, overlying, and underlying
Radiographic Evaluation
- Radiographs must always be weightbearing (WB)
- Angles and dangles change when weightbearing (WB) vs non-weightbearing (NWB)
- Metatarsus Adductus Angle (MAA)
- Normal: 0-15
- Mild: 16-25
- Moderate: 26-35
- Severe: > 35
- Metatarsus adductus limits correction; consider metatarsus adductus correction
- Intermetatarsal Angle (IMA)
- Normal: 0-10
- Mild/moderate deformity: 10-15
- Severe deformity: > 15
- Hallux Abductus Angle (HAA) reference value is < 15°, which is normal
- Hallux Interphalangeal Abductus Angle (HAIA) reference Value is <10°, which is normal
- Increased HAIA is diagnostic for hallux interphalangeus
- Proximal Articular Set Angle (PASA) reference value is 0 – 8°, which is normal
- Distal Articular Set Angle (DASA) reference value is 7 – 12°, which is normal
- Metatarsal Protrusion Distance reference value is +/- 2mm, which is normal
- Tibial Sesamoid Position reference value are:
- 1 = normal
- 4 = centered on bisection of metatarsal
- Joint Positions:
- Congruous joint: lines are parallel
- Deviated joint: lines intersect outside the joint space
- Subluxed joint: lines intersect inside the joint space
- Metatarsal Head Shape:
- Round is most unstable
- Square is stable
- Square with ridge is most stable
- Medial Cuneiform Obliquity
- Oblique is unstable
- "Atavistic" cuneiform
- Atavism is a modification of a biological structure, whereby an ancestral genetic trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary change in previous generations
- Sesamoid Axial View shows sesamoid subluxation, crista erosion, and arthritic changes
- Lateral View assesses met primus elevatus, Navicular-Cuneiform (NC) sag, rearfoot position, equinus, and hammertoes
Anatomy
- A - Subcutaneous tissue plane
- B - Joint capsule
- C - Medial collateral ligament
- D - Tibial suspensory ligament
- I - Adductor hallucis insertion
- J - Extensor tendons
- H - Deep intermetatarsal ligament
- Adductor hallucis tendon (cut)
- inserts along fibular sesamoid as well as the proximal phalanx
- Lateral collateral ligament
- Fibular suspensory ligament
- Safe Zones
Surgical
- Incision medial to the Extensor Hallucis Longus (EHL) is straight medial
- Surgical indications include: pain, deformity, inability to fit into appropriate shoe-gear, and ulceration
- Procedure categories include:
- Soft tissue (with or without medial eminence resection)
- Proximal phalangeal osteotomy
- Distal metatarsal osteotomy (DMO)
- Shaft/diaphyseal osteotomies
- First metatarsal cuneiform joint arthrodesis (Lapidus)
- First metatarsal phalangeal joint arthrodesis
- Juvenile bunionectomy
- Soft tissue procedures include: Silver bunionectomy, McBride bunionectomy, modified McBride bunionectomy, and medial capsulorrhaphy
Silver Bunionectomy
- Resection of the medial eminence of the metatarsal head, with no deformity correction and no reduction of the Intermetatarsal Angle
- Post-op course is based on protection of incision with generally immediate weightbearing in Post-Op shoe
- Has minimal utility as an isolated procedure
- Appropriate if the goal is to remove the medial prominence only
- Can accelerate reoccurrence by weakening medial structures
- Proper orientation of saw while resecting the medial eminence is critical
- Medial groove must be preserved (tibial sesamoid articulation)
- The head should not be "staked" as this violates the medial groove or increases the risk of hallux varus
McBride Bunionectomy
- This is rebalancing of the soft tissue structures of the first MTPJ
- It derotates the toe but will not correct frontal plane deformity in the metatarsal
- It aligns the sesamoid apparatus and removes or reduces tracking
- Is rarely an isolated procedure, with the modified McBride bunionectomy performed as an adjunct procedure with other techniques
- Steps of a true McBride bunionectomy include: resection of the medial eminence, excision of the fibular sesamoid, transfer of the adductor hallucis tendon to the first metatarsal, and medial capsulorrhaphy - tightening of the medial capsule
- Fibular sesamoidectomy has fallen out of favor due to increased risk of hallux varus
- Steps of a modified McBride bunionectomy include: removal of medial eminence (if needed), blunt dissection down to the lateral MTPJ capsule, release or transfer of adductor hallucis tendon, division of the fibular sesamoid suspensory ligament and division of the transverse metatarsal ligament
Medial First MTPJ Capsulorrhaphy
- This is reefing/plication of the medial joint capsule during closure -Reefing is nautical term for folding a sail to reduce surface area as a safety precaution in strong winds -Plication is the tightening of stretched or weakened tissues by folding of the excess in tucks
- Excision of resultant capsule and is not an isolated procedure
Proximal Phalangeal Osteotomies
- There are Distal Akin, Oblique Akin and Proximal Akin
- Originally described by Akin in 1925
- Original procedure included resection of medial eminence of 1st metatarsal head and medial base of proximal phalanx plus medial closing base wedge phalangeal osteotomy
- Akin is described by region the osteotomy is performed
- Abnormal Distal Articular Set Angle uses Proximal AKin
- Abnormal interphalangeus angle uses Distal Akin
- "Cheater" Akin is further correction needed following initial procedure
- Structural deformity is within the hallux
- Distal Akin structural deformity corrects hallux interphalngeus when normal is equal to 10°
- Oblique Akin
- Popular due to ability to place a screw across the osteotomy
- Corrects Distal Articular Set Angle & interphalangeus
- Common "cheater" Akin
- Proximal Akin corrects abnormal DASA and is a common "cheater" Akin
Distal Metatarsal Osteotomies
- Includes Reverdin, Reverdin-Green, Reverdin-Laird, Austin, Biplanar Austin, Bicorrectional Austin, and Youngswick-Austin.
- It is dependent on metatarsal width, versatility, as well as Uniplanar, Biplanar, Unicorrectional, and Bicorrectional capabilities.
- Capable of performing a uniplane and biplane correction but cannot correct frontal plane deformity.
- Metatarsal length can also be adjusted
- Reverdin Osteotomy:
-Corrects PASA
-Lateral cortex kept intact, acting as a hinge with the sesamoid articulations
- Has no IMA correction
- Reverdin-Green: -Corrects PASA -Lateral cortex kept intact (hinge) -Spares the sesamoid articulations -Has no IMA correction
- Reverdin-Laird Osteotomy: -Can corrects PASA with an optional wedge -Corrects IMA with a complete osteotomy that that translate the capital fragments and spares the sesamoid articulations
- Austin (Chevron) Osteotomy corrects the IMA
- Biplanar Austin: Corrects IMA and allows for plantarflexion
- Bicorrectional Austin: Corrects PASA and IMA but is technically difficult
- Youngswick-Austin: Corrects IMA, provides plantarflexion and shortening, and is useful for long & mildly elevated 1st metatarsals
Metatarsal Shaft Osteotomies
- Includes Kalish-Austin and Scarf procedure
- Kalish Osteotomy: This is a long arm Austin, corrects IMA but cannot correct PASA, and is easier to use of 2 screws
- SCARF carpentry term – scarf joint that corrects IMA, and also correct PASA
- SCARF is controversial because of its utility compared to a Distal Metatarsal Osteotomies that those it can correct higher Intermetatarsal Angles and dependent on metatarsal width.
- Trouging involves: a specific complication of the traditional scarf and can elevate the capital fragment.
Lapidus
- It is the most versatile of all bunion procedures and is capable of triplanar correction, to include Transverse plane – IMA, Sagittal plane – Met primus elevatus, and Frontal plane – Metatarsal rotation but has higher risk of complications such as nerve entrapment, non-union, and that the lever arm- exerts a dorsiflexory force at the fusion site with traditionally Non-Weight Bearing status at 6-8 weeks
- This is triplanar deformity correction
1st MTPJ Fusion
- May be more appropriate in older patients even with a non-arthritic joint as a treatment of choice for an “end-stage” bunion deformity (bunion with arthrosis)
- Positioning critically in achieving satisfactory results
- Newer constructs also allow for earlier WB
- Can perform the fusion as a primary or revision procedure
HAV Correction Complications
- Hallux Varus is when the hallux assumes an adducted position in the transverse plane with medial structures get the mechanical advantage over the lateral structures from: -Latrogenic-overcorrection of HAV -Traumatic causes -Metabolic-immunologic arthropathies -Neuromuscular dysfunction
- Excessive medial capsulorrhaphy from soft tissue procedures can usually result in under-correction or over-correction
- DO NOT Stake of the metatarsal, or violate the tibial sesamoid articulation - DO NOT perform Fibular sesamoidectomy
- Negative IMA means that subluxation of capital fragment is post operatively as a result ofInitial over-correction from Latrogenic hallux varus -If you must choose between under correcting and bunion and over correcting a bunion, always go with under correction -Revision of a hallux varus is difficult if you want to keep the joint with fusion is the gold-standard treatment -Latrogenic Hallux varus Treatment options: Reverse DMO, Reverse Akin, Tibial sesamoidectomy. Tight rope and Fusion
Cases
- Case # 1 reveals:46-year-old female present with left bunion pain who has tried shoe-gear change and custom orthotics for substantial pain but the past medical history unremarkable with PE as a severe HAV deformity with a hypermobile first ray and ROM of the hallux is track-bound without crepitus
- Case # 2: 42-year-old female presents with right bunion pain that failed conservative measures and PMH reveals history of with Gastric bypass and PE has severe HAV deformity with a hypermobile first ray but blood work that shows low Vitamin D-12 levels that resulted in patient being placed on 50,000 IU of vitamin D q week after deformity discussed the patient was not an ideal surgical candidate, so the surgery risks versus and safe and easy procedure were discussed
- Case # 3: 68-year-old female presents for evaluation and treatment of a painful bunion deformity has no issues caring lots of cats and Past Medical History unremarkable who had Palpable pulses and an Instantaneous Capillary Refill Time
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.