Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of cartilage in the skeletal system?
What is the primary function of cartilage in the skeletal system?
- To facilitate blood cell production
- To form the major structural framework of the body
- To store minerals and fat
- To provide flexibility and smooth surfaces for movement (correct)
Which type of connective tissue is primarily found in the external ear and epiglottis?
Which type of connective tissue is primarily found in the external ear and epiglottis?
- Elastic cartilage (correct)
- Fibrocartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
- Compact bone connective tissue
Which part of a long bone contains yellow bone marrow?
Which part of a long bone contains yellow bone marrow?
- Medullary cavity (correct)
- Epiphyseal line
- Periosteum
- Articular cartilage
What are the key structural units of compact bone called?
What are the key structural units of compact bone called?
What is the role of collagen fibers in bone tissue?
What is the role of collagen fibers in bone tissue?
Which curvature of the spine is associated with an excessive outward curve, often referred to as 'hunchback'?
Which curvature of the spine is associated with an excessive outward curve, often referred to as 'hunchback'?
What type of skeletal bone shape is characterized by a length greater than width, such as the femur?
What type of skeletal bone shape is characterized by a length greater than width, such as the femur?
What is the main purpose of the periosteum in bone structure?
What is the main purpose of the periosteum in bone structure?
What is a characteristic of irregular bones?
What is a characteristic of irregular bones?
Where are sesamoid bones typically located?
Where are sesamoid bones typically located?
Which of the following best describes the diaphysis of a long bone?
Which of the following best describes the diaphysis of a long bone?
What is the primary function of sesamoid bones?
What is the primary function of sesamoid bones?
What happens to the epiphyseal plate when growth ceases?
What happens to the epiphyseal plate when growth ceases?
Which of the following bones is commonly recognized as a sesamoid bone?
Which of the following bones is commonly recognized as a sesamoid bone?
What type of bone primarily makes up the epiphyses of long bones?
What type of bone primarily makes up the epiphyses of long bones?
Which statement regarding irregular bones is incorrect?
Which statement regarding irregular bones is incorrect?
How many thoracic vertebrae are in the vertebral column?
How many thoracic vertebrae are in the vertebral column?
What are the components of the thoracic cage?
What are the components of the thoracic cage?
Which parts make up the structure of the sternum?
Which parts make up the structure of the sternum?
What is the total number of lumbar vertebrae in the vertebral column?
What is the total number of lumbar vertebrae in the vertebral column?
Which vertebrae serve as the anchor points for ribs?
Which vertebrae serve as the anchor points for ribs?
What function does the thoracic cage primarily serve?
What function does the thoracic cage primarily serve?
Where are the costal cartilages located?
Where are the costal cartilages located?
What does the transverse process of a thoracic vertebra articulate with?
What does the transverse process of a thoracic vertebra articulate with?
Which two bones are joined by the squamous suture?
Which two bones are joined by the squamous suture?
Which bones are connected by the lambdoid suture?
Which bones are connected by the lambdoid suture?
Which bones are joined by the sagittal suture?
Which bones are joined by the sagittal suture?
What two bones make up the hard palate?
What two bones make up the hard palate?
What is the primary function of the occipital condyles?
What is the primary function of the occipital condyles?
What is the function of the carotid canal?
What is the function of the carotid canal?
What is the primary function of the jugular foramen?
What is the primary function of the jugular foramen?
What is the role of the sella turcica?
What is the role of the sella turcica?
What feature is located at the top of the sternum?
What feature is located at the top of the sternum?
Which part of the rib articulates with a vertebra?
Which part of the rib articulates with a vertebra?
What distinguishes true ribs from false ribs?
What distinguishes true ribs from false ribs?
What is the purpose of the xiphoid process in the thoracic cage?
What is the purpose of the xiphoid process in the thoracic cage?
Which rib type is classified as floating ribs?
Which rib type is classified as floating ribs?
Which notch on the sternum allows for the attachment of the clavicles?
Which notch on the sternum allows for the attachment of the clavicles?
What is typically used to locate the proper position for CPR?
What is typically used to locate the proper position for CPR?
Which type of cartilage connects the ribs to the sternum?
Which type of cartilage connects the ribs to the sternum?
Flashcards
Bone Tissue
Bone Tissue
Hard, dense connective tissue forming the adult skeleton.
Cartilage
Cartilage
Semi-rigid connective tissue found at joints, enabling movement.
Types of Cartilage
Types of Cartilage
Includes hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage, varying in flexibility.
Function of Skeletal System
Function of Skeletal System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long Bones
Long Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short Bones
Short Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flat Bones
Flat Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Irregular Bones
Irregular Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sesamoid Bones
Sesamoid Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sutural Bones
Sutural Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphysis
Diaphysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiphyses
Epiphyses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiphyseal Plate
Epiphyseal Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Cartilage
Articular Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medullary Cavity
Medullary Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periosteum
Periosteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endosteum
Endosteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compact Bone
Compact Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spongy Bone
Spongy Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteon
Osteon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lacunae
Lacunae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertebral Column
Vertebral Column
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scoliosis
Scoliosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kyphosis
Kyphosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lordosis
Lordosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
True Ribs
True Ribs
Signup and view all the flashcards
False Ribs
False Ribs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foramina
Foramina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thoracic Cage
Thoracic Cage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coccyx
Coccyx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Bone Tissue and Cartilage
- Bone (osseous tissue) is a hard, dense connective tissue forming most of the adult skeleton.
- Cartilage, a semi-rigid connective tissue, is found where bones move (e.g., ribcage, joints).
- Hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage are types of cartilage with varying flexibility.
- The skeletal system (bones and cartilage) supports the body, facilitates movement, protects organs, produces blood cells, and stores minerals and fat.
Bone Classification
- Long bones: Tubular shafts (diaphysis) with wider ends (epiphyses). Examples include the femur and humerus.
- Short bones: Roughly cube-shaped. Examples include carpals and tarsals.
- Flat bones: Thin, flattened, and often curved. Examples include cranial bones and ribs.
- Irregular bones: Complex shapes that don't fit other categories. Examples include vertebrae and facial bones.
- Sesamoid bones: Small, round bones in tendons, reducing pressure. The patella is an example.
- Sutural bones: Small bones found within sutures of the skull.
Long Bone Structure
- Diaphysis: The long, tubular shaft of a long bone.
- Epiphyses: The wider ends of a long bone. Contains spongy bone.
- Epiphyseal plate: Hyaline cartilage in children enabling longitudinal bone growth. Becomes the epiphyseal line after growth ceases.
- Articular cartilage: Covers the ends of bones in joints, providing smooth surfaces.
- Medullary cavity: Hollow space within the diaphysis, containing yellow bone marrow (fat).
- Periosteum: Tough, fibrous membrane covering the bone's outer surface.
- Endosteum: Membrane lining the medullary cavity.
- Compact bone: Dense bone tissue forming the diaphysis's outer layer.
- Spongy bone: Porous bone tissue found in epiphyses and within compact bone. Contains trabeculae (bone struts).
- Red bone marrow (hematopoietic tissue): Produces blood cells, found in spongy bone.
Compact Bone Histology
- Osteon (Haversian system): Basic unit of compact bone.
- Lamellae: Concentric rings of bone matrix in an osteon.
- Central (Haversian) canal: Contains blood vessels and nerves at the center of an osteon.
- Perforating (Volkmann's) canals: Channels connecting central canals.
- Lacunae: Small cavities housing osteocytes (bone cells).
- Canaliculi: Tiny canals connecting lacunae, allowing nutrient and waste exchange.
Axial Skeleton
- Vertebral column: Cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), lumbar (lower back) curvatures. Intervertebral discs cushion vertebrae.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal lateral curvature of the spine.
- Kyphosis: Excessive thoracic curvature (hunchback).
- Lordosis: Excessive lumbar curvature (swayback).
- Fontanelles: Soft spots in infant skulls, allowing for brain growth.
- Skull bones: Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxilla, palatine, vomer, mandible. Sutures connect skull bones. Important foramina include the foramen magnum, optic canal, and jugular foramen.
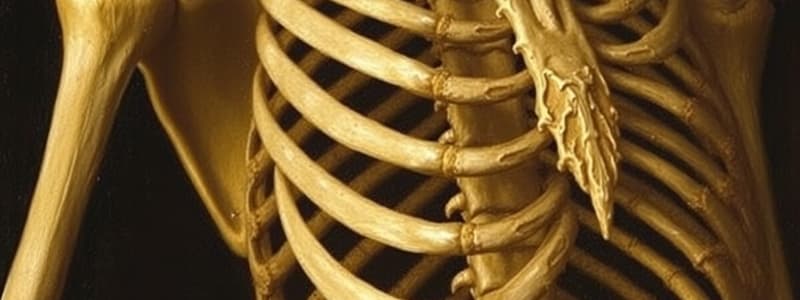
- Thoracic cage: Sternum (manubrium, body, xiphoid process) and ribs (true, false, floating). Protects the heart and lungs.
- Ribs: Articulate with thoracic vertebrae posteriorly and sternum (for true ribs) anteriorly.
Number of Vertebrae
- Thoracic vertebrae: 12
- Lumbar vertebrae: 5
- The sacrum and coccyx are also parts of the vertebral column. The sacrum articulates with the iliac bones of the pelvis.
True vs. False Ribs
- True ribs: Directly attach to the sternum via their costal cartilages.
- False ribs: Attach to the sternum indirectly via the costal cartilage of the 7th rib or do not attach to the sternum at all (floating ribs).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.