Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of bone fills the space between the outer and inner plates and the alveolar bone proper?
What type of bone fills the space between the outer and inner plates and the alveolar bone proper?
- Cancellous bone
- Spongy bone (correct)
- Cortical bone
- Compact bone
What is the characteristic of Type 1 trabeculae in spongy bone?
What is the characteristic of Type 1 trabeculae in spongy bone?
- Thin and fragile
- Regular and horizontal in a ladder-like arrangement (correct)
- Irregularly arranged and delicate
- Thick and compact
What is the approximate percentage of inorganic component in bone composition?
What is the approximate percentage of inorganic component in bone composition?
- 50%
- 25%
- 67% (correct)
- 33%
What is the primary function of bone marrow in the alveolar bone?
What is the primary function of bone marrow in the alveolar bone?
What is the composition of bone marrow in young bone?
What is the composition of bone marrow in young bone?
What is the term for isolated areas where the root is denuded of bone and covered only by periosteum and overlying gingiva?
What is the term for isolated areas where the root is denuded of bone and covered only by periosteum and overlying gingiva?
Which of the following is NOT a predisposing factor for fenestrations and dehiscences?
Which of the following is NOT a predisposing factor for fenestrations and dehiscences?
What is the interdental septum composed of?
What is the interdental septum composed of?
During which type of ossification is alveolar bone formed?
During which type of ossification is alveolar bone formed?
What is the process of replacing old bone with new bone?
What is the process of replacing old bone with new bone?
What is the type of collagen found in bone?
What is the type of collagen found in bone?
What is the function of canaliculi in alveolar bone?
What is the function of canaliculi in alveolar bone?
What is the component of bone that provides structure and strength?
What is the component of bone that provides structure and strength?
At what stage of fetal development do mandible and maxilla form a groove that is opened toward the surface of the oral cavity?
At what stage of fetal development do mandible and maxilla form a groove that is opened toward the surface of the oral cavity?
What consists of compact bone and forms the outer and inner plates of the alveolar process?
What consists of compact bone and forms the outer and inner plates of the alveolar process?
What is the characteristic of the outer cortical plate in the maxilla?
What is the characteristic of the outer cortical plate in the maxilla?
What type of bone is found in the spongy bone structure?
What type of bone is found in the spongy bone structure?
What is the function of the bundle bone?
What is the function of the bundle bone?
What is the characteristic of the lamina dura?
What is the characteristic of the lamina dura?
What is the region where the cortical plate is fused with the alveolar bone proper?
What is the region where the cortical plate is fused with the alveolar bone proper?
What is the difference between the cortical plates in the maxilla and mandible?
What is the difference between the cortical plates in the maxilla and mandible?
What is the characteristic of the buccal plates?
What is the characteristic of the buccal plates?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
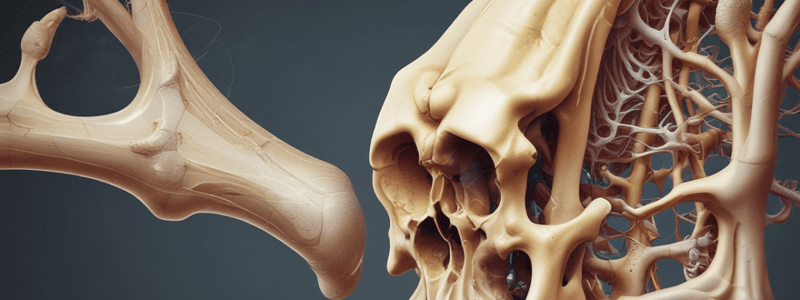
Alveolar Bone
- Covered by periosteum
- Filled with spongy bone, which consists of heavy trabeculae with bone marrow spaces
- Trabeculae are of two main types:
- Type 1: regular and horizontal in a ladder-like arrangement, commonly seen in the mandible
- Type 2: irregularly arranged, numerous, and delicate, more common in the maxilla
Bone Marrow
- Red in young bone and yellow in old bone
- Consists of:
- Blood-forming elements
- Osteogenic cells
- Adipose tissue
Interdental Septum
- Consists of cancellous bone bordered by the socket walls of approximating teeth and facial and lingual cortical plates
- Can have irregular windows appear in the bone adjacent to roots if they are too close together
Embryology of Alveolar Bone
- Forms near the end of the 2nd month of fetal life
- Mandible and maxilla form a groove that opens towards the surface of the oral cavity
- Bony septa form gradually as tooth germs develop
Osteogenesis
- Process of bone formation
- Alveolar bone is formed during fetal growth by intramembranous ossification
- Consists of a calcified matrix with osteocytes enclosed within spaces called lacunae
- Osteocytes extend processes into canaliculi that radiate from the lacunae
Bone Composition
- 67% inorganic (hydroxyapatite crystals, calcium, phosphates, hydroxyl, carbonate, sodium, magnesium, and fluorine)
- 33% organic (non-collagenous proteins, collagen type I, osteocalcin, osteonectin, phosphoproteins, and bone morphogenic protein)
Fenestrations and Dehiscences
- Isolated areas where the root is denuded of bone and covered only by periosteum and overlying gingiva are termed fenestrations
- When the denuded area extends through the marginal bone, it is called a dehiscence
- Predisposing factors:
- Prominent root contour
- Malposition
- Labial portion of the root combined with a thin bony plate
- More common on facial bone than on lingual bone
- More common anteriorly than posteriorly
- Often occurs bilaterally
Bone Turnover (Remodeling)
- Replacement of old bone by new bone
- Occurs in physiologic growth movements
Alveolar Process
- Defined as the parts of the maxilla and mandible that form and support the sockets of the teeth
- Forms when the tooth erupts to provide osseous attachment to the forming periodontal ligament
- Disappears gradually after the tooth is lost
Alveolar Bone Proper
- Surrounds the roots of the tooth and gives attachment to the principal fibers of the periodontal ligament
- Histologically, it is bundle bone and lamellared bone
Bundle Bone
- The bone that lines the socket in which Sharpey's fibers are embedded
- Perforated with many small foramina for blood vessels and nerves
- Contains more calcium salts per unit area than other bone
- Also known as lamina dura due to its radiopacity
Supporting Alveolar Bone
- The bone that surrounds the alveolar bone proper and gives support to the socket
- Consists of cortical plates and spongy bone (cancellous bone)
Cortical Plates
- Consists of compact bone and forms the outer and inner plates of the alveolar process
- Thinner in maxilla than in mandible
- Thickest in the premolar and molar region of the mandible
- Buccal plates are thin, but lingual plates are heavy
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.