Podcast
Questions and Answers
The ______ are the "arms" of the neuron, which are branch extensions that come out of different parts of the neuron.
The ______ are the "arms" of the neuron, which are branch extensions that come out of different parts of the neuron.
dendrites
The ______ is the center of the neuron.
The ______ is the center of the neuron.
cell body
An elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal is called the ______.
An elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal is called the ______.
axon
Neuron-to-neuron connections are made onto the ______ and cell bodies of other neurons.
Neuron-to-neuron connections are made onto the ______ and cell bodies of other neurons.
Synapses process ______ that are chemical messengers that neurons release to affect other cells across a synapse.
Synapses process ______ that are chemical messengers that neurons release to affect other cells across a synapse.
The cells that receive the signal from neurotransmitters are called ______ cells.
The cells that receive the signal from neurotransmitters are called ______ cells.
The ______ Nervous System (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
The ______ Nervous System (CNS) is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
The ______ controls most of the functions of the body, including awareness, movement, thinking, speech, and the 5 senses.
The ______ controls most of the functions of the body, including awareness, movement, thinking, speech, and the 5 senses.
The ______ cord is a tube-like structure that carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
The ______ cord is a tube-like structure that carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
The spinal cord is covered by three thin layers of protective tissue called ______.
The spinal cord is covered by three thin layers of protective tissue called ______.
The brain structure is composed of three main parts: the ______, midbrain and hindbrain, each with multiple parts.
The brain structure is composed of three main parts: the ______, midbrain and hindbrain, each with multiple parts.
The ______ nervous system (PNS) is a network of nerves that runs throughout the head, neck, and body.
The ______ nervous system (PNS) is a network of nerves that runs throughout the head, neck, and body.
The PNS carries messages to and from the ______ nervous system (the brain and spinal cord).
The PNS carries messages to and from the ______ nervous system (the brain and spinal cord).
The muscles, glands, and organs that the PNS transmits signals to from the CNS are known as ______.
The muscles, glands, and organs that the PNS transmits signals to from the CNS are known as ______.
The SNS takes the lead when the body needs to get through a period of ______, and then the PNS returns things to normal.
The SNS takes the lead when the body needs to get through a period of ______, and then the PNS returns things to normal.
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) prepares the body for physical and mental activity, such as in times of ______ or stress.
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) prepares the body for physical and mental activity, such as in times of ______ or stress.
The ______ gland produces a fluid that protects sperm and aids its mobility.
The ______ gland produces a fluid that protects sperm and aids its mobility.
The ______ is the inner lining of the uterus.
The ______ is the inner lining of the uterus.
The ______ serves as a passageway for sperm, menstrual flow, and childbirth.
The ______ serves as a passageway for sperm, menstrual flow, and childbirth.
The ______ delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract.
The ______ delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract.
The ______ is the lower, narrow part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
The ______ is the lower, narrow part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
______ is responsible for deepening the voice, growing facial hair, and increasing muscle mass in males.
______ is responsible for deepening the voice, growing facial hair, and increasing muscle mass in males.
The ______ phase of the menstrual cycle involves egg growth and estrogen production.
The ______ phase of the menstrual cycle involves egg growth and estrogen production.
During the ______ phase, the uterus lining thickens and prepares for pregnancy.
During the ______ phase, the uterus lining thickens and prepares for pregnancy.
A ______ is a method used to prevent pregnancy.
A ______ is a method used to prevent pregnancy.
One of the early theories of evolution was developed by ______.
One of the early theories of evolution was developed by ______.
A key idea of Lamarck's theory is called ______, which proposes that an organism's body parts develop or shrink based on how much they are used.
A key idea of Lamarck's theory is called ______, which proposes that an organism's body parts develop or shrink based on how much they are used.
Another key idea of Lamarck's theory is ______.
Another key idea of Lamarck's theory is ______.
One sign of an STD might be unusual ______ from the penis or vagina.
One sign of an STD might be unusual ______ from the penis or vagina.
A ______ can help reduce the risk of contracting an STD.
A ______ can help reduce the risk of contracting an STD.
The process by which species change over time is called ______.
The process by which species change over time is called ______.
The variety of life on Earth is called ______.
The variety of life on Earth is called ______.
Parapatric speciation occurs when groups within a species become ______ isolated, preventing gene flow between them.
Parapatric speciation occurs when groups within a species become ______ isolated, preventing gene flow between them.
Microevolution refers to small changes in the ______ of genes in a population over time.
Microevolution refers to small changes in the ______ of genes in a population over time.
Adaptive radiation is the process by which a single ______ species rapidly evolves into multiple distinct species.
Adaptive radiation is the process by which a single ______ species rapidly evolves into multiple distinct species.
Organisms that obtain energy from the foods they consume are called ______.
Organisms that obtain energy from the foods they consume are called ______.
A ______ is a position in the food chain where organisms are grouped based on their feeding relationships.
A ______ is a position in the food chain where organisms are grouped based on their feeding relationships.
A community of living organisms and their physical environment that interact with each other is called an ______.
A community of living organisms and their physical environment that interact with each other is called an ______.
A close and long-term interaction between two different species living together, where at least one of them benefits, is called ______.
A close and long-term interaction between two different species living together, where at least one of them benefits, is called ______.
Organisms that use light energy from the sun to produce food are called ______.
Organisms that use light energy from the sun to produce food are called ______.
Darwin's role involved collecting and documenting plant and animal ______.
Darwin's role involved collecting and documenting plant and animal ______.
Natural selection is a process where species best adapted to their environment survive and ______.
Natural selection is a process where species best adapted to their environment survive and ______.
Fossils usually provide evidence of evolution found in ______ layers.
Fossils usually provide evidence of evolution found in ______ layers.
Darwin's finches are an example of ______ radiation.
Darwin's finches are an example of ______ radiation.
In artificial selection, humans intentionally breed plants or animals to produce specific ______.
In artificial selection, humans intentionally breed plants or animals to produce specific ______.
Allopatric speciation occurs when a population is ______ separated.
Allopatric speciation occurs when a population is ______ separated.
The nitrogen base sequences in the genetic code are largely the same in almost every ______.
The nitrogen base sequences in the genetic code are largely the same in almost every ______.
Comparative morphology shows that many animals have similar ______ but different functions.
Comparative morphology shows that many animals have similar ______ but different functions.
Flashcards
Dendrites
Dendrites
Branch extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons.
Cell Body
Cell Body
The central part of a neuron that contains the nucleus.
Axon
Axon
An elongated fiber that transmits neural signals away from the cell body.
Synapse
Synapse
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reflex
Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endorphins
Endorphins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium
Endometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis and Urethra
Penis and Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervix
Cervix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone
Testosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen
Estrogen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone
Progesterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Condoms
Condoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signs and Symptoms of STDs
Signs and Symptoms of STDs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Use and Disuse
Use and Disuse
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Birth Control
Types of Birth Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biodiversity
Biodiversity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Natural Selection
Natural Selection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Artificial Selection
Artificial Selection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Darwin's Role
Darwin's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fossil Records
Fossil Records
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biochemical Evidence
Biochemical Evidence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Comparative Morphology and Anatomy
Comparative Morphology and Anatomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Darwin's Finches
Darwin's Finches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allopatric Speciation
Allopatric Speciation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parapatric Speciation
Parapatric Speciation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microevolution
Microevolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adaptive Radiation
Adaptive Radiation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trophic Levels
Trophic Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biotic Factors
Biotic Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abiotic Factors
Abiotic Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symbiotic Relationship
Symbiotic Relationship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autotrophs
Autotrophs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Involuntary Response
Involuntary Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Somatic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homeostasis
Homeostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Body Regulation
- Nervous system is the major regulatory system, controlling mental activity (thought, learning, memory).
- Works with the endocrine system to maintain homeostasis (internal equilibrium).
- Essential for communication within the body.
- Stimulus-response coordination is vital.
- Stimulus is anything triggering a reaction.
- Homeostasis is the body's ability to adapt and maintain internal equilibrium.
Nervous System Components
- Receptors: Detect stimuli.
- Control Center: Processes info (e.g., brain).
- Effectors: Respond to signals (e.g., muscles).
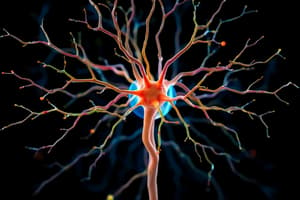
Neurons
- Transmit signals electrically and chemically in the brain and nervous system, connecting neurons, muscles, and tissues.
- Composed of dendrites (branch extensions), cell body (center), and axon (long fiber transmitting signals).
Neuron Classes
- Sensory neurons: Receive info from inside/outside the body and send to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Motor neurons: Receive directives from CNS and convey commands to muscles/glands.
- Interneurons: Connect other neurons within the CNS.
Transmission of Nerve Impulses
- Synapses are neuron-to-neuron connections.
- Two types: Axon splits into multiple branches terminating in synaptic knobs, hormonal secretion enables synaptic impulse transmission.
Neurotransmitters
- Chemical messengers released by neurons to affect other cells.
- Examples include serotonin, acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and endorphins, each with specific effects.
Reflexes
- Involuntary, fast responses to stimuli that protect the body.
- Occur through neural pathways called reflex arcs.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- The brain is the processing center for functions like awareness, movement, thought, etc.
- The spinal cord carries messages between the brain and body.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- A network of nerves throughout the body.
- Connects the CNS to the body.
- Divided into somatic (voluntary movements) and autonomic (involuntary functions like heart rate) systems.
- Includes sympathetic (stress responses like "fight-or-flight") and parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) systems.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.