Podcast
Questions and Answers
What muscle attaches to the medial side of the occlusal plane?
What muscle attaches to the medial side of the occlusal plane?
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor
- Masseter
- Medial pterygoid (correct)
- Buccinator
Where does the lingual nerve emerge between?
Where does the lingual nerve emerge between?
- Lateral pterygoid muscle and TMJ capsule
- Superior and inferior heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle
- Medial and inferior pterygoid muscles
- Medial and lateral pterygoid muscles (correct)
Which muscle is involved in moving the jaw forward?
Which muscle is involved in moving the jaw forward?
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor
- Medial pterygoid (correct)
- Masseter
- Buccinator
What is the common origin for both the Buccinator muscle and Pharyngeal constrictor muscle?
What is the common origin for both the Buccinator muscle and Pharyngeal constrictor muscle?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the superficial face?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the superficial face?
Which muscle assists in mastication but is not directly involved in mastication?
Which muscle assists in mastication but is not directly involved in mastication?
'V3' refers to which branch of the trigeminal nerve?
'V3' refers to which branch of the trigeminal nerve?
'Pterygomandibular triangle' is located between which two muscles?
'Pterygomandibular triangle' is located between which two muscles?
Which nerve innervates the bicuspids, canines, and incisors?
Which nerve innervates the bicuspids, canines, and incisors?
Which branch of the mandibular nerve carries taste fibers from the anterior tongue?
Which branch of the mandibular nerve carries taste fibers from the anterior tongue?
Which artery provides the primary blood supply to the mandible?
Which artery provides the primary blood supply to the mandible?
Which nerve branch innervates the anterior digastric and mylohyoid muscles?
Which nerve branch innervates the anterior digastric and mylohyoid muscles?
Which artery supplies the pterygopalatine fossa?
Which artery supplies the pterygopalatine fossa?
Which venous structure drains the infratemporal fossa?
Which venous structure drains the infratemporal fossa?
Which nerve branch may attach to the inferior alveolar nerve in the mylohyoid groove of the mandible?
Which nerve branch may attach to the inferior alveolar nerve in the mylohyoid groove of the mandible?
Which artery supplies the lateral pterygoid muscle?
Which artery supplies the lateral pterygoid muscle?
What is the primary function of the parotid gland?
What is the primary function of the parotid gland?
Which nerve innervates the parotid gland's secretomotor function?
Which nerve innervates the parotid gland's secretomotor function?
Which of the following structures does NOT traverse through the parotid gland?
Which of the following structures does NOT traverse through the parotid gland?
What is the primary function of the infratemporal fossa?
What is the primary function of the infratemporal fossa?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the parotid gland?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the parotid gland?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the masticator space?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the masticator space?
What is the primary function of the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve?
What is the primary function of the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the fascial compartment surrounding the infratemporal fossa?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the fascial compartment surrounding the infratemporal fossa?
Which of the following motor nuclei innervates the muscles of mastication?
Which of the following motor nuclei innervates the muscles of mastication?
Which of the following is not a function of the tensor tympani muscle?
Which of the following is not a function of the tensor tympani muscle?
Which of the following nerves innervates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
Which of the following nerves innervates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
Which of the following branches of the trigeminal nerve innervates the parotid gland, TMJ, and lateral scalp?
Which of the following branches of the trigeminal nerve innervates the parotid gland, TMJ, and lateral scalp?
What is the function of the trigeminal ganglion?
What is the function of the trigeminal ganglion?
Which of the following nerves innervates the mylohyoid muscle?
Which of the following nerves innervates the mylohyoid muscle?
What is the function of the meningeal branch of the trigeminal nerve?
What is the function of the meningeal branch of the trigeminal nerve?
Which of the following nerves passes through the mental foramen and innervates the lower lip, skin, and gingiva?
Which of the following nerves passes through the mental foramen and innervates the lower lip, skin, and gingiva?
What is the first movement during TMJ opening?
What is the first movement during TMJ opening?
What muscle contracts to allow the disc to move forwards during jaw opening?
What muscle contracts to allow the disc to move forwards during jaw opening?
What causes the 'pops and clicks' sometimes experienced in the jaw joint?
What causes the 'pops and clicks' sometimes experienced in the jaw joint?
Which muscle is responsible for the second movement of the TMJ opening, which involves sliding within the superior joint space?
Which muscle is responsible for the second movement of the TMJ opening, which involves sliding within the superior joint space?
What plays a role in balancing the posterior pull of the elastic superior retrodiscal lamina to keep the TMJ disc positioned between the two bones?
What plays a role in balancing the posterior pull of the elastic superior retrodiscal lamina to keep the TMJ disc positioned between the two bones?
What can cause abnormal TMJ movements where the condyle may move off the articular eminence?
What can cause abnormal TMJ movements where the condyle may move off the articular eminence?
During jaw closure, which head of the lateral pterygoid muscle contracts?
During jaw closure, which head of the lateral pterygoid muscle contracts?
'Minor assistance in jaw movements' is provided by which group of muscles?
'Minor assistance in jaw movements' is provided by which group of muscles?
Where is the lingual tonsil located?
Where is the lingual tonsil located?
Which structure forms arches around the tonsil?
Which structure forms arches around the tonsil?
What oral cavity structure is innervated by CN IX?
What oral cavity structure is innervated by CN IX?
Which bones make up the oral cavity?
Which bones make up the oral cavity?
What type of epithelium lines the oral cavity?
What type of epithelium lines the oral cavity?
Where is the hard palate located?
Where is the hard palate located?
Which tonsil detects pathogens?
Which tonsil detects pathogens?
What separates the nasopharynx from the oropharynx?
What separates the nasopharynx from the oropharynx?
What serves as the attachment site for buccinator and superior constrictor muscles?
What serves as the attachment site for buccinator and superior constrictor muscles?
What is the function of the palatoglossus muscle?
What is the function of the palatoglossus muscle?
What condition is characterized by abnormal growths on the hard palate?
What condition is characterized by abnormal growths on the hard palate?
What structure is found within the soft palate and is part of the lymphoid tissue ring surrounding the oropharynx?
What structure is found within the soft palate and is part of the lymphoid tissue ring surrounding the oropharynx?
Which of the following is NOT a border of the hard palate?
Which of the following is NOT a border of the hard palate?
What structure is found at the posterior end of the soft palate?
What structure is found at the posterior end of the soft palate?
Which of the following muscles is NOT involved in the movement of the soft palate?
Which of the following muscles is NOT involved in the movement of the soft palate?
What is the function of the palatopharyngeus muscle?
What is the function of the palatopharyngeus muscle?
What condition is characterized by a cystic lining within the nasopalatine duct?
What condition is characterized by a cystic lining within the nasopalatine duct?
Which of the following structures is NOT found on the soft palate?
Which of the following structures is NOT found on the soft palate?
Which muscle is responsible for sealing the nasopharynx from the oropharynx?
Which muscle is responsible for sealing the nasopharynx from the oropharynx?
Which artery provides the primary blood supply to the soft palate and palatine glands?
Which artery provides the primary blood supply to the soft palate and palatine glands?
What is the function of the palatine aponeurosis?
What is the function of the palatine aponeurosis?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the soft palate?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the soft palate?
Which muscle is innervated by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V3)?
Which muscle is innervated by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V3)?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the anterior hard palate and nasal septum?
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the anterior hard palate and nasal septum?
Which muscle attaches to the auditory tube and the petrous temporal bone?
Which muscle attaches to the auditory tube and the petrous temporal bone?
What is the function of the nasopalatine nerve?
What is the function of the nasopalatine nerve?
Which structure is the site of attachment for the soft palate muscles?
Which structure is the site of attachment for the soft palate muscles?
Which nerve innervates the muscles responsible for elevating the soft palate?
Which nerve innervates the muscles responsible for elevating the soft palate?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Muscles of Mastication
- Innervated by Motor CN V (Trigeminal Nerve)
- Origin from 2nd branchial arch
- Trigeminal ganglion contains pseudounipolar nerve cell bodies, no synapse, primary sensory nerve fibers from the face
- Motor nucleus for masticatory muscles, mylohyoid, anterior belly of digastric, tensor tympani
Trigeminal Nuclei
- Receive proprioceptive fiber synapses going to the brain, forming a reflex arc
- Example: jaw jerk reflex when biting cheek/tongue
Trigeminal Ganglion
- Cell bodies of the trigeminal ganglion contain:
- Touch from face, mouth, etc.
- Principal/main (pontine) nuclei
- Spinal trigeminal nuclei
- Extends to C3
Trigeminal Stem
- Medial pterygoid nerve
- Tensor tympani nerve
- Meningeal branch
- V3 anterior division motor branches
- Deep temporal nerves (2)
- Masseteric nerve
- Lateral pterygoid nerve
- Sensory branch: Long buccal nerve
- Penetrates the buccinator but does not innervate V3 posterior division
Sensory Branches
- Auriculotemporal nerve: Parotid gland, TMJ, and lateral scalp
- Lingual nerve: Lingual gingiva and anterior 2/3 of the tongue
- Medial to the inferior alveolar nerve
- Inferior alveolar nerve: Mylohyoid, mental, and mucosa
- Incisive: Terminal branch stays in bone at the 2nd bicuspid
- Innervates bicuspids, canines, and incisors
- Molars innervated prior to split
Motor Branches
- Mylohyoid branch: Motor innervation to the anterior digastric and the mylohyoid
- Primarily a motor nerve but also has sensory branches
- In the mylohyoid groove of the mandible
- Branches may dive into the bone and attach to the IA nerve
- Chorda tympani:
- Branch of CN VII
- Carries SSA taste fibers from the anterior tongue
- Secretomotor fibers to salivary glands (Submandibular and Sublingual glands)
- Joins lingual nerve of V3 in the infratemporal fossa
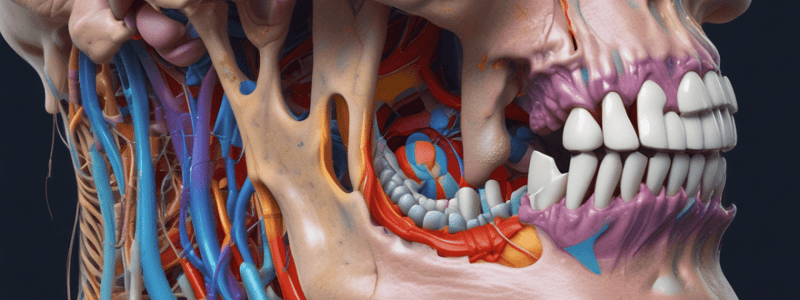
Blood Supply
- Maxillary artery:
- Mandibular (DAM AI)
- External carotid to inferior border of the lateral pterygoid muscle
- Deep auricular
- Anterior tympanic
- Middle meningeal
- Accessory meningeal (not present in everyone)
- Enters the skull through the foramen ovale
- Inferior alveolar: Primary blood supply to the mandible
- Gives rise to the mylohyoid, mental, and incisive branches
- Pterygoid (DM Less Big Ladies Man)
- Portion that crosses the lateral pterygoid muscle
- Deep temporal (2)
- Medial pterygoid
- Lateral pterygoid
- Buccal
- Lingual
- Masseteric
- Pterygopalatine (SPPAID)
- Portion in the pterygopalatine fossa
- Follows branches of V2
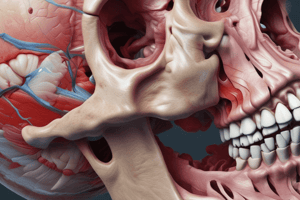
TMJ and Jaw Movements
- TMJ opening: 1st movement is rotation (hinging within the inferior joint space)
- 2nd rotation is translation (sliding/translation within the superior joint space)
- Lateral movements: Superficial muscle contraction on the side of movement + deep muscle contraction of the opposite side
- Opening:
- Disc translates forward with the mandible
- Condyle rotates posteriorly over its head
- Superior retrodiscal lamina stretches, allowing disc to move forwards
- Closing: Superior head of lateral pterygoid muscle contracts
- Inferior head is quiet, balancing posterior pull of elastic superior retrodiscal lamina, keeping the disc positioned between the two bones
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.