Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary goal of reconstructive foot and ankle surgery?
What is the primary goal of reconstructive foot and ankle surgery?
- To correct anatomical deformities
- To enhance aesthetic appearance
- To minimize pain during surgery
- To restore function and improve mobility (correct)
The study of gait is primarily concerned with the interaction of the foot and which other segments?
The study of gait is primarily concerned with the interaction of the foot and which other segments?
- Upper body and head
- Proximal skeletal segments (correct)
- Other lower extremity joints
- Surface and climate conditions
Which aspect of the human foot is essential for effective bipedal ambulation?
Which aspect of the human foot is essential for effective bipedal ambulation?
- Being rigid and inflexible
- Providing compliance and energy storage (correct)
- Reducing muscle involvement
- Increasing overall foot size
Which field does NOT contribute insight into the mechanical behavior of the human foot?
Which field does NOT contribute insight into the mechanical behavior of the human foot?
What must a surgeon comprehend to effectively plan surgical procedures on the foot?
What must a surgeon comprehend to effectively plan surgical procedures on the foot?
Which factor is highlighted as influencing the mobility of the foot?
Which factor is highlighted as influencing the mobility of the foot?
What recent insights are gained from kinematic studies concerning foot motion?
What recent insights are gained from kinematic studies concerning foot motion?
What role do muscles and tendons play in the context of the foot's biomechanics?
What role do muscles and tendons play in the context of the foot's biomechanics?
What is biomechanics primarily concerned with?
What is biomechanics primarily concerned with?
What unit is commonly used to measure the frequency of repeated events in biomechanics?
What unit is commonly used to measure the frequency of repeated events in biomechanics?
How much force does 1 kg of mass exert due to gravity?
How much force does 1 kg of mass exert due to gravity?
What is the formula for calculating moment of force?
What is the formula for calculating moment of force?
Where is the center of gravity located in an upright human?
Where is the center of gravity located in an upright human?
What is the impact of the angle of the force vector on moment of force?
What is the impact of the angle of the force vector on moment of force?
What kind of studies often apply axial load to simulate body weight?
What kind of studies often apply axial load to simulate body weight?
What is the primary measurement unit for mass in biomechanics?
What is the primary measurement unit for mass in biomechanics?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
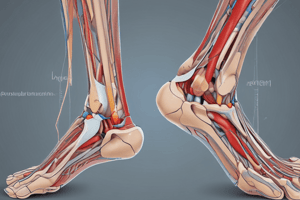
Biomechanics of the Foot and Ankle
- The main goal of reconstructive foot and ankle surgery is to restore function to the appendage, improving the patient’s mobility.
- This chapter focuses on the biomechanics of the foot and ankle, relevant to surgical procedures.
- Biomechanics is a broad discipline covering various areas of study related to the mechanics of a living body, especially the forces exerted by muscles and gravity on the skeletal structure.
- Gait studies and force plate studies commonly utilize milliseconds as the primary unit for time.
- Repeated events over short periods are measured in frequency, expressed in Hertz (Hz), with 1 Hz equating to one cycle per second.
- The mass of an object is typically measured in kilograms (kg).
- The force applied by earth's gravity on a mass of 1 kg is approximately 9.81 N.
- Cadaver studies often simulate body weight by applying axial load to a limb. A 70-kg adult generates a downward force of 686.7 N from gravity.
- The center of mass, often referred to as the center of gravity, is thought to be located slightly anterior to the lumbosacral junction in an upright standing human.
- The moment of force, also known as moment or torque, is calculated as M = F × D, where M represents the moment of force in Newton-meters (N-m), F is the force in Newton (N), and D is the distance in meters (m).
- The angle of the force vector significantly influences the magnitude of the moment of force.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.