Podcast
Questions and Answers
What hormones play a vital role in milk production and milk ejection reflex?
What hormones play a vital role in milk production and milk ejection reflex?
- Prolactin and Oxytocin (correct)
- Estrogen and Progesterone
- FSH and LH
- Testosterone and Relaxin
Which part of the breast acts as a storage area for milk?
Which part of the breast acts as a storage area for milk?
- Acini cells
- Lactiferous sinuses (correct)
- Lobes
- Lactiferous ducts
Where does fertilization of the egg typically occur after ovulation?
Where does fertilization of the egg typically occur after ovulation?
- In the ovary
- In the vaginal canal
- In the ampulla of the fallopian tube (correct)
- In the uterine cavity
What is the lifespan of sperm cells after entering the female reproductive tract?
What is the lifespan of sperm cells after entering the female reproductive tract?
Which type of pelvis is considered the most rounded and optimal for childbirth?
Which type of pelvis is considered the most rounded and optimal for childbirth?
What cell type in the mammary glands is primarily responsible for the actual production of milk?
What cell type in the mammary glands is primarily responsible for the actual production of milk?
What initiates the release of oxytocin during breastfeeding?
What initiates the release of oxytocin during breastfeeding?
Which gland produces prolactin and oxytocin?
Which gland produces prolactin and oxytocin?
How long does the fertilized egg typically remain in the fallopian tube before moving to the uterus?
How long does the fertilized egg typically remain in the fallopian tube before moving to the uterus?
What happens to the levels of estrogen and progesterone during early pregnancy?
What happens to the levels of estrogen and progesterone during early pregnancy?
What is the primary site of implantation within the uterus?
What is the primary site of implantation within the uterus?
What occurs if implantation occurs in the myometrium instead of the endometrium?
What occurs if implantation occurs in the myometrium instead of the endometrium?
Which layer of the uterus is primarily responsible for contraction during labor?
Which layer of the uterus is primarily responsible for contraction during labor?
What does the term 'placenta accreta' refer to?
What does the term 'placenta accreta' refer to?
Which layer of the uterus is the outermost and serves a protective function?
Which layer of the uterus is the outermost and serves a protective function?
During normal delivery, which sequence of events regarding the placenta occurs?
During normal delivery, which sequence of events regarding the placenta occurs?
What could be a consequence of placenta accreta during delivery?
What could be a consequence of placenta accreta during delivery?
What is one of the key functions of the endometrium?
What is one of the key functions of the endometrium?
What might indicate that implantation has occurred abnormally?
What might indicate that implantation has occurred abnormally?
Which layer of the uterus is considered the thickest and highly muscular?
Which layer of the uterus is considered the thickest and highly muscular?
What hormonal change is primarily associated with the first half of the menstrual cycle?
What hormonal change is primarily associated with the first half of the menstrual cycle?
Which of the following statements is true about determining the fertile window?
Which of the following statements is true about determining the fertile window?
What is the role of testosterone in the development of male reproductive organs?
What is the role of testosterone in the development of male reproductive organs?
How many consecutive months should irregular menstrual cycles be monitored?
How many consecutive months should irregular menstrual cycles be monitored?
Which chromosomes do the sperm produced by the testes carry?
Which chromosomes do the sperm produced by the testes carry?
During which menstrual cycle phase does Estrogen dominate?
During which menstrual cycle phase does Estrogen dominate?
At what week of pregnancy do the primitive testes begin to develop in a fetus?
At what week of pregnancy do the primitive testes begin to develop in a fetus?
How is an irregular cycle characterized in comparison to a regular cycle?
How is an irregular cycle characterized in comparison to a regular cycle?
What is the calculation to find the shortest cycle's estimate for ovulation?
What is the calculation to find the shortest cycle's estimate for ovulation?
What chromosome combination will result in a female offspring?
What chromosome combination will result in a female offspring?
What is produced by the ovaries?
What is produced by the ovaries?
Which hormone is not directly induced by the ovaries during the menstrual cycle?
Which hormone is not directly induced by the ovaries during the menstrual cycle?
Which duct is responsible for the development of male reproductive structures?
Which duct is responsible for the development of male reproductive structures?
On which day of the menstrual cycle is the level of Estrogen lowest?
On which day of the menstrual cycle is the level of Estrogen lowest?
What is the primary role of Luteinizing Hormone (LH) in the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary role of Luteinizing Hormone (LH) in the menstrual cycle?
What determines whether the mesonephric duct will develop into male reproductive organs?
What determines whether the mesonephric duct will develop into male reproductive organs?
How do the primitive gonadal tissues transform into male and female reproductive organs?
How do the primitive gonadal tissues transform into male and female reproductive organs?
What should a woman consider if her cycle length varies significantly?
What should a woman consider if her cycle length varies significantly?
What is the primary function of the corpus luteum during the early stages of pregnancy?
What is the primary function of the corpus luteum during the early stages of pregnancy?
Which event occurs first during fertilization?
Which event occurs first during fertilization?
What triggers the secretion of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) in early pregnancy?
What triggers the secretion of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) in early pregnancy?
Which hormone produced by the placenta promotes fetal growth and stimulates amino acid uptake?
Which hormone produced by the placenta promotes fetal growth and stimulates amino acid uptake?
What role does the enzyme Acrosin play in fertilization?
What role does the enzyme Acrosin play in fertilization?
What happens if an egg is fertilized by a sperm carrying an XX chromosome?
What happens if an egg is fertilized by a sperm carrying an XX chromosome?
At what age does puberty typically start in boys?
At what age does puberty typically start in boys?
Which of the following is NOT a male secondary sex characteristic?
Which of the following is NOT a male secondary sex characteristic?
What hormone is primarily responsible for the development of the mesonephric duct into male reproductive structures?
What hormone is primarily responsible for the development of the mesonephric duct into male reproductive structures?
Which structure regresses if testosterone levels remain low during early development?
Which structure regresses if testosterone levels remain low during early development?
During which phase does the average growth spurt occur in boys?
During which phase does the average growth spurt occur in boys?
What is the role of the hypothalamus during the pubertal development phase?
What is the role of the hypothalamus during the pubertal development phase?
Which of the following is a correct statement about the timeline of puberty in girls and boys?
Which of the following is a correct statement about the timeline of puberty in girls and boys?
What anatomical structure is associated with a landmark for station zero during labor?
What anatomical structure is associated with a landmark for station zero during labor?
Which term describes the process occurring when the fetus bounces in the amniotic fluid?
Which term describes the process occurring when the fetus bounces in the amniotic fluid?
Which of the following is commonly referred to as the sitting bones?
Which of the following is commonly referred to as the sitting bones?
What is the correct anatomical term for the internal rotation of the limb during movement?
What is the correct anatomical term for the internal rotation of the limb during movement?
What characteristic describes the ischial spine in relation to the coccyx?
What characteristic describes the ischial spine in relation to the coccyx?
During labor, which movement of the fetus is indicated by flexing at the joints?
During labor, which movement of the fetus is indicated by flexing at the joints?
What is meant by the term 'engagement' in labor context?
What is meant by the term 'engagement' in labor context?
What physiological feature facilitates the bouncing motion of the fetus inside the uterus?
What physiological feature facilitates the bouncing motion of the fetus inside the uterus?
Which motion is characterized as moving a body part away from the midline?
Which motion is characterized as moving a body part away from the midline?
Which of the following describes the landmark for station zero in terms of the fetal position?
Which of the following describes the landmark for station zero in terms of the fetal position?
What is the primary role of the corpus luteum during early pregnancy?
What is the primary role of the corpus luteum during early pregnancy?
Which of the following describes the process of capacitation in sperm cells?
Which of the following describes the process of capacitation in sperm cells?
What occurs during fertilization?
What occurs during fertilization?
In which part of the female reproductive system does fertilization typically occur?
In which part of the female reproductive system does fertilization typically occur?
What is the function of Human Placental Lactogen (HPL) during pregnancy?
What is the function of Human Placental Lactogen (HPL) during pregnancy?
What is the role of acini cells in the lactation process?
What is the role of acini cells in the lactation process?
How does oxytocin contribute to the breastfeeding process?
How does oxytocin contribute to the breastfeeding process?
Which hormonal condition is observed when a woman becomes pregnant?
Which hormonal condition is observed when a woman becomes pregnant?
What process is primarily triggered by the baby's sucking during breastfeeding?
What process is primarily triggered by the baby's sucking during breastfeeding?
What is the purpose of the lactiferous sinuses?
What is the purpose of the lactiferous sinuses?
In which part of the female reproductive system does fertilization occur?
In which part of the female reproductive system does fertilization occur?
What is the significance of the fimbrae in the reproductive system?
What is the significance of the fimbrae in the reproductive system?
Which of the following is true regarding the lifespan of sperm?
Which of the following is true regarding the lifespan of sperm?
Which part of the breast is primarily involved in the release of milk during breastfeeding?
Which part of the breast is primarily involved in the release of milk during breastfeeding?
What is the result of increased levels of progesterone in a pregnant woman?
What is the result of increased levels of progesterone in a pregnant woman?
What is the primary effect of progesterone on the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary effect of progesterone on the endometrium during the menstrual cycle?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the development of the Graafian follicle?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the development of the Graafian follicle?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle is estrogen at its highest level?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle is estrogen at its highest level?
What happens to the blood supply to the endometrium during the first half of the menstrual cycle?
What happens to the blood supply to the endometrium during the first half of the menstrual cycle?
What is the role of FSHRF in the menstrual cycle?
What is the role of FSHRF in the menstrual cycle?
What is the first effect of FSH on the ovaries?
What is the first effect of FSH on the ovaries?
What is the consequence of low estrogen levels during the initial days of the menstrual cycle?
What is the consequence of low estrogen levels during the initial days of the menstrual cycle?
Which structure is formed from the mature Graafian follicle after ovulation?
Which structure is formed from the mature Graafian follicle after ovulation?
What triggers the hypothalamus to release FSHRF during the menstrual cycle?
What triggers the hypothalamus to release FSHRF during the menstrual cycle?
What characterizes the endometrium's vascularity by the end of the menstrual cycle if fertilization does not occur?
What characterizes the endometrium's vascularity by the end of the menstrual cycle if fertilization does not occur?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Reproductive Development
- Gonads are the primary reproductive organs: testes in males and ovaries in females.
- Testes produce sperm which carry either X or Y chromosomes.
- Ovaries produce egg cells (ova) that always carry XX chromosomes.
- The combination of chromosomes (X from sperm and X from egg) determines the sex of the individual.
Gender Determination
- Gender is determined during conception based on the chromosome combination:
- XX combination results in a female.
- XY combination results in a male.
- During the 5th week of pregnancy, primitive gonadal tissues develop two ducts: mesonephric and paramesonephric.
- Testosterone, produced by primitive testes, influences the development of male reproductive organs.
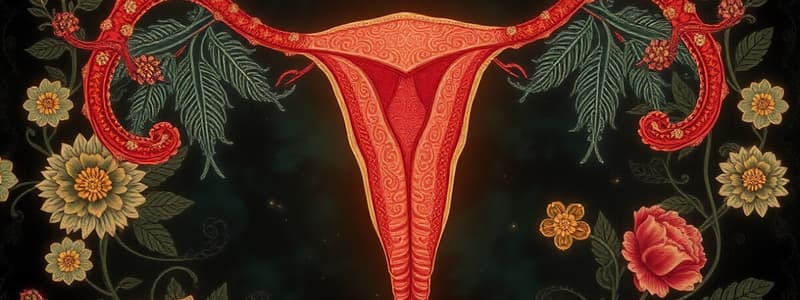
Functions of the Uterus
- The uterus has three main functions:
- Site of implantation (endometrium) where fertilized egg attaches.
- Houses and nourishes the developing fetus.
- Aids in labor and delivery through uterine contractions.
- If implantation occurs deeper in the myometrium, this can cause complications like placenta accreta.
Placenta and Complications
- The placenta typically separates from the endometrium after childbirth; complications arise if it is deeply implanted.
- Placenta accreta occurs when the placenta remains attached to the uterus, risking severe hemorrhage during delivery.
Breast Anatomy and Milk Production
- Breast lobes are connected to lactiferous ducts which lead to lactiferous sinuses (storage for milk).
- Prolactin, from the anterior pituitary gland, stimulates milk production in acini cells.
- Oxytocin, from the posterior pituitary gland, triggers milk ejection during breastfeeding.
Hormonal Regulation in Menstrual Cycle
- Menstrual cycle hormones:
- FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) leads follicular development.
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone) triggers ovulation.
- Estrogen predominates in the first half of the cycle; progesterone in the second half.
Fertilization Process
- Viable sperm can survive up to 5 days and must reach the egg in the fallopian tube for fertilization.
- Fertilization occurs when a sperm successfully penetrates the egg, leading to nuclear fusion and the start of pregnancy.
Embryo Development
- After fertilization, the embryo (blastocyst) adheres to the uterus wall to receive oxygen and nutrients.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is produced by the placenta, promoting fetal growth.
Summary of Hormones and Functions
- Prolactin stimulates milk production while oxytocin causes milk ejection.
- Estrogen and progesterone are critical for the menstrual cycle and supporting pregnancy.
- Monitoring menstrual cycles helps identify irregularities and estimate fertility windows.
Male and Female Reproductive Development
- Mesonephric duct develops into male reproductive organs; paramesonephric duct forms female organs.
- Fertilization by sperm carrying XX results in female if testosterone levels remain low by the 10th week of pregnancy.
Secondary Sex Characteristics in Males
- Males experience secondary sex characteristics such as:
- Weight increase
- Broadened shoulders
- Testes growth
- Facial, axillary, and pubic hair growth
- Voice deepening due to androgens
- Penile growth
- Increased height
- Initiation of spermatogenesis
Pubertal Development
- Puberty typically starts between ages 9 and 17.
- Growth spurts occur earlier in girls than boys.
- Average age for onset: 9-12 years for girls, 12-14 years for boys.
Male Reproductive Anatomy
- Male reproductive system comprises external and internal structures.
- External structures:
- Penis: covered by foreskin (prepuce).
- Scrotum: pouch of skin that holds and regulates testicular temperature.
Female Reproductive Anatomy and Milk Production
- Mammary glands consist of lobes connected to lactiferous ducts, which transport milk.
- Prolactin from the anterior pituitary gland stimulates milk production; Oxytocin from the posterior pituitary initiates milk ejection.
- Suction by the infant triggers the release of oxytocin, leading to the milk ejection reflex.
Pelvic Types
- True pelvis serves as the birth canal.
- Four types of pelvic shapes:
- Gynecoid: most favorable for childbirth
- Others: android, anthropoid, and platypelloid have varying implications for labor
Ovarian Cycle and Hormonal Regulation
- Follicular phase characterized by low estrogen, triggering hypothalamus to start a new cycle.
- Estrogen stimulates the release of FSH from the anterior pituitary, promoting ovarian follicle development.
- Graafian follicle, containing mature egg cells, is formed through estrogen influence.
Fertilization and Early Pregnancy
- Viable sperm enter the cervix and journey to the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
- Fertilization occurs when sperm penetrates the egg, marking the beginning of pregnancy.
- The blastocyst adheres to the uterine wall, receiving oxygen and nutrients from the mother.
- Human Placental Lactogen: produced by the placenta, promotes fetal growth and prepares mammary glands for lactation.
Important Hormones
- Prolactin: stimulates milk production.
- Oxytocin: facilitates uterine contractions and milk ejection during breastfeeding.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG): produced early in pregnancy, maintains corpus luteum for continued estrogen and progesterone production.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.