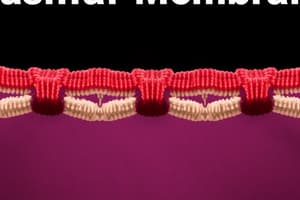
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the fluid mosaic model describe about biological membranes?
What does the fluid mosaic model describe about biological membranes?
- Membranes are impermeable to all substances.
- Membranes have a uniform distribution of proteins and lipids.
- Membranes are rigid structures made entirely of proteins.
- Membranes are primarily composed of lipids with embedded proteins. (correct)
What is meant by membrane asymmetry?
What is meant by membrane asymmetry?
- The ability of proteins to migrate freely across the bilayer.
- The uniform distribution of membrane components throughout the bilayer.
- The presence of the same types of lipids on both sides of the membrane.
- Chemical composition differences between the inner and outer layers of the membrane. (correct)
Which option correctly identifies a major mechanism of membrane transport?
Which option correctly identifies a major mechanism of membrane transport?
- Selective filtration
- Facilitated migration
- Osmotic regulation
- Passive diffusion (correct)
How does facilitated diffusion differ from passive diffusion?
How does facilitated diffusion differ from passive diffusion?
Which statement is true regarding active transport?
Which statement is true regarding active transport?
In relation to phospholipid asymmetry, which statement is correct?
In relation to phospholipid asymmetry, which statement is correct?
What distinguishes oligosaccharides in membranes?
What distinguishes oligosaccharides in membranes?
Which of the following substances typically uses passive diffusion to cross membranes?
Which of the following substances typically uses passive diffusion to cross membranes?
What occurs to ATP after it binds to an actin monomer during polymerization?
What occurs to ATP after it binds to an actin monomer during polymerization?
Which type of intermediate filament protein is found in epithelial cells?
Which type of intermediate filament protein is found in epithelial cells?
What is a key structural feature of intermediate filaments?
What is a key structural feature of intermediate filaments?
What primary function do intermediate filaments serve in cells subjected to mechanical stress?
What primary function do intermediate filaments serve in cells subjected to mechanical stress?
Where are intermediate filaments typically located within a cell?
Where are intermediate filaments typically located within a cell?
What is the primary function of the sodium pump (Na+/K+-ATPase)?
What is the primary function of the sodium pump (Na+/K+-ATPase)?
Which of the following types of receptors are involved in transducing signals without the ligand entering the cell?
Which of the following types of receptors are involved in transducing signals without the ligand entering the cell?
Which receptor type is characterized by making seven passes through the membrane?
Which receptor type is characterized by making seven passes through the membrane?
What triggers a conformational change in a ligand-gated ion channel?
What triggers a conformational change in a ligand-gated ion channel?
What is a common feature of enzyme-linked receptors?
What is a common feature of enzyme-linked receptors?
How does a G protein–coupled receptor initiate a cellular response?
How does a G protein–coupled receptor initiate a cellular response?
What is the role of ligands in the context of membrane receptors?
What is the role of ligands in the context of membrane receptors?
Which receptor class is involved in ion channel opening upon ligand binding?
Which receptor class is involved in ion channel opening upon ligand binding?
What mechanism describes the sodium pump's ability to move sodium ions against their gradient?
What mechanism describes the sodium pump's ability to move sodium ions against their gradient?
What is the primary function of endocytosis?
What is the primary function of endocytosis?
Which endocytosis process is characterized by the uptake of large macromolecules or bacteria?
Which endocytosis process is characterized by the uptake of large macromolecules or bacteria?
What type of vesicle is formed during phagocytosis?
What type of vesicle is formed during phagocytosis?
What differentiates pinocytosis from phagocytosis?
What differentiates pinocytosis from phagocytosis?
Which protein is essential for the pinching off of coated vesicles in receptor-mediated endocytosis?
Which protein is essential for the pinching off of coated vesicles in receptor-mediated endocytosis?
What do the ligand–receptor complexes form during receptor-mediated endocytosis?
What do the ligand–receptor complexes form during receptor-mediated endocytosis?
After the clathrin coat is released, what is the vesicle referred to as?
After the clathrin coat is released, what is the vesicle referred to as?
What happens to the portion of the endosome that contains ligands during receptor-mediated endocytosis?
What happens to the portion of the endosome that contains ligands during receptor-mediated endocytosis?
What is the outcome for the portion of the endosome containing receptors?
What is the outcome for the portion of the endosome containing receptors?
Which type of endocytosis is specifically involved in the uptake of fluid and dissolved substances?
Which type of endocytosis is specifically involved in the uptake of fluid and dissolved substances?
What is the primary component of the cytoplasm?
What is the primary component of the cytoplasm?
What percentage of the cytoplasm is typically water?
What percentage of the cytoplasm is typically water?
Which of the following metabolic pathways take place in the cytoplasm?
Which of the following metabolic pathways take place in the cytoplasm?
What is the term for the concentrated inner area of the cytoplasm?
What is the term for the concentrated inner area of the cytoplasm?
Which ions are typically dissolved in the cytosol?
Which ions are typically dissolved in the cytosol?
What is cytoplasmic streaming in plants associated with?
What is cytoplasmic streaming in plants associated with?
Which of the following statements about cytosol is true?
Which of the following statements about cytosol is true?
What effect does increased cell growth have on cytosol pH?
What effect does increased cell growth have on cytosol pH?
What is groundplasm in the context of the cytoplasm?
What is groundplasm in the context of the cytoplasm?
What role does the cytosol play in signal transduction?
What role does the cytosol play in signal transduction?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Membrane Organization
- Fluid mosaic model depicts membranes as "protein icebergs in a lipid sea."
- Integral proteins possess lateral mobility and can rearrange based on various interactions including with peripheral proteins and cytoskeletal filaments.
- Membrane asymmetry exists with different chemical compositions on inner and outer bilayer halves.
- Oligosaccharides are found exclusively on the extracellular surface of the plasma membrane.
- Outer bilayer is richer in phosphatidyl choline and sphingomyelin; inner bilayer has more phosphatidyl serine and phosphatidyl ethanolamine.
Membrane Functions
- Cell membranes maintain selective permeability, crucial for preserving homeostasis and preventing the entry of harmful substances.
- Three primary methods enable molecules to traverse membranes:
- Passive diffusion allows substances to move along concentration gradients without energy expenditure.
- Facilitated diffusion assists molecules like glucose through specific membrane components without energy use.
- Active transport requires energy (ATP) for molecules to cross membranes against their concentration gradient; an example is the sodium pump (Na+/K+-ATPase).
Signal Transduction
- Integral receptor proteins on cell membranes are vital for intercellular communication, binding specific signal molecules (ligands) without themselves entering the cell.
- Major receptor classes include:
- Ligand-gated ion channels allow ion passage upon ligand binding.
- Enzyme-linked receptors can activate associated enzymes (e.g., protein kinases) upon ligand binding.
- G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs) have a structure that passes through the membrane seven times.
- Steroid hormone receptors play roles in signaling pathways within cells.
Endocytosis
- Cells can internalize extracellular materials through endocytosis, forming membrane-limited vesicles.
- Types of endocytosis include:
- Phagocytosis (cell eating) for engulfing large substances or bacteria, forming phagosomes.
- Pinocytosis (cell drinking) for taking in small amounts of fluid and solutes via smaller vesicles.
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves ligand binding to receptors, leading to vesicle formation through clathrin-coated pits.
Cytoplasm
- Cytoplasm is the site of numerous metabolic activities, including glycolysis and cell division.
- Composed of cytosol (liquid with various solutes), organelles, and inclusions; cytosol contains around 70% water.
- The cytoplasmic matrix supports organelles, enabling signaling and metabolic processes within cells.
Cytosol
- Cytosol excludes the nucleus and is rich in dissolved ions and macromolecules; it facilitates signal transduction and maintains cellular functions.
- pH of human cytosol ranges from 7.0 to 7.4, influenced by cellular growth and metabolic activity.
- Ions within cytosol include K+, Na+, Cl-, Mg2+, Ca2+, and bicarbonate.
Intermediate Filaments
- Intermediate filaments are ropelike structures providing tensile strength and durability, formed by protein subunits specific to cell types.
- They stabilize cell structure, particularly in cell types exposed to mechanical stress (e.g., skin, muscle).
- Located throughout the cytoplasm, they form networks around the nucleus and contribute to maintaining cell shape.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.