Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary waste product produced during aerobic respiration?
What is the primary waste product produced during aerobic respiration?
- Carbon dioxide (correct)
- Nitrogen
- Carbon monoxide
- Oxygen
Which structure is responsible for containing rings of cartilage in the respiratory system?
Which structure is responsible for containing rings of cartilage in the respiratory system?
- Air sacs
- Trachea (correct)
- Bronchioles
- Larynx
How does oxygen enter the blood during gas exchange in the air sacs?
How does oxygen enter the blood during gas exchange in the air sacs?
- It is actively transported into the blood.
- It is absorbed through thicker cell layers.
- It diffuses from the air sac into the blood capillary. (correct)
- It is released from carbon dioxide molecules.
Which component of the respiratory system helps in expelling carbon dioxide from the body?
Which component of the respiratory system helps in expelling carbon dioxide from the body?
What is primarily responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood?
What is primarily responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood?
What structure is crucial for the expansion of the lungs during breathing?
What structure is crucial for the expansion of the lungs during breathing?
What is the main role of capillaries in the context of lung function?
What is the main role of capillaries in the context of lung function?
Which structure allows air to move from the throat to the lungs?
Which structure allows air to move from the throat to the lungs?
What does oxyhaemoglobin do when it reaches the cells?
What does oxyhaemoglobin do when it reaches the cells?
How does the diaphragm contribute to breathing?
How does the diaphragm contribute to breathing?
Which statement accurately describes plasma?
Which statement accurately describes plasma?
What makes red blood cells unique compared to other cells?
What makes red blood cells unique compared to other cells?
What is one of the key requirements for cellular respiration?
What is one of the key requirements for cellular respiration?
Why is glucose important for the body?
Why is glucose important for the body?
What role do mitochondria play in cells?
What role do mitochondria play in cells?
What is the approximate number of red blood cells in every cubic centimeter of blood?
What is the approximate number of red blood cells in every cubic centimeter of blood?
What is required for an object to maintain circular motion?
What is required for an object to maintain circular motion?
What happens when an object experiences balanced forces?
What happens when an object experiences balanced forces?
Which statement correctly describes the moment of a force?
Which statement correctly describes the moment of a force?
What occurs when the moments on both sides of a pivot are equal and opposite?
What occurs when the moments on both sides of a pivot are equal and opposite?
How does a parachute affect a falling object's speed?
How does a parachute affect a falling object's speed?
What is the independent variable in the experiment involving dissolving salt in water?
What is the independent variable in the experiment involving dissolving salt in water?
How does the solubility of salts generally change with temperature?
How does the solubility of salts generally change with temperature?
Which solvent is nail polish soluble in?
Which solvent is nail polish soluble in?
What does a distance/time graph represent?
What does a distance/time graph represent?
How is average speed calculated?
How is average speed calculated?
What is the standard unit for measuring speed?
What is the standard unit for measuring speed?
What effect do unbalanced forces have on an object?
What effect do unbalanced forces have on an object?
When a ball hits a racket, what must be true for the ball to change direction?
When a ball hits a racket, what must be true for the ball to change direction?
What is the primary function of mitochondria in a cell?
What is the primary function of mitochondria in a cell?
What is the role of hemoglobin in red blood cells?
What is the role of hemoglobin in red blood cells?
What is formed when oxygen combines with hemoglobin in red blood cells?
What is formed when oxygen combines with hemoglobin in red blood cells?
Which type of blood cell is characterized by having a nucleus?
Which type of blood cell is characterized by having a nucleus?
What is the definition of a saturated solution?
What is the definition of a saturated solution?
How does temperature affect the solubility of most solutes in water?
How does temperature affect the solubility of most solutes in water?
What is the function of antibodies produced by certain white blood cells?
What is the function of antibodies produced by certain white blood cells?
What is the primary characteristic of a concentrated solution?
What is the primary characteristic of a concentrated solution?
What is the role of the solute in a solution?
What is the role of the solute in a solution?
What does it mean when a solution is described as transparent?
What does it mean when a solution is described as transparent?
Which of the following is an example of a solvent?
Which of the following is an example of a solvent?
How does chromatography help scientists?
How does chromatography help scientists?
What happens to sugar particles when they dissolve in water?
What happens to sugar particles when they dissolve in water?
Which statement accurately describes a solution?
Which statement accurately describes a solution?
What is a chromatogram?
What is a chromatogram?
Why might public health scientists use chromatography?
Why might public health scientists use chromatography?
Flashcards
What is aerobic respiration?
What is aerobic respiration?
The process of chemical reactions within cells that uses oxygen to release energy from food.
Why do we need oxygen?
Why do we need oxygen?
Oxygen is taken into the lungs when breathing, travels through the bloodstream, and is delivered to every cell in the body.
What is respiration?
What is respiration?
The process of taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. It involves the lungs, airways, and muscles.
What are alveoli?
What are alveoli?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are capillaries?
What are capillaries?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does gas exchange happen?
How does gas exchange happen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is hemoglobin?
What is hemoglobin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the diaphragm?
What is the diaphragm?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is plasma?
What is plasma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which blood vessels surround alveoli?
Which blood vessels surround alveoli?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What makes red blood cells unusual?
What makes red blood cells unusual?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is breathing?
What is breathing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are mitochondria?
What are mitochondria?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is cellular respiration?
What is cellular respiration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Haemoglobin
Haemoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Blood Cells
White Blood Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Solute
Solute
Signup and view all the flashcards
Solvent
Solvent
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saturated Solution
Saturated Solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a solvent?
What is a solvent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a solute?
What is a solute?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a solution?
What is a solution?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is dissolving?
What is dissolving?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is chromatography?
What is chromatography?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a pure substance?
What is a pure substance?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a mixture?
What is a mixture?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does it mean for a substance to be transparent?
What does it mean for a substance to be transparent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are solvents?
What are solvents?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does temperature affect the solubility of a substance?
How does temperature affect the solubility of a substance?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a distance/time graph?
What is a distance/time graph?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is speed?
What is speed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the units of speed?
What are the units of speed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do unbalanced forces affect direction?
How do unbalanced forces affect direction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a force diagram?
What is a force diagram?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why does an object moving in a circle change direction?
Why does an object moving in a circle change direction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unbalanced Force
Unbalanced Force
Signup and view all the flashcards
Friction
Friction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Turning Effect of a Force
Turning Effect of a Force
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moment of a Force
Moment of a Force
Signup and view all the flashcards
Balanced Moment
Balanced Moment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Respiration
- Respiration is a series of chemical reactions occurring inside every living cell.
- Aerobic respiration uses oxygen, producing carbon dioxide as a waste product.
- Air contains oxygen; breathing takes air into the lungs, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream.
- Blood delivers oxygen to cells for respiration.
- Blood carries carbon dioxide waste from cells back to the lungs.
- The respiratory system encompasses organs involved in oxygen intake and carbon dioxide removal.
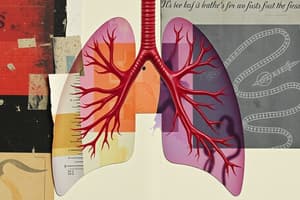
Human Respiratory System Structure
- A diagram shows the respiratory system's structures.
- White spaces represent airways (bronchi and bronchioles) that carry air to and from the lungs.
- The trachea, sometimes called the windpipe, has rings of cartilage to prevent collapse, enabling airflow.
- The trachea branches into two bronchi, one for each lung, which further divide into smaller bronchioles.
- Bronchioles lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli (air sacs), where gas exchange occurs.
- Blood capillaries surround alveoli to facilitate oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
Gas Exchange in Air Sacs
- The alveoli's thin walls (single layer of cells) facilitate rapid gas exchange.
- Oxygen moves from the air sacs to the blood.
- Carbon dioxide moves from the blood to the air sacs.
- Blood arriving at the lungs has less oxygen and more carbon dioxide.
- Air in the alveoli has more oxygen and less carbon dioxide.
- Diffusion moves gases across the thin cell layers.
Breathing
- Breathing involves the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
- Inhaling: intercostal muscles contract, raising ribs; diaphragm contracts, expanding the chest cavity; reduced pressure allows air to enter the lungs.
- Exhaling: intercostal muscles relax, lowering ribs; diaphragm relaxes, decreasing chest cavity volume; increased pressure pushes air out of the lungs.
Blood
- Blood plasma is mainly water, carrying glucose and carbon dioxide.
- Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, responsible for transporting oxygen.
- White blood cells defend against pathogens.
- Red blood cells lack nuclei and mitochondria, maximizing space for hemoglobin.
Delivering Requirements for Respiration in Cells
- Cells need energy for survival.
- Respiration, a chemical reaction in mitochondria, provides this energy.
- Glucose and oxygen are crucial reactants, while carbon dioxide and water are products.
- Blood circulates constantly, transporting glucose, oxygen, and waste products.
Using Energy to Stay Alive
- Energy for bodily functions comes from food (carbohydrates).
- Digestive system converts carbohydrates into glucose.
- Glucose enters bloodstream, supplying cells with energy.
- Mitochondria, within cells, use oxygen and glucose for aerobic respiration, generating ATP (energy).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on the respiratory system with this quiz focused on key structures, functions, and processes involved in respiration and gas exchange. From oxygen transport to the role of the diaphragm, this quiz covers essential concepts from Biology Chapter 10.