Podcast
Questions and Answers
What occurs when both sides of the trunk muscles activate simultaneously?
What occurs when both sides of the trunk muscles activate simultaneously?
- Lateral flexion with axial rotation
- Unilateral activation of deep abdominal muscles
- Pure flexion or extension (correct)
- No movement occurs
Which muscles make up the erector spinae group?
Which muscles make up the erector spinae group?
- Iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis (correct)
- Rotators, multifidi, and spinalis
- Transversospinalis, iliocostalis, and rotators
- Semispinalis, intertransversarius, and interspinalis
What movement is primarily produced during unilateral activation of the trunk muscles?
What movement is primarily produced during unilateral activation of the trunk muscles?
- Full extension
- Pure flexion
- Lateral flexion with some degree of extension (correct)
- Pure axial rotation
Which group of muscles is primarily responsible for trunk stabilization?
Which group of muscles is primarily responsible for trunk stabilization?
In which plane does lateral flexion occur during trunk movement?
In which plane does lateral flexion occur during trunk movement?
Which of the following muscles is primarily involved in fine motor control due to crossing one or two intervertebral junctions?
Which of the following muscles is primarily involved in fine motor control due to crossing one or two intervertebral junctions?
What is one potential reason for altered timing in spinal stabilizers associated with low back pain?
What is one potential reason for altered timing in spinal stabilizers associated with low back pain?
Which abdominal muscle layer is primarily responsible for compressing the abdomen and stabilizing the lower back?
Which abdominal muscle layer is primarily responsible for compressing the abdomen and stabilizing the lower back?
What characteristic of the internal obliques allows them to produce the largest amount of isometric force among the abdominal muscles?
What characteristic of the internal obliques allows them to produce the largest amount of isometric force among the abdominal muscles?
What is the primary role of the multifidi muscles?
What is the primary role of the multifidi muscles?
What happens prior to the firing of the anterior deltoid when an individual is prepared to raise their arm?
What happens prior to the firing of the anterior deltoid when an individual is prepared to raise their arm?
Which muscle group is described as running from spinous process to spinous process and contributing to fine motor control?
Which muscle group is described as running from spinous process to spinous process and contributing to fine motor control?
Which muscle group would be most likely to control lateral flexion of the spine?
Which muscle group would be most likely to control lateral flexion of the spine?
Which muscle serves as a primary indicator of spinal stability through its meshing with the thoracolumbar fascia?
Which muscle serves as a primary indicator of spinal stability through its meshing with the thoracolumbar fascia?
How do the tendinous intersections in the rectus abdominis muscle contribute to its function?
How do the tendinous intersections in the rectus abdominis muscle contribute to its function?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Bilateral vs. Unilateral Trunk Muscle Contraction
- Bilateral activation of back muscles produces flexion or extension.
- Unilateral activation results in extension, lateral flexion, and axial rotation.
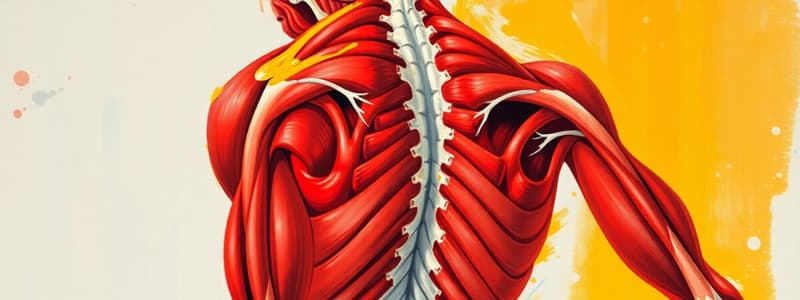
Deep Muscles of the Posterior Trunk
- Erector Spinae Group: Spinalis, longissimus, iliocostalis muscles; originates with a common tendon and inserts on the ribs. Moment arm size varies, influencing lateral flexion. Lateral flexion occurs in the frontal plane around a vertical axis of rotation.
- Transversospinal Group: Semispinalis, multifidi, and rotator muscles; varying lengths and depths; impacts fine vs. gross motor control. Rotators involved in fine motor control due to crossing only one or two intervertebral junctions.
- Multifidi: Clinically significant; altered timing and intramuscular fat are linked to low back pain.
- Short Segmental Group: Interspinalis and intertransversarius muscles; span one intervertebral segment; involved in fine motor control.
Anterior Lateral Trunk Muscles (Abdominal Muscles)
- Rectus Abdominis: Superficial; tendinous intersections; potential role in reducing muscle fiber shortening.
- External Oblique (Externus Abdominis): Originates on ribs; courses inferior and medial; "pocket muscles".
- Internal Oblique: Originates on iliac crest; courses superior and medial; largest physiological cross-sectional area; produces the most isometric force.
- Transverse Abdominis: Deepest; "corset muscle"; compresses abdomen, stabilizes lower back; meshes with thoracolumbar fascia.
Deep Abdominal Muscle Role in Spinal Stabilization
- Study using EMG showed deep abdominal muscles (internal oblique and transverse abdominis) activate before the anterior deltoid during arm raising.
- This anticipatory activation stabilizes the spine before motion.
Muscle Actions and Planes of Motion
- Oblique muscles produce flexion (sagittal plane), lateral flexion (frontal plane), and rotation (horizontal plane).
- Unilateral activation of obliques:
- Lateral flexion occurs to the same side for both external and internal obliques.
- Rotation occurs to the opposite side for external obliques and the same side for internal obliques.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.