Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the epiblast in the bilaminar disc formation?
What is the primary role of the epiblast in the bilaminar disc formation?
When does bilaminar disc formation occur post-fertilization?
When does bilaminar disc formation occur post-fertilization?
Which layer of the bilaminar disc is responsible for the development of extraembryonic structures?
Which layer of the bilaminar disc is responsible for the development of extraembryonic structures?
What significant change occurs during gastrulation?
What significant change occurs during gastrulation?
Signup and view all the answers
What is true about the primitive streak during gastrulation?
What is true about the primitive streak during gastrulation?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the primary umbilical vesicle primarily facilitate?
What does the primary umbilical vesicle primarily facilitate?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the formation of the bilaminar disc establish in terms of embryo orientation?
What does the formation of the bilaminar disc establish in terms of embryo orientation?
Signup and view all the answers
Which germ layer is NOT part of the bilaminar disc?
Which germ layer is NOT part of the bilaminar disc?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of epiblast cells during the formation of the primitive streak?
What is the role of epiblast cells during the formation of the primitive streak?
Signup and view all the answers
Which germ layer is primarily responsible for developing the central and peripheral nervous systems?
Which germ layer is primarily responsible for developing the central and peripheral nervous systems?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the significance of gastrulation in embryonic development?
What is the significance of gastrulation in embryonic development?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure forms as a fluid-filled space early in embryonic development?
Which structure forms as a fluid-filled space early in embryonic development?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cells line the roof of the amniotic cavity?
What type of cells line the roof of the amniotic cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures does not arise from the mesoderm?
Which of the following structures does not arise from the mesoderm?
Signup and view all the answers
What eventually forms the amniotic membrane surrounding the amniotic cavity?
What eventually forms the amniotic membrane surrounding the amniotic cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the amniotic cavity as the embryo develops?
What happens to the amniotic cavity as the embryo develops?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the process by which the bilaminar disc transforms into the trilaminar disc?
What is the process by which the bilaminar disc transforms into the trilaminar disc?
Signup and view all the answers
Which germ layer is responsible for forming the skin and nervous system?
Which germ layer is responsible for forming the skin and nervous system?
Signup and view all the answers
What can result from errors during the formation of the embryonic disc?
What can result from errors during the formation of the embryonic disc?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the yolk sac in early embryonic development?
What is the primary function of the yolk sac in early embryonic development?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures are formed from the mesoderm?
Which of the following structures are formed from the mesoderm?
Signup and view all the answers
During which week of gestation does the trilaminar disc form?
During which week of gestation does the trilaminar disc form?
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of the trilaminar disc forms the lining of the respiratory system?
Which layer of the trilaminar disc forms the lining of the respiratory system?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the initial structure of the embryo before gastrulation occurs?
What is the initial structure of the embryo before gastrulation occurs?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the next expected process in embryonic development after the formation of the bilaminar embryonic disc?
What is the next expected process in embryonic development after the formation of the bilaminar embryonic disc?
Signup and view all the answers
What does a significantly larger yolk sac than expected during an early ultrasound most likely indicate?
What does a significantly larger yolk sac than expected during an early ultrasound most likely indicate?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most probable diagnosis for a missed period and ultrasound findings of a bilaminar embryonic disc with no yolk sac or fetal heart tones?
What is the most probable diagnosis for a missed period and ultrasound findings of a bilaminar embryonic disc with no yolk sac or fetal heart tones?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the syncytiotrophoblast layer during early pregnancy?
What is the primary role of the syncytiotrophoblast layer during early pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
Which condition is likely indicated by an ultrasound showing an irregular chorionic sac with abnormal trophoblast invasion in the first trimester?
Which condition is likely indicated by an ultrasound showing an irregular chorionic sac with abnormal trophoblast invasion in the first trimester?
Signup and view all the answers
What developmental stage follows the successful completion of gastrulation?
What developmental stage follows the successful completion of gastrulation?
Signup and view all the answers
In early pregnancy, what abnormal finding could indicate the potential for a spontaneous abortion?
In early pregnancy, what abnormal finding could indicate the potential for a spontaneous abortion?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the expected physiological function of hCG secreted by the syncytiotrophoblast?
What is the expected physiological function of hCG secreted by the syncytiotrophoblast?
Signup and view all the answers
Where is the most likely implantation site of the blastocyst in a healthy pregnancy?
Where is the most likely implantation site of the blastocyst in a healthy pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most important role of the hypoblast at 5 weeks of gestation?
What is the most important role of the hypoblast at 5 weeks of gestation?
Signup and view all the answers
What structure is most likely to be underdeveloped if there is a defect in the differentiation of the epiblast?
What structure is most likely to be underdeveloped if there is a defect in the differentiation of the epiblast?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of hCG during the early stages of pregnancy?
What is the primary function of hCG during the early stages of pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the syncytiotrophoblast during early pregnancy?
What is the primary function of the syncytiotrophoblast during early pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the yolk sac during early pregnancy?
What is the primary role of the yolk sac during early pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer contributes to the formation of the fetal portion of the placenta?
Which layer contributes to the formation of the fetal portion of the placenta?
Signup and view all the answers
What significant structure is formed as a result of trophoblast layer activity during early pregnancy?
What significant structure is formed as a result of trophoblast layer activity during early pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
What complication can arise from abnormal development of the chorionic sac?
What complication can arise from abnormal development of the chorionic sac?
Signup and view all the answers
During implantation, where is the blastocyst ideally nestled?
During implantation, where is the blastocyst ideally nestled?
Signup and view all the answers
Why is the primitive streak important during embryonic development?
Why is the primitive streak important during embryonic development?
Signup and view all the answers
At what stage of pregnancy is the amniotic cavity primarily established?
At what stage of pregnancy is the amniotic cavity primarily established?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a recognized function of the chorionic sac?
Which of the following is NOT a recognized function of the chorionic sac?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the extraembryonic mesoderm contribute to in pregnancy?
What does the extraembryonic mesoderm contribute to in pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
What initial action occurs during the attachment phase of implantation?
What initial action occurs during the attachment phase of implantation?
Signup and view all the answers
What critical role does the chorion play in pregnancy?
What critical role does the chorion play in pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
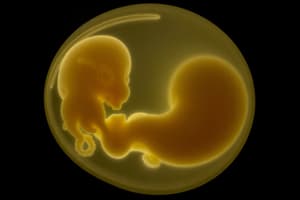
Bilaminar Disc Formation
- Bilaminar Disc Formation occurs around day 8-9 post-fertilization
- Inner cell mass differentiates into two layers (epiblast and hypoblast)
- Creates a flat, two-layered structure called the bilaminar embryonic disc
- Fundamental in establishing the embryo's body plan
- Precursor to more complex differentiation
Two Layers of the Bilaminar Disc
Epiblast
- Columnar layer of cells on the dorsal side of the bilaminar disc
- Crucial for development of the entire embryo proper
- Basis for all three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
Hypoblast
- Layer of cuboidal cells on the ventral side of the bilaminar disc
- Contributes to extraembryonic structures (e.g., yolk sac)
- Doesn't directly form part of the embryo
Associated Structures
Amniotic Cavity
- Forms within the epiblast layer
- Expands to cushion embryo during development
- Stable environment
Primary Umbilical Vesicle (Primary Yolk Sac)
- Formed by hypoblast-derived cells
- Site for initial nutrient exchange
- Hematopoiesis (blood formation) before placenta develops
Importance of Bilaminar Disc Formation
- Establishes embryo's dorsal-ventral polarity
- Prepares embryo for gastrulation (next critical stage)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the crucial stages of bilaminar disc formation, which occurs around day 8-9 post-fertilization. Understand the differentiation of the inner cell mass into epiblast and hypoblast layers and their roles in embryonic development and body plan establishment.