Podcast
Questions and Answers
What do the letters C and M in the Prague C & M Criteria stand for?
What do the letters C and M in the Prague C & M Criteria stand for?
- Extent of disease and Risk of cancer (correct)
- Concentration and Measurement
- Circumference and Mobility
- Cancer and Mortality
A flat columnar mucosa is considered a finding during the examination phase.
A flat columnar mucosa is considered a finding during the examination phase.
True (A)
What type of intervention is recommended if LGD is detected?
What type of intervention is recommended if LGD is detected?
MDT discussion and therapeutic intervention
The protocol specifies a _____ biopsy every cm during the Seattle Biopsy Protocol.
The protocol specifies a _____ biopsy every cm during the Seattle Biopsy Protocol.
Match the following terms with their correct definitions:
Match the following terms with their correct definitions:
What is the primary purpose of fundoplication in gastrointestinal surgery?
What is the primary purpose of fundoplication in gastrointestinal surgery?
The complete wrap fundoplication (Nissen's) involves a 270° wrap around the esophagus.
The complete wrap fundoplication (Nissen's) involves a 270° wrap around the esophagus.
Name one common complication associated with Nissen's fundoplication.
Name one common complication associated with Nissen's fundoplication.
Collis gastroplasty is primarily indicated for __________ shortening.
Collis gastroplasty is primarily indicated for __________ shortening.
Match the types of fundoplication with their descriptions:
Match the types of fundoplication with their descriptions:
Which of the following is NOT a protective factor against GERD?
Which of the following is NOT a protective factor against GERD?
Obesity is considered a risk factor for GERD.
Obesity is considered a risk factor for GERD.
What is the gold standard investigation for diagnosing GERD?
What is the gold standard investigation for diagnosing GERD?
The most common clinical feature of GERD is __________.
The most common clinical feature of GERD is __________.
Match the following treatments with their corresponding advice:
Match the following treatments with their corresponding advice:
Which of the following procedures is suitable for patients with minimal or no hiatus hernia?
Which of the following procedures is suitable for patients with minimal or no hiatus hernia?
Barrett's esophagus is characterized by columnar epithelium replacing squamous epithelium.
Barrett's esophagus is characterized by columnar epithelium replacing squamous epithelium.
What are the pathognomonic findings on biopsy for Barrett's esophagus?
What are the pathognomonic findings on biopsy for Barrett's esophagus?
The type of Barrett's esophagus characterized by a length greater than 3 cm is called __________.
The type of Barrett's esophagus characterized by a length greater than 3 cm is called __________.
Match the following identification methods to their corresponding findings:
Match the following identification methods to their corresponding findings:
What is the common appearance of ulcers seen in CMV esophagitis?
What is the common appearance of ulcers seen in CMV esophagitis?
Esophageal candidiasis is most commonly seen in immunocompetent patients.
Esophageal candidiasis is most commonly seen in immunocompetent patients.
What is the peak age for eosinophilic esophagitis?
What is the peak age for eosinophilic esophagitis?
The endoscopic appearance of eosinophilic esophagitis may include _____ mucosa.
The endoscopic appearance of eosinophilic esophagitis may include _____ mucosa.
Match the type of esophageal infection with its characteristic feature:
Match the type of esophageal infection with its characteristic feature:
Which procedure has the highest risk of GERD as a complication?
Which procedure has the highest risk of GERD as a complication?
Type 3 achalasia is best managed with Heller's myotomy.
Type 3 achalasia is best managed with Heller's myotomy.
What is the primary indication for using botulinum toxin in achalasia management?
What is the primary indication for using botulinum toxin in achalasia management?
Pneumatic dilation is most effective for patients who are _____ years old and older.
Pneumatic dilation is most effective for patients who are _____ years old and older.
Match the management type to its appropriate achalasia type:
Match the management type to its appropriate achalasia type:
What is the earliest clinical feature of esophageal issues related to achalasia?
What is the earliest clinical feature of esophageal issues related to achalasia?
Nocturnal coughing is a classical feature of esophageal complications.
Nocturnal coughing is a classical feature of esophageal complications.
What does the Chicago Classification of Achalasia specifically evaluate?
What does the Chicago Classification of Achalasia specifically evaluate?
The condition known as _____ pneumonia is the most common complication associated with esophageal disorders.
The condition known as _____ pneumonia is the most common complication associated with esophageal disorders.
Match the parameters of the Achalasia-Eckardt Score with their corresponding points.
Match the parameters of the Achalasia-Eckardt Score with their corresponding points.
What is a common complication associated with Zenker's Diverticulum?
What is a common complication associated with Zenker's Diverticulum?
Halitosis is an uncommon symptom of Zenker's Diverticulum.
Halitosis is an uncommon symptom of Zenker's Diverticulum.
What investigative choice is primarily used for diagnosing Zenker's Diverticulum?
What investigative choice is primarily used for diagnosing Zenker's Diverticulum?
Zenker's Diverticulum is primarily located on the _____ of midline at final position.
Zenker's Diverticulum is primarily located on the _____ of midline at final position.
Match the following management options for Zenker's Diverticulum with their descriptions:
Match the following management options for Zenker's Diverticulum with their descriptions:
What is the main goal of treatment for eosinophilia in gastrointestinal surgery?
What is the main goal of treatment for eosinophilia in gastrointestinal surgery?
Obesity is NOT considered a risk factor for GERD.
Obesity is NOT considered a risk factor for GERD.
Name one common complication associated with surgical interventions in gastrointestinal procedures.
Name one common complication associated with surgical interventions in gastrointestinal procedures.
Barrett's esophagus typically involves the replacement of squamous epithelium with __________ epithelium.
Barrett's esophagus typically involves the replacement of squamous epithelium with __________ epithelium.
Match the following surgical procedures with their purpose:
Match the following surgical procedures with their purpose:
Which investigation is primarily confirmatory for Distal Esophageal Spasm (DES)?
Which investigation is primarily confirmatory for Distal Esophageal Spasm (DES)?
Distal Esophageal Spasm is more common in males than in females.
Distal Esophageal Spasm is more common in males than in females.
What is the appearance described in a barium swallow for Distal Esophageal Spasm?
What is the appearance described in a barium swallow for Distal Esophageal Spasm?
Achalasia and cancer are conditions that require ________ for work up.
Achalasia and cancer are conditions that require ________ for work up.
Match the type of esophageal diverticulum with its location:
Match the type of esophageal diverticulum with its location:
What is an effective treatment for Distal Esophageal Spasm?
What is an effective treatment for Distal Esophageal Spasm?
Patients with reoccurring chest pain and normal cardiac enzymes may be experiencing DES.
Patients with reoccurring chest pain and normal cardiac enzymes may be experiencing DES.
What is the less common type of esophageal motility disorder that has a high amplitude contraction?
What is the less common type of esophageal motility disorder that has a high amplitude contraction?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Prague C & M Criteria
- Determines the extent of disease and risk of cancer in Barrett's esophagus
- C: Circumferential extent (how much of the esophagus is affected)
- M: Maximum extent (the length of the affected area)
Seattle Biopsy Protocol
- Suggests taking biopsies every centimeter in all 4 quadrants of the esophagus when investigating Barrett's esophagus
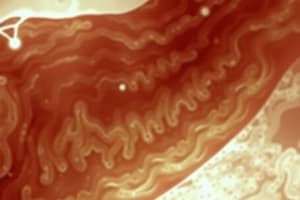
Barrett's Esophagus
- Specialized intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus
- Caused by the replacement of squamous epithelium with columnar epithelium
- Pathognomonic findings: red velvety mucosa and goblet cells on biopsy
- Clinical features: similar to GERD, but less responsive to treatment, and an increased risk of adenocarcinoma
- Types: Long Segment (>3 cm), Short Segment (< 3 cm), Cardia Metaplasia/Microscopic Barrett's (identified with chromoendoscopy i.e Lugol's iodine or methylene blue)
Initial Examination for Barrett's Esophagus
- Repeat OGD + biopsy every 3-5 years
- If flat columnar mucosa is found, systematic cold biopsy is performed
- Dysplasia diagnosis requires confirmation by two independent pathologists
Management of Barrett's Esophagus based on biopsy
-
No Dysplasia:
-
OGD every 6 months until a consecutive evidence of non-dysplastic Barrett's esophagus is confirmed
-
LGD (Low-grade dysplasia)
-
MDT (Multidisciplinary team) discussion
-
Therapeutic intervention
-
HGD (High-grade dysplasia) or Cancer:
-
Surgery: Esophagectomy
-
Endoscopic RFA (radiofrequency ablation)
Esophageal Infections
-
Esophageal Candidiasis:
- Seen in immunocompromised patients
- Commonly associated with oral thrush
- Diagnosis: Endoscopy (shaggy deposits) and Barium swallow (worm-like ulcers)
- Treatment: Antifungals
-
CMV (Cytomegalo Virus):
- Seen after organ transplant
- Commonly associated with Immunosuppressants and GVHD (Graft vs host disease)
- Appearance: Geographical/serpiginous ulcers
-
Herpes Infection:
- Associated with Herpes labialis
- Appearance: Small ulcers & raised margins
Feline Esophagus
- GERD: Affects the upper 1/3 of the esophagus
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Most commonly affects the lower 1/3
- Clinical presentation: Chronic immune mediated disease with esophageal dysfunction
- Eosinophilia and fibrosis is caused when food antigens trigger an immune response
- Peak age: 20-30 years
- Investigations: Endoscopy (crepe paper mucosa, furrows, rings) & biopsy (eosinophilia: >15-20 eosinophils/HPF)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
-
Protective factors:
-
Intra-abdominal esophagus length (3–5 cm - most significant factor)
-
Diaphragmatic Crura
-
Angle of His
-
Mucosal fold arrangement (least contribution)
-
Pathogenesis:
-
Intra-abdominal esophagus length below 2 cm
-
Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) pressure below 6 mmHg (leading to GERD and increased TLOSR - Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation)
-
Risk factors: Obesity and Decreased H.pylori rates
-
Clinical Features:
-
Retrosternal burn (Heartburn) - most common
-
Water brash
-
Pharyngitis/Laryngitis
-
Dental caries
-
Chronic cough and wheezing
Investigations for GERD
- Gold Standard: 24 hr pH monitoring
- Endoscopy: Indication: inconclusive endoscopy or planned intervention
- pH probe: Inserted 5 cm proximal to GE junction. Stop PPI 5-10 days before for accuracy.
- Demeester score: > 14.72 suggests GERD
GERD Treatment
-
Lifestyle Changes:
- Weight reduction
- Avoid fried, fatty, spicy food, citrus, chocolate, mint
- Eat small, frequent meals
- Dine 2-3 hours before sleeping
-
Medications:
- PPIs (Proton pump inhibitors)
- Prokinetics
- Antacids
Surgical Management of GERD
-
Indications:
- Failure of medical management
- GERD complications
- Associated with sliding hiatal hernia
- Patient wishes to discontinue medical management
-
Surgeries:
- Fundoplication
- Collis Gastroplasty
Fundoplication
-
Principles of Surgery:
-
Restore intra-abdominal esophagus length to ≥ 3 cm
-
Tighten diaphragmatic crura around the esophagus
-
Wrap fundus around the esophagus
-
Preserve the vagus nerve
-
Re-establish the angle of His
-
Types of Fundoplication:
-
Complete wrap (Nissen's): 360° - Most common complication: Gas bloat syndrome
-
Partial wrap: - Dor: 180° anterior wrap - Toupet: 180°-270° posterior - Belsey Mark: 270° anterior
Collis Gastroplasty
- Indication: Esophageal shortening
Newer Modalities for GERD
- Polymer injection around LES to tighten sphincter:
- High recurrence, not preferred
Esophageal Motility Disorders
Achalasia
-
Pathophysiology:
-
Impaired relaxation of the LES, resulting in difficulty swallowing
-
Chicago Classification of Achalasia:
-
Type 1 (Classic Achalasia): 100% failed peristalsis without POP (Pan oesophageal pressurization)
-
Type 2: 100% failed peristalsis with POP in ≥ 20% swallows
-
Type 3: ≥ 20% swallows with premature spastic contractions, failed peristalsis, and POP may be present
-
Clinical Features:
-
Classic Triad: - Dysphagia (Initially liquids > solids) - Weight Loss - Regurgitation (Earliest Feature)
-
Other Clinical Features: - Heartburn - Nocturnal coughing - Post-prandial choking
-
Complications:
-
Aspiration pneumonia (most common)
-
Lung abscess
-
Investigations:
-
Manometry: 10C → ↑ IRP (Increased resting pressure), failure of LES relaxation
-
Endoscopy: Rule out cancer
-
Barium Swallow: To visualize the esophagus
-
Achalasia - Eckardt Score:
- Scores weight loss, dysphagia, retrosternal pain, and regurgitation (0-3 points each)
-
Management:
-
Medications:
- Botox: Inject botulinum toxin to relax the LES (Highest rate of recurrence, repeat administration can lead to fibrosis)
- Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) & Nitrates: Primarily for symptomatic relief
-
Balloon (Pneumatic) dilation: - Deflated balloon inserted into the esophagus and inflated. Serial dilatations offer similar efficacy to surgical myotomy. - Best responders: Age > 45 years, Females, previously undilated esophagus, Type A achalasia. - Risk of perforation: Decreases with balloon < 30 mm
-
Surgical Treatments:
- Heller's Myotomy: Cuts the LES muscle 6 cm proximal and 2-3 cm distal to the GE junction
- POEM (Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy): A type of NOTES (Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery) procedure. Cuts the LES muscle through the mouth
Distal Esophageal Spasm (DES)
-
Features:
-
5x less common than achalasia
-
Females > males
-
Motor abnormality of the lower 2/3 of the esophageal body
-
Contractions: Repetitive, simultaneous, and high amplitude (↑ DCI)
-
Investigations:
-
ECG: Rule out angina
-
Barium Swallow: Rosary bead or corkscrew appearance
-
Manometry: Confirmatory
-
Treatment:
-
POEM: Very good response
-
CCB (Ca²⁺ channel blockers) / Nitrates
Approach to Motility Disorders
-
Differentiating factors:
-
Female: With regurgitation, nocturnal cough, dysphagia, and weight loss.
-
Patient: With chest pain similar to angina, but normal cardiac enzymes.
-
Differentials:
-
Achalasia, Cancer: Endoscopy, Manometry, Barium swallow
-
DES, Angina: ECG, Manometry, Barium swallow
Esophageal Diverticula
- Types:
-
Zenker's (Upper Esophageal):
- Causes:
- Pulsion (increased pressure)
- Tuberculosis (TB), Histoplasmosis
- Appearance: False diverticulum (only mucosa)
- Rx: Large/symptomatic: Diverticulectomy
- Causes:
-
Mid Esophageal (Para-bronchial):
- Appearance: True diverticulum of esophagus (traction diverticula)
-
Lower Esophageal (Epiphrenic):
- Causes: Pulsion, False diverticulum
- Rx: Symptomatic: Surgery
-
Zenker's Diverticulum (Crico-pharyngeal achalasia)
- Associated Risks: Increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma
- Pathophysiology: Outpouches through Killian's dehiscence created by discordant muscle contractions, increasing pressure.
- Clinical Features:
- Regurgitation (Earliest symptom)
- Halitosis (Bad oral odor)
- Dysphagia (Difficulty swallowing)
- Complications:
- Aspiration pneumonia (Most common)
- Lung abscess
- Investigation: Barium swallow
- Management:
- Diverticulectomy:
- Large (>2 cm) & symptomatic cases
- Linear stapler > LASER
- Cricopharyngeal myotomy: Reduces recurrence
- Endoscopic diverticulopexy with cricopharyngeal myotomy
- Diverticulectomy:
Abbreviations
- BO: Barrett's esophagus
- HGD: High-grade dysplasia
- LGD: Low-grade dysplasia
- MDT: Multidisciplinary team
- OAC: Esophageal adenocarcinoma
- OGD: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.