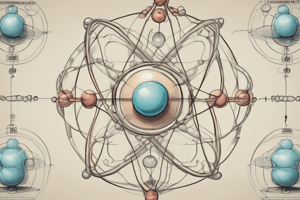
Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which atomic model introduces energy levels and electron spin?
Which atomic model introduces energy levels and electron spin?
- Bohr's Atomic Model (correct)
- Quantum Mechanical Model
- Rutherford's Atomic Model
- Electron Configuration Model
What type of nuclear reaction involves the combination of two or more atomic nuclei?
What type of nuclear reaction involves the combination of two or more atomic nuclei?
- Nuclear Fusion (correct)
- Nuclear Fission
- Radioactive Decay
- Electron Configuration
Which principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom?
Which principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom?
- Hund's Rule
- Pauli's Exclusion Principle
- Aufbau Principle (correct)
- Electron Spin Theory
What determines the magnetic behavior of electrons?
What determines the magnetic behavior of electrons?
Which atomic model introduces wave-particle duality, where electrons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior?
Which atomic model introduces wave-particle duality, where electrons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior?
What type of decay involves the emission of alpha particles?
What type of decay involves the emission of alpha particles?
Which rule states that when filling orbitals with equal energy, electrons occupy each orbital singly before pairing?
Which rule states that when filling orbitals with equal energy, electrons occupy each orbital singly before pairing?
What is the process by which unstable atomic nuclei release energy and particles to become more stable?
What is the process by which unstable atomic nuclei release energy and particles to become more stable?
সালা কতবার দিনে পড়া হয়?
সালা কতবার দিনে পড়া হয়?
তাওহিদের তিনটি বিভাগ কি?
তাওহিদের তিনটি বিভাগ কি?
জাকাত প্রদানের হার কত?
জাকাত প্রদানের হার কত?
জাকাত কত ধরনের লোককে দেওয়া হয়?
জাকাত কত ধরনের লোককে দেওয়া হয়?
সাওম কি?
সাওম কি?
সালা কত রাকআতে হয়?
সালা কত রাকআতে হয়?
হজ্জ করা কতবার করা হয়?
হজ্জ করা কতবার করা হয়?
ইবাদাত কি?
ইবাদাত কি?
রোজা কতটি মাসে পালন করা হয়?
রোজা কতটি মাসে পালন করা হয়?
হজ্জের সময় কবে?
হজ্জের সময় কবে?
রোজার উদ্দেশ্য কী?
রোজার উদ্দেশ্য কী?
হজ্জের অন্যতম রসম কী?
হজ্জের অন্যতম রসম কী?
কারা রোজা থেকে অব্যাহতি পায়?
কারা রোজা থেকে অব্যাহতি পায়?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Atomic Models
- Rutherford's Atomic Model (1911):
- Atom consists of a small, dense nucleus (protons and neutrons) surrounded by electrons
- Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells
- Bohr's Atomic Model (1913):
- Improved Rutherford's model by introducing energy levels and electron spin
- Electrons jump to higher energy levels by absorbing energy and fall to lower levels by emitting energy
- Quantum Mechanical Model:
- Introduces wave-particle duality, where electrons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior
- Electron probability distributions are described by atomic orbitals
Nuclear Reactions
- Nuclear Fusion:
- Two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy
- Examples: proton-proton chain, triple-alpha process
- Nuclear Fission:
- A heavy atomic nucleus splits into two or more lighter nuclei, releasing energy
- Examples: nuclear power plants, atomic bombs
- Radioactive Decay:
- Unstable atomic nuclei release energy and particles to become more stable
- Types: alpha, beta, gamma decay
Electron Configuration
- Aufbau Principle:
- Electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom
- Orbitals are filled in a specific order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, ...
- Hund's Rule:
- When filling orbitals with equal energy, electrons occupy each orbital singly before pairing
- Example: carbon atom (1s² 2s² 2p²)
- Electron Spin and Orbitals:
- Electrons have an intrinsic spin of 1/2, which determines their magnetic behavior
- Atomic orbitals are described by their shape, size, and orientation in space
Atomic Models
- Atom consists of a small, dense nucleus (protons and neutrons) surrounded by electrons in Rutherford's Atomic Model
- Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells in Rutherford's model
- Bohr's Atomic Model introduces energy levels and electron spin, with electrons jumping to higher energy levels by absorbing energy and falling to lower levels by emitting energy
- Quantum Mechanical Model introduces wave-particle duality, where electrons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior
- Electron probability distributions are described by atomic orbitals in the Quantum Mechanical Model
Nuclear Reactions
- Nuclear Fusion combines two or more atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy
- Examples of Nuclear Fusion include the proton-proton chain and triple-alpha process
- Nuclear Fission splits a heavy atomic nucleus into two or more lighter nuclei, releasing energy
- Examples of Nuclear Fission include nuclear power plants and atomic bombs
- Radioactive Decay releases energy and particles as unstable atomic nuclei become more stable
- Types of Radioactive Decay include alpha, beta, and gamma decay
Electron Configuration
- The Aufbau Principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom
- Orbitals are filled in a specific order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p,... according to the Aufbau Principle
- Hund's Rule states that when filling orbitals with equal energy, electrons occupy each orbital singly before pairing
- The electron spin of 1/2 determines the magnetic behavior of electrons
- Atomic orbitals are described by their shape, size, and orientation in space
Ibadat in Islam
- Acts of worship in Islam, obligatory on every Muslim, to develop a strong relationship with Allah and cultivate righteousness and morality.
Salah (Prayer)
- Second pillar of Islam, performed five times a day.
- Direct connection between the believer and Allah.
- Five daily prayers: Fajr (dawn), Dhuhr (noon), Asr (afternoon), Maghrib (sunset), and Isha (night).
- Each prayer consists of a series of rak'ahs (units), including recitation of the Quran, bowing, prostrating, and sitting.
- Can be performed individually or in congregation.
Tawhid (Oneness of Allah)
- Fundamental concept of Islam, affirming the oneness of Allah.
- Belief that Allah is the only God, with no partners or associates.
- Divided into three categories: Tawhid ar-Rububiyyah (oneness of lordship), Tawhid al-Asma was-Sifat (oneness of names and attributes), and Tawhid al-Ibadah (oneness of worship).
Zakat (Charity)
- Third pillar of Islam, compulsory charity.
- Means of purifying one's wealth and soul.
- Paid on excess wealth, typically 2.5% of one's annual savings.
- Eight categories of eligible recipients: Fuqara (poor), Masakin (needy), Al-'Amileen (zakat collectors), Mu'allafatul Qulub (those who have been inclined to Islam), Ar-Riqaab (slaves), Ghaarimeen (debtors), Fisabeelillah (those fighting for Allah's cause), and Ibnus-Sabeel (travelers).
Sawm (Fasting)
- Fourth pillar of Islam, observed during the month of Ramadan.
- Means of developing self-control, empathy, and gratitude.
- Involves abstaining from food, drink, and other physical needs from dawn to sunset.
- Exceptions for those who are ill, traveling, or experiencing menstrual bleeding.
Hajj (Pilgrimage)
- Fifth pillar of Islam, once-in-a-lifetime obligation for those who are physically and financially able.
- Journey to the holy city of Makkah, Saudi Arabia, during the month of Dhu al-Hijjah.
- Involves several rituals, including: Ihram (donning a sacred gown), Tawaf (circumambulating the Ka'bah), Sa'y (running between Safa and Marwah), Wuquf (standing on the plain of Arafat), and stoning the pillars of Jamarat.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.