Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is an example of a synovial joint?
Which of the following is an example of a synovial joint?
- Symphysis
- Gomphosis
- Shoulder joint (correct)
- Suture
What type of joint movement is characterized by the bending and straightening of a limb?
What type of joint movement is characterized by the bending and straightening of a limb?
- Circumduction
- Abduction
- Flexion (correct)
- Rotation
Which classification describes a joint that allows movement around a single axis?
Which classification describes a joint that allows movement around a single axis?
- Multiaxial
- Synarthrosis
- Biaxial
- Uniaxial (correct)
Which type of movement occurs when a limb moves away from the midline of the body?
Which type of movement occurs when a limb moves away from the midline of the body?
What type of synovial joint allows movement in two different planes?
What type of synovial joint allows movement in two different planes?
Which of the following joints demonstrates multiaxial movement?
Which of the following joints demonstrates multiaxial movement?
Which of the following describes a joint that does not allow any movement?
Which of the following describes a joint that does not allow any movement?
Which of the following joints allows for a rotational movement?
Which of the following joints allows for a rotational movement?
Which of the following joints allows for rotation as its primary movement?
Which of the following joints allows for rotation as its primary movement?
Which type of synovial joint is characterized by a concave surface fitting into a convex surface, allowing for multiple movements?
Which type of synovial joint is characterized by a concave surface fitting into a convex surface, allowing for multiple movements?
What movement type decreases the angle between two adjacent bones?
What movement type decreases the angle between two adjacent bones?
Which joint movement is associated with the action of raising the foot upwards towards the shin?
Which joint movement is associated with the action of raising the foot upwards towards the shin?
Which type of joint allows movement in two planes?
Which type of joint allows movement in two planes?
Which action would best be described as moving a body part away from the midline?
Which action would best be described as moving a body part away from the midline?
What type of synovial joint is primarily responsible for gliding movements?
What type of synovial joint is primarily responsible for gliding movements?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of uniaxial joints?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of uniaxial joints?
Which of the following is NOT a classification of synovial joints?
Which of the following is NOT a classification of synovial joints?
What type of synovial joint allows movement in only one plane or axis?
What type of synovial joint allows movement in only one plane or axis?
Which type of movement is associated with condylar joints?
Which type of movement is associated with condylar joints?
What is the primary function of bursae in synovial joints?
What is the primary function of bursae in synovial joints?
Which of the following can experience multiaxial movements?
Which of the following can experience multiaxial movements?
The elongated bursae around tendons are referred to as what?
The elongated bursae around tendons are referred to as what?
Which of the following describes the movement at a hinge joint?
Which of the following describes the movement at a hinge joint?
In terms of joint movement, a wave-like motion is most likely a characteristic of which type of joint?
In terms of joint movement, a wave-like motion is most likely a characteristic of which type of joint?
Flashcards
Articulations (Joints)
Articulations (Joints)
Points of contact between bones, cartilage, or teeth.
Arthrology
Arthrology
The study of joints.
Synarthrosis
Synarthrosis
Immobile joint.
Amphiarthrosis
Amphiarthrosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diarthrosis
Diarthrosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrous Joints
Fibrous Joints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suture (Fibrous)
Suture (Fibrous)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Syndesmosis
Syndesmosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gomphosis
Gomphosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synovial Joint
Synovial Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bursa
Bursa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tendon Sheaths
Tendon Sheaths
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat Pads
Fat Pads
Signup and view all the flashcards
Classification of Synovial Joints
Classification of Synovial Joints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plane Joint
Plane Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hinge Joint
Hinge Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pivot Joint
Pivot Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Condylar Joint
Condylar Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saddle Joint
Saddle Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ball-and-Socket Joint
Ball-and-Socket Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gliding Motion
Gliding Motion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angular Motion
Angular Motion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rotational Motion
Rotational Motion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Special Movements
Special Movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Articulations (Joints)
- Joints are the points of contact between bones, cartilage, or teeth.
- The study of joints is called arthrology
- Joints have varying degrees of stability and mobility
- More mobility means less stability, and more stability means less mobility
Classifications of Joints
- Classified by structure: Fibrous, Cartilaginous, Synovial
- Classified by function:
- Synarthrosis: immobile joint
- Amphiarthrosis: slightly movable joint
- Diarthrosis: freely moveable joint
Fibrous Joints
- Bones are held together by dense connective tissue
- No joint cavity
- Types:
- Suture: Synarthrosis, joint between skull bones
- Syndesmosis: Amphiarthrosis, joint between parallel bones (radius and ulna, tibia and fibula)
- Gomphosis: Joint between the tooth root and alveolar bone (alveolar socket) of the jaw
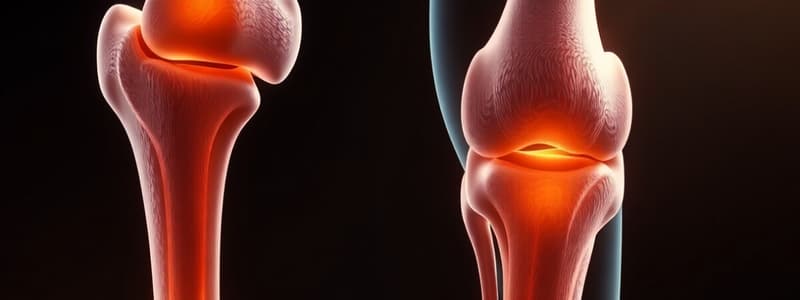
Synovial Joint
- A typical synovial joint includes:
- Articular cartilage that covers the ends of bones
- Synovial membrane on the inside of the joint capsule
- Joint cavity containing synovial fluid
- Ligaments that provide support and limit movement
Accessory Structures of Synovial Joints
- Bursa: Sacs outside most synovial joints
- Contains synovial fluid and reduces friction
- Found where ligaments, muscles, tendons and/or bones rub
- Tendon Sheaths: Elongated bursae around tendons
- Found where tendons rub together in confined areas (wrist and ankle)
- Fat Pads: Provide padding and protection within the joint
Classification of Synovial Joints
- Classified by the shape of the articular surface and type of movement
- Types:
- Plane joint (uniaxial)
- Hinge joint (uniaxial)
- Pivot joint (uniaxial)
- Condylar joint (biaxial)
- Saddle joint (biaxial)
- Ball-and-socket joint (multiaxial)
Movements of Synovial Joints
- Four types:
- Gliding motion: Articular surface slides back and forth or side-to-side (no angle change)
- Angular Motion: Increases or decreases the angle between bones
- Flexion, extension, hyperextension, lateral flexion, abduction, adduction, circumduction
- Rotational Motion: A bone turns on it's longitudinal axis: Lateral rotation, medial rotation, pronation, supination
- Special movements: Occur only at specific joints
- Depression vs. elevation, dorsiflexion vs.plantar flexion, inversion vs. eversion, protraction vs.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.