Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the oblique manner in which the ureters pierce the bladder wall?
What is the primary function of the oblique manner in which the ureters pierce the bladder wall?
- To facilitate the back-flow of urine
- To decrease the diameter of the ureters
- To increase intramural pressure
- To create a one-way valve and prevent back-flow of urine (correct)
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the upper 1/3 of the ureter?
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the upper 1/3 of the ureter?
- Common iliac arteries
- Abdominal aorta
- Renal arteries (correct)
- Internal iliac arteries
What is the purpose of the ureteric vasculature?
What is the purpose of the ureteric vasculature?
- To facilitate the flow of urine
- To create a one-way valve
- To supply blood to the ureters (correct)
- To increase intramural pressure
What is the most likely location of a pelvic kidney?
What is the most likely location of a pelvic kidney?
What is the primary investigation used to diagnose renal calculi?
What is the primary investigation used to diagnose renal calculi?
What is the main reason why renal calculi may become lodged in the ureter?
What is the main reason why renal calculi may become lodged in the ureter?
What is the significance of the ureteropelvic junction (UPJ)?
What is the significance of the ureteropelvic junction (UPJ)?
What is the congenital abnormality associated with recurrent infections?
What is the congenital abnormality associated with recurrent infections?
What is the widest part of the prostatic urethra?
What is the widest part of the prostatic urethra?
What is the longitudinal midline ridge on the posterior wall of the prostatic urethra?
What is the longitudinal midline ridge on the posterior wall of the prostatic urethra?
Where do the ejaculatory ducts open?
Where do the ejaculatory ducts open?
What characteristic is typical of the membranous part of the urethra?
What characteristic is typical of the membranous part of the urethra?
What is the function of the external urethral sphincter?
What is the function of the external urethral sphincter?
What is characteristic of the spongy part of the urethra?
What is characteristic of the spongy part of the urethra?
What is located in the glans of the penis?
What is located in the glans of the penis?
How many bends does the urethra have?
How many bends does the urethra have?
What is the typical colour of the kidneys?
What is the typical colour of the kidneys?
Which of the following is NOT part of the upper urinary tract?
Which of the following is NOT part of the upper urinary tract?
What is the location of the kidneys in the body?
What is the location of the kidneys in the body?
What is the name of the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder?
What is the name of the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder?
What is the name of the part of the lower urinary tract that is associated with the male reproductive system?
What is the name of the part of the lower urinary tract that is associated with the male reproductive system?
What is the shape of the kidneys?
What is the shape of the kidneys?
What percentage of the prostate gland is made up of the peripheral zone?
What percentage of the prostate gland is made up of the peripheral zone?
Which zone of the prostate gland is most prone to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
Which zone of the prostate gland is most prone to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)?
Which artery is involved in the arterial supply of the prostate gland?
Which artery is involved in the arterial supply of the prostate gland?
Where does the lymphatic drainage of the prostate gland drain into?
Where does the lymphatic drainage of the prostate gland drain into?
What is the function of the bulbourethral glands?
What is the function of the bulbourethral glands?
How is the prostate gland typically examined?
How is the prostate gland typically examined?
What is the location of the central zone of the prostate gland?
What is the location of the central zone of the prostate gland?
What is the location of the bulbourethral glands?
What is the location of the bulbourethral glands?
What is the characteristic shape of kidneys that have not separated?
What is the characteristic shape of kidneys that have not separated?
What type of trauma can cause injuries to the kidneys and renal vasculature?
What type of trauma can cause injuries to the kidneys and renal vasculature?
What is the characteristic pain pattern associated with renal calculi?
What is the characteristic pain pattern associated with renal calculi?
What is the purpose of the renal punch test?
What is the purpose of the renal punch test?
What is the preferred imaging modality for renal calculi?
What is the preferred imaging modality for renal calculi?
What is a common complication of renal calculi?
What is a common complication of renal calculi?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
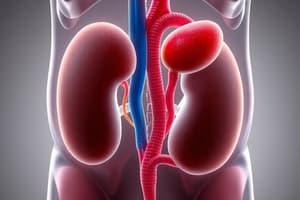
The Kidneys
- Bilateral, bean-shaped organs, reddish-brown in color, located in the posterior abdomen
- Enter the base of the bladder in the upper outer aspect
- Ureters pierce the bladder wall in an oblique manner, creating a one-way valve
- High intramural pressure collapses the ureters, preventing back-flow of urine
Ureteric Vasculature
- Upper 1/3: renal arteries (close to kidneys)
- Middle 1/3: abdominal aorta, testicular/ovarian arteries, common iliac arteries
- Lower 1/3: internal iliac arteries
Uterine Constrictions
- Regions along the ureters become narrower:
- Ureteropelvic junction (UPJ)
- Pelvic inlet
- Ureterovesicular junction (UVJ)
- Sites where renal calculi (renal stones) may become lodged due to decreased width
- Investigation: CT scan of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder (CT-KUB)
Clinical Correlations
- Recurrent infections: associated with congenital abnormalities
- Development of kidneys: ascend and carry vasculature
- Investigations necessary
- Pelvic kidney: kidneys develop in the pelvic region and ascend to the lumbar retroperitoneal area
- Horseshoe kidneys: kidneys have not separated, remain fused into a single horseshoe-shaped structure
Trauma to the Back
- Stab wounds/penetrating trauma to the back can cause injuries to the kidneys and renal vasculature
- Blunt trauma following a motor vehicle accident (MVA)
Urinary Tract Stones - Renal Calculi
- Referred pain from the kidney
- Loin-to-groin pain, keeps going down into the scrotum (males)/labia (females) associated with renal calculi
- Can be familial and recurrent
Complications and Imaging
- Complications: infection, obstruction
- Imaging: CT KUB - kidney-urinary-bladder
- Renal stones show up as white; vertebra appear white in a CT
- X-ray shows radio-opaque areas (not the preferred imaging modality)
Prostate
- Widest part: 3-4cm
- Urethral crest: longitudinal midline ridge on posterior wall
- Depression on either side: prostatic sinus
- Dome-like elevation: seminal colliculus - important landmark in biopsy
- Ejaculatory ducts open on each side of the prostatic utricle
Parts of the Urethra
- Membranous part: narrow and least distensible, passes through the deep perineal pouch
- Spongy part/penile urethra: most mobile, longest, surrounded by corpus spongiosum of penis
- Openings of bulbourethral glands present
- Easy to characterize
- In the glans (head) of the penis, the urethra dilates to form the navicular fossa
- 2 bends - important in catheterisation
Prostate Zones
- Peripheral zone: main body of the gland (65%), located posteriorly
- Central zone: middle lobe, surrounds ejaculatory ducts
- Transition zone: located centrally, surrounds the urethra
- Anterior zone: fibromuscular stroma, merges with the tissue of the urogenital diaphragm
Prostate Vascular Supply, Venous Drainage, and Innervation
- Arterial supply: inferior vesical artery, middle rectal artery
- Venous drainage: prostatic venous plexus → interior iliac vein
- Receives deep dorsal vein of penis and vesical veins
- Lymphatics: drain into internal iliac nodes
- Innervation: inferior hypogastric plexus, sympathetic stimulation stimulates smooth muscle of prostate during ejaculation
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.