Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the process by which the spleen removes nuclei from blood cells without destroying the erythrocytes?
What is the process by which the spleen removes nuclei from blood cells without destroying the erythrocytes?
- Pitting (correct)
- Phagocytosis
- Culling
- Hematopoiesis
Which component of the spleen consists of reticular cells and fibers (cords of Billroth) and surrounds the splenic sinuses?
Which component of the spleen consists of reticular cells and fibers (cords of Billroth) and surrounds the splenic sinuses?
- Malpighian corpuscles
- Hemosiderin
- White pulp
- Red pulp (correct)
What does leukopenia refer to?
What does leukopenia refer to?
- Blood cell production
- Follicles in the white pulp of the spleen, containing many lymphocytes
- Abnormal decrease of white blood corpuscles; may be drug induced (correct)
- Pigment released from hemoglobin process
What is the oxygen-binding protein found in red blood cells?
What is the oxygen-binding protein found in red blood cells?
What are the irregular channels lined by endothelial cells or flattened reticular cells in the spleen known as?
What are the irregular channels lined by endothelial cells or flattened reticular cells in the spleen known as?
What is the function of white blood cells?
What is the function of white blood cells?
Erythrocyte refers to which of the following?
Erythrocyte refers to which of the following?
Hematopoiesis relates to which process?
Hematopoiesis relates to which process?
What does hemosiderin represent in the context of the spleen?
What does hemosiderin represent in the context of the spleen?
What is the term for splenic follicles containing many lymphocytes?
What is the term for splenic follicles containing many lymphocytes?
What is the condition where there is more than one spleen?
What is the condition where there is more than one spleen?
Which ligament helps to hold the spleen in place by connecting it to the stomach?
Which ligament helps to hold the spleen in place by connecting it to the stomach?
What is the term for the alkaline fluid found in the lymphatic vessels?
What is the term for the alkaline fluid found in the lymphatic vessels?
Which structure serves as the posterior medial border of the pancreas and joins with the superior mesenteric vein to form the main portal vein?
Which structure serves as the posterior medial border of the pancreas and joins with the superior mesenteric vein to form the main portal vein?
What is the specific term for the reticuloendothelial cells found in the liver and spleen?
What is the specific term for the reticuloendothelial cells found in the liver and spleen?
What is the term for the left upper quadrant of the abdomen that contains the left lobe of the liver, spleen, and stomach?
What is the term for the left upper quadrant of the abdomen that contains the left lobe of the liver, spleen, and stomach?
Which ligament is located in the middle of the spleen and serves as the site where vessels and lymph nodes enter and exit the spleen?
Which ligament is located in the middle of the spleen and serves as the site where vessels and lymph nodes enter and exit the spleen?
What is the term for a wandering spleen that has migrated from its normal location in the left upper quadrant?
What is the term for a wandering spleen that has migrated from its normal location in the left upper quadrant?
Match the following terms related to the spleen with their descriptions:
Match the following terms related to the spleen with their descriptions:
Match the following structures with their location in the spleen:
Match the following structures with their location in the spleen:
Match the following terms related to blood cells with their functions in the spleen:
Match the following terms related to blood cells with their functions in the spleen:
Match the following ligaments with their connections to the spleen:
Match the following ligaments with their connections to the spleen:
Match the following terms related to blood production with their descriptions:
Match the following terms related to blood production with their descriptions:
Match the following anatomy terms with their definitions:
Match the following anatomy terms with their definitions:
Match the following terms related to the spleen with their descriptions:
Match the following terms related to the spleen with their descriptions:
Match the following ligaments with their connections to the spleen:
Match the following ligaments with their connections to the spleen:
Match the following physiology terms with their definitions:
Match the following physiology terms with their definitions:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
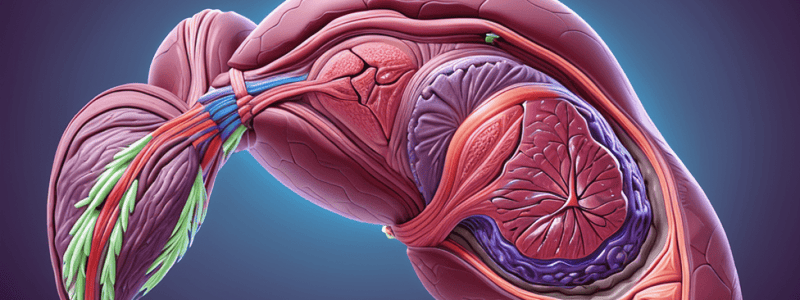
Spleen Functionality and Anatomy
- The spleen removes nuclei from blood cells through a filtering process, preserving erythrocytes intact.
- Cords of Billroth, found in the spleen, consist of reticular cells and fibers, encircling splenic sinuses.
- Irregular channels in the spleen lined by endothelial cells or flattened reticular cells are crucial for blood filtration.
- A wandering spleen is a condition where the spleen has abnormally migrated from its typical position in the left upper quadrant.
Blood Components and Functions
- Leukopenia refers to a lower-than-normal white blood cell count, impacting immune response.
- Erythrocytes are red blood cells that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
- The oxygen-binding protein found in erythrocytes is hemoglobin, essential for oxygen transport throughout the body.
- White blood cells (leukocytes) function to defend against infections and respond to pathogens.
Hematological Processes
- Hematopoiesis is the process of blood cell production, occurring primarily in the bone marrow.
- Hemosiderin represents a storage form of iron, often accumulated in the spleen and associated with iron metabolism.
Anatomical Structure and Ligaments
- Splenic follicles, rich in lymphocytes, are vital for the immune response within the spleen.
- The spleen is anchored to the stomach by the gastrosplenic ligament.
- The splenic hilum is the central area where vessels and lymph nodes enter and exit the spleen.
- The left upper quadrant of the abdomen contains the left lobe of the liver, spleen, and stomach, known for housing critical organs.
- Reticuloendothelial cells, critical for phagocytosis, are present in the liver and spleen.
Venous Structures
- The posterior medial border of the pancreas articulates with the superior mesenteric vein, forming the main portal vein, a key component for blood flow to the liver.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.