Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the extent of the pharynx?
What is the extent of the pharynx?
- From the base of the skull to the 12th thoracic vertebra
- From the base of the skull down to the 6th cervical vertebra (correct)
- From the base of the skull down to the sacrum
- From the base of the skull down to the 6th thoracic vertebra
Which part of the pharynx communicates with nasal cavities through the choanae?
Which part of the pharynx communicates with nasal cavities through the choanae?
- Oropharynx
- Laryngeopharynx
- Hypopharynx
- Nasopharynx (correct)
What type of epithelium lines the oropharynx and laryngeopharynx?
What type of epithelium lines the oropharynx and laryngeopharynx?
- Simple squamous epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium
- Stratified squamous epithelium (correct)
- Ciliated columnar epithelium
What is the widest part of the pharynx?
What is the widest part of the pharynx?
What covers the external aspect of the pharynx?
What covers the external aspect of the pharynx?
How many parts is the pharynx divided into?
How many parts is the pharynx divided into?
The nasopharynx extends from the base of the skull down to the level of the ___________.
The nasopharynx extends from the base of the skull down to the level of the ___________.
Which structure connects the nasopharynx with the nasal cavities?
Which structure connects the nasopharynx with the nasal cavities?
What is the role of the salpingopharyngeus muscle in the nasopharynx?
What is the role of the salpingopharyngeus muscle in the nasopharynx?
What helps to keep the nasopharynx permanently opened for free breathing?
What helps to keep the nasopharynx permanently opened for free breathing?
Which part of the pharynx extends from the level of the soft palate down to the level of the upper of the epiglottis?
Which part of the pharynx extends from the level of the soft palate down to the level of the upper of the epiglottis?
What connects the oropharynx with the mouth cavity?
What connects the oropharynx with the mouth cavity?
Where are the valleculae located in the oropharynx?
Where are the valleculae located in the oropharynx?
What is responsible for the nerve supply of the palatine tonsil?
What is responsible for the nerve supply of the palatine tonsil?
Which component surrounds the openings into the digestive and respiratory tracts?
Which component surrounds the openings into the digestive and respiratory tracts?
What is the main function of laryngopharynx?
What is the main function of laryngopharynx?
Where do the veins of the pharynx collect into?
Where do the veins of the pharynx collect into?
Which nerve supplies the nasopharynx mainly?
Which nerve supplies the nasopharynx mainly?
Which nerve supplies the stylopharyngeus muscle?
Which nerve supplies the stylopharyngeus muscle?
What is the additional nerve supply for the cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor?
What is the additional nerve supply for the cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor?
Where does the lymph drainage from the pharynx go after retropharyngeal lymph nodes?
Where does the lymph drainage from the pharynx go after retropharyngeal lymph nodes?
What does not form the pharyngeal plexus?
What does not form the pharyngeal plexus?
Which muscle elevates the larynx and pharynx upwards in the second stage of swallowing?
Which muscle elevates the larynx and pharynx upwards in the second stage of swallowing?
Which muscle arises from the inferior border of the pharyngeal end of the cartilage of the auditory tube?
Which muscle arises from the inferior border of the pharyngeal end of the cartilage of the auditory tube?
What structure passes through a gap between the superior pharyngeal constrictor and the cranium?
What structure passes through a gap between the superior pharyngeal constrictor and the cranium?
Which muscle forms a continuous sling around the lower end of the pharynx?
Which muscle forms a continuous sling around the lower end of the pharynx?
What is the function of the cricopharyngeus muscle during swallowing?
What is the function of the cricopharyngeus muscle during swallowing?
What structure passes through a gap between the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictors?
What structure passes through a gap between the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictors?
From where does the middle constrictor arise?
From where does the middle constrictor arise?
Which structure is covered by a thin layer of fascia called the buccopharyngeal fascia?
Which structure is covered by a thin layer of fascia called the buccopharyngeal fascia?
What prevents suction of air into the esophagus during swallowing?
What prevents suction of air into the esophagus during swallowing?
What passes through a gap between the middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictors?
What passes through a gap between the middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictors?
What prevents herniation of pharyngeal mucous membrane through dehiscence of Killian during swallowing?
What prevents herniation of pharyngeal mucous membrane through dehiscence of Killian during swallowing?
What is the composition of the pharyngeal wall from inside to outside?
What is the composition of the pharyngeal wall from inside to outside?
Which part of the pharynx communicates with the laryngeal cavity?
Which part of the pharynx communicates with the laryngeal cavity?
What type of epithelium lines the nasopharynx?
What type of epithelium lines the nasopharynx?
Where does the oropharynx communicate with?
Where does the oropharynx communicate with?
What is the extent of the pharynx?
What is the extent of the pharynx?
Which nerve mainly supplies the nasopharynx?
Which nerve mainly supplies the nasopharynx?
Which artery supplies the dorsal lingual branches from the lingual artery?
Which artery supplies the dorsal lingual branches from the lingual artery?
Where do the veins of the pharynx collect before draining into the pharyngeal venous plexus?
Where do the veins of the pharynx collect before draining into the pharyngeal venous plexus?
Which nerve mainly forms the pharyngeal plexus?
Which nerve mainly forms the pharyngeal plexus?
What is the additional nerve supply for the cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor?
What is the additional nerve supply for the cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor?
Which nerve mainly provides sensory supply to the nasopharynx?
Which nerve mainly provides sensory supply to the nasopharynx?
Which muscle is NOT supplied by the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus?
Which muscle is NOT supplied by the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus?
What is responsible for supplying the greater palatine and pharyngeal arteries of the maxillary artery?
What is responsible for supplying the greater palatine and pharyngeal arteries of the maxillary artery?
Where do the lymph drainage from the retropharyngeal lymph nodes go next?
Where do the lymph drainage from the retropharyngeal lymph nodes go next?
What prevents suction of air into the esophagus during swallowing?
What prevents suction of air into the esophagus during swallowing?
Which nerve mainly supplies the nasopharynx?
Which nerve mainly supplies the nasopharynx?
What covers the external aspect of the pharynx?
What covers the external aspect of the pharynx?
What is the main function of laryngopharynx?
What is the main function of laryngopharynx?
What is responsible for the nerve supply of the palatine tonsil?
What is responsible for the nerve supply of the palatine tonsil?
What forms the tonsillar hemi capsule at oropharynx?
What forms the tonsillar hemi capsule at oropharynx?
Which muscle elevates the larynx and pharynx upwards in the second stage of swallowing?
Which muscle elevates the larynx and pharynx upwards in the second stage of swallowing?
What structure connects the nasopharynx with the nasal cavities?
What structure connects the nasopharynx with the nasal cavities?
What does the nasopharynx communicate with laterally?
What does the nasopharynx communicate with laterally?
Which structure is responsible for keeping the nasopharynx permanently opened for free breathing?
Which structure is responsible for keeping the nasopharynx permanently opened for free breathing?
What is the function of the salpingopharyngeus muscle in the nasopharynx?
What is the function of the salpingopharyngeus muscle in the nasopharynx?
Where is the adenoid face located?
Where is the adenoid face located?
What structure is usually enlarged in children and obstructs the nasopharynx, causing difficult nasal breathing?
What structure is usually enlarged in children and obstructs the nasopharynx, causing difficult nasal breathing?
Which muscle overlies the torus levatorius in the nasopharynx?
Which muscle overlies the torus levatorius in the nasopharynx?
Where are the valleculae located in the oropharynx?
Where are the valleculae located in the oropharynx?
Which structure is related to the median glosso-epiglottic fold and lateral glosso-epiglottic folds in the oropharynx?
Which structure is related to the median glosso-epiglottic fold and lateral glosso-epiglottic folds in the oropharynx?
Which artery mainly supplies the palatine tonsil?
Which artery mainly supplies the palatine tonsil?
What is a common site of foreign body location in the laryngopharynx?
What is a common site of foreign body location in the laryngopharynx?
The pharynx extends from the base of the skull down to the 7th cervical vertebra.
The pharynx extends from the base of the skull down to the 7th cervical vertebra.
The oropharynx is lined with respiratory epithelium.
The oropharynx is lined with respiratory epithelium.
The nasopharynx communicates with the laryngeal cavity through the inlet of the larynx.
The nasopharynx communicates with the laryngeal cavity through the inlet of the larynx.
The fibrous layer of the pharyngeal wall is called the pharyngeal basilar fascia.
The fibrous layer of the pharyngeal wall is called the pharyngeal basilar fascia.
The laryngeopharynx is the widest part of the pharynx.
The laryngeopharynx is the widest part of the pharynx.
The buccopharyngeal fascia covers the internal aspect of the pharynx.
The buccopharyngeal fascia covers the internal aspect of the pharynx.
The nasopharynx communicates with the oropharynx through the pharyngeal isthmus.
The nasopharynx communicates with the oropharynx through the pharyngeal isthmus.
The tubal elevation in the nasopharynx is produced by the cartilage of the auditory tube.
The tubal elevation in the nasopharynx is produced by the cartilage of the auditory tube.
The tonsillar hemicapsule is an extension from the pharyngeobasilar fascia and is related to the lateral surface of the palatine tonsil.
The tonsillar hemicapsule is an extension from the pharyngeobasilar fascia and is related to the lateral surface of the palatine tonsil.
The tonsil is mainly supplied by the descending palatine artery and dorsal lingual branch of the lingual artery.
The tonsil is mainly supplied by the descending palatine artery and dorsal lingual branch of the lingual artery.
The piriform fossa is bound laterally by the thyroid cartilage and thyrohyoid membrane.
The piriform fossa is bound laterally by the thyroid cartilage and thyrohyoid membrane.
The Waldeyer's Ring of lymphoid tissue has no afferent lymph vessels.
The Waldeyer's Ring of lymphoid tissue has no afferent lymph vessels.
The laryngopharynx communicates with the esophagus inferiorly and with the larynx via the laryngeal inlet anteroinferiorly.
The laryngopharynx communicates with the esophagus inferiorly and with the larynx via the laryngeal inlet anteroinferiorly.
The piriform fossa is a common site of foreign body location and is bound laterally by the thyroid cartilage and epiglottis.
The piriform fossa is a common site of foreign body location and is bound laterally by the thyroid cartilage and epiglottis.
The pharyngobasilar fascia attaches below to the petrous temporal bone and medial to the carotid canal.
The pharyngobasilar fascia attaches below to the petrous temporal bone and medial to the carotid canal.
The median glosso-epiglottic fold connects the back of the tongue to the front of the epiglottis.
The median glosso-epiglottic fold connects the back of the tongue to the front of the epiglottis.
The tonsillar crypts are present on the lateral surface of the palatine tonsil, leading to deep recesses.
The tonsillar crypts are present on the lateral surface of the palatine tonsil, leading to deep recesses.
The tubal tonsil is a collection of lymphoid tissue around the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube.
The tubal tonsil is a collection of lymphoid tissue around the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube.
The pterygomandibular raphe diminishes in thickness to form the tonsillar hemi capsule at the oropharynx.
The pterygomandibular raphe diminishes in thickness to form the tonsillar hemi capsule at the oropharynx.
The pharyngeal raphe strengthens the posterior border of the medial pterygoid plate.
The pharyngeal raphe strengthens the posterior border of the medial pterygoid plate.
The superior constrictor arises from the greater and lesser horns of the hyoid bone.
The superior constrictor arises from the greater and lesser horns of the hyoid bone.
The middle constrictor has two functional parts, thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus.
The middle constrictor has two functional parts, thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus.
The palatopharyngeus muscle descends in the salpingopharyngeal fold to join the stylopharyngeus muscle.
The palatopharyngeus muscle descends in the salpingopharyngeal fold to join the stylopharyngeus muscle.
The buccopharyngeal fascia covers the internal surface of the pharyngeal constrictors.
The buccopharyngeal fascia covers the internal surface of the pharyngeal constrictors.
During swallowing, the cricopharyngeus muscle acts as a sphincter at the upper end of the pharynx.
During swallowing, the cricopharyngeus muscle acts as a sphincter at the upper end of the pharynx.
Gaps between pharyngeal constrictor muscles leave four openings for structures to enter or leave the pharynx.
Gaps between pharyngeal constrictor muscles leave four openings for structures to enter or leave the pharynx.
The levator veli palatini passes through a gap between the middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictors.
The levator veli palatini passes through a gap between the middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictors.
All three longitudinal muscles insert into the posterior border of the thyroid cartilage.
All three longitudinal muscles insert into the posterior border of the thyroid cartilage.
The pharynx widens and shortens to receive the food bolus during stage 1 of deglutition.
The pharynx widens and shortens to receive the food bolus during stage 1 of deglutition.
Solid food is masticated and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow during stage 1 of deglutition.
Solid food is masticated and mixed with saliva to form a soft bolus that is easier to swallow during stage 1 of deglutition.
The ascending pharyngeal artery is a branch of the external carotid artery.
The ascending pharyngeal artery is a branch of the external carotid artery.
The veins of the pharynx collect into the pharyngeal venous plexus internal to the superior constrictor.
The veins of the pharynx collect into the pharyngeal venous plexus internal to the superior constrictor.
The nasopharynx is mainly supplied by the pharyngeal branch from the pterygo-palatine ganglion, which is a branch of the maxillary nerve.
The nasopharynx is mainly supplied by the pharyngeal branch from the pterygo-palatine ganglion, which is a branch of the maxillary nerve.
The glossopharyngeal nerve mainly supplies the oropharynx and laryngopharynx.
The glossopharyngeal nerve mainly supplies the oropharynx and laryngopharynx.
The cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor has additional nerve supply from the recurrent and internal laryngeal nerves.
The cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor has additional nerve supply from the recurrent and internal laryngeal nerves.
The sensory nerve supply of the nasopharynx is mainly by the glossopharyngeal nerve through the pharyngeal plexus.
The sensory nerve supply of the nasopharynx is mainly by the glossopharyngeal nerve through the pharyngeal plexus.
All the constrictors and longitudinal muscles of the pharynx are supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve through the pharyngeal plexus.
All the constrictors and longitudinal muscles of the pharynx are supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve through the pharyngeal plexus.
The ventral lingual branches are supplied by the lingual artery.
The ventral lingual branches are supplied by the lingual artery.
The lymph drainage from the pharynx goes directly into the deep cervical lymph nodes.
The lymph drainage from the pharynx goes directly into the deep cervical lymph nodes.
The motor nerve supply of all the constrictors and longitudinal muscles of the pharynx is provided by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
The motor nerve supply of all the constrictors and longitudinal muscles of the pharynx is provided by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
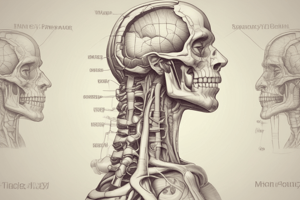
Pharynx
- The pharynx extends from the base of the skull down to the 7th cervical vertebra.
- The pharynx is divided into three parts: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
Nasopharynx
- The nasopharynx extends from the base of the skull down to the level of the soft palate.
- The nasopharynx communicates with the nasal cavities through the choanae.
- The nasopharynx is lined with respiratory epithelium.
- The nasopharynx is mainly supplied by the pharyngeal branch from the pterygo-palatine ganglion, which is a branch of the maxillary nerve.
- The salpingopharyngeus muscle helps to keep the nasopharynx permanently opened for free breathing.
- The tubal elevation in the nasopharynx is produced by the cartilage of the auditory tube.
- The adenoid face is located in the nasopharynx.
- The nasopharynx is usually enlarged in children and obstructs the nasopharynx, causing difficult nasal breathing.
Oropharynx
- The oropharynx extends from the level of the soft palate down to the level of the upper border of the epiglottis.
- The oropharynx communicates with the mouth cavity through the oropharyngeal isthmus.
- The oropharynx is lined with respiratory epithelium.
- The valleculae are located in the oropharynx.
- The glossopharyngeal nerve mainly supplies the oropharynx.
Laryngopharynx
- The laryngopharynx is the widest part of the pharynx.
- The laryngopharynx communicates with the esophagus inferiorly and with the larynx via the laryngeal inlet anteroinferiorly.
- The laryngopharynx is lined with respiratory epithelium.
- The laryngopharynx is mainly supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Pharyngeal Constrictors
- The pharyngeal constrictors are divided into three parts: superior, middle, and inferior constrictors.
- The superior constrictor arises from the medial pterygoid plate and pterygoid hamulus.
- The middle constrictor arises from the inferior border of the hyoid bone.
- The inferior constrictor has two functional parts, thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus.
- The cricopharyngeus muscle acts as a sphincter at the upper end of the pharynx during swallowing.
- The buccopharyngeal fascia covers the internal surface of the pharyngeal constrictors.
Nerve Supply
- The pharynx is supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, and maxillary nerve.
- The pharyngeal plexus is formed by the glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, and maxillary nerve.
- The recurrent and internal laryngeal nerves provide additional nerve supply to the cricopharyngeus part of the inferior constrictor.
Blood Supply
- The pharynx is supplied by the ascending pharyngeal artery, a branch of the external carotid artery.
- The palatine tonsil is mainly supplied by the descending palatine artery and dorsal lingual branch of the lingual artery.
Lymphatic Drainage
- The lymph drainage from the pharynx goes to the retropharyngeal lymph nodes.
- The lymph drainage from the retropharyngeal lymph nodes goes to the cervical lymph nodes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.