Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the approximate weight of the parotid gland?
What is the approximate weight of the parotid gland?
- 25 g (correct)
- 30 g
- 35 g
- 15 g
Which nerve supplies the skin over the parotid gland?
Which nerve supplies the skin over the parotid gland?
- Trigeminal nerve
- Great auricular nerve (correct)
- Facial nerve
- Lingual nerve
What forms the capsule of the parotid gland?
What forms the capsule of the parotid gland?
- The deep lamina of the deep cervical fascia
- The investing layer of the deep cervical fascia (correct)
- The parotidomasseteric fascia
- The superficial lamina of the deep cervical fascia
What is the characteristic of parotid swellings?
What is the characteristic of parotid swellings?
Which disease is caused by a specific virus and affects the salivary glands?
Which disease is caused by a specific virus and affects the salivary glands?
What is the characteristic of viral parotitis or mumps?
What is the characteristic of viral parotitis or mumps?
What is the shape of the parotid gland?
What is the shape of the parotid gland?
What is the direction of the apex of the parotid gland?
What is the direction of the apex of the parotid gland?
What structure does the apex of the parotid gland overlap?
What structure does the apex of the parotid gland overlap?
Which nerve is related to the superior surface of the parotid gland?
Which nerve is related to the superior surface of the parotid gland?
What structure is the anteromedial surface of the parotid gland grooved by?
What structure is the anteromedial surface of the parotid gland grooved by?
What is the posteromedial surface of the parotid gland related to?
What is the posteromedial surface of the parotid gland related to?
Which structure is not covered by the superficial surface of the parotid gland?
Which structure is not covered by the superficial surface of the parotid gland?
What is the relation of the internal carotid artery to the styloid process?
What is the relation of the internal carotid artery to the styloid process?
What emerges from the apex of the parotid gland?
What emerges from the apex of the parotid gland?
What is the relation of the parotid fascia to the parotid gland?
What is the relation of the parotid fascia to the parotid gland?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
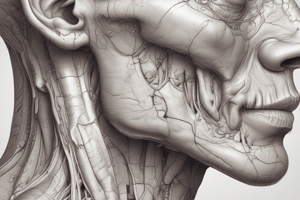
Parotid Gland Anatomy
- The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands, weighing approximately 25 grams.
- It is situated below the external acoustic meatus, between the ramus of the mandible and the sternocleidomastoid.
- The gland overlaps the ramus of the mandible, sternocleidomastoid, and masseter muscle.
Capsule of Parotid Gland
- The investing layer of the deep cervical fascia forms a capsule for the gland.
- The capsule is supplied by the great auricular nerve.
- The fascia splits between the angle of the mandible and the mastoid process to enclose the gland.
- The stylomandibular ligament separates the parotid gland from the submandibular salivary gland.
Clinical Anatomy
- Parotid swellings are very painful due to the unyielding nature of the parotid fascia.
- Mumps is an infectious disease of the salivary glands, usually the parotid, caused by a specific virus.
- Viral parotitis or mumps does not suppurate and its complications are orchitis and pancreatitis.
External Features
- The gland resembles a three-sided pyramid with its apex directed downwards.
- The gland has four surfaces: superior (base of the pyramid), superficial, anteromedial, and posteromedial.
- The surfaces are separated by three borders: anterior, posterior, and medial/pharyngeal edge.
Relations
- The apex of the gland overlaps the posterior belly of the digastric and the adjoining part of the carotid triangle.
- The cervical branch of the facial nerve and the two divisions of the retromandibular vein emerge near the apex.
- The superior surface is related to the cartilaginous part of the external acoustic meatus, posterior surface of the temporomandibular joint, superficial temporal vessels, and auriculotemporal nerve.
- The superficial surface is covered with skin, superficial fascia, parotid fascia, and deep parotid lymph nodes.
- The anteromedial surface is grooved by the posterior border of the ramus of the mandible and related to the masseter, lateral surface of the temporomandibular joint, posterior border of the ramus of the mandible, medial pterygoid, and emerging branches of the facial nerve.
- The posteromedial surface is moulded to the mastoid and styloid processes and related to the mastoid process, sternocleidomastoid, posterior belly of the digastric, styloid process, external carotid artery, and facial nerve.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.