Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of Morison's Pouch?
What is the main function of Morison's Pouch?
- It is a space where most of the liver's blood supply originates.
- It is a space that separates the liver from the stomach.
- It is a potential space between the liver and left kidney.
- It is a potential space between the liver and right kidney that can fill with blood or fluid. (correct)
How much of the total cardiac output does the liver receive?
How much of the total cardiac output does the liver receive?
- 5%
- 27% (correct)
- 15%
- 35%
Which blood vessel supplies 75% of the liver's blood supply?
Which blood vessel supplies 75% of the liver's blood supply?
- Hepatic portal vein (correct)
- Celiac trunk
- Splenic vein
- Hepatic artery
What happens during the Hepatic Arterial Buffer Response?
What happens during the Hepatic Arterial Buffer Response?
Which vessel contains all absorbed substances from the intestines except chylomicrons?
Which vessel contains all absorbed substances from the intestines except chylomicrons?
What percentage of the liver's oxygen supply comes from the hepatic artery?
What percentage of the liver's oxygen supply comes from the hepatic artery?
What is the function of bile in the digestive system?
What is the function of bile in the digestive system?
Where are bile canaliculi found?
Where are bile canaliculi found?
What is the role of cystic duct in the digestion process?
What is the role of cystic duct in the digestion process?
What is the significance of enterohepatic circulation?
What is the significance of enterohepatic circulation?
How do bile-binding resins like cholestyramine affect high blood cholesterol?
How do bile-binding resins like cholestyramine affect high blood cholesterol?
What happens if bile is excluded from the small intestine?
What happens if bile is excluded from the small intestine?
What is the primary source of new bile acids in the body?
What is the primary source of new bile acids in the body?
Which organelle is involved in the synthesis of new bile acids in the liver?
Which organelle is involved in the synthesis of new bile acids in the liver?
Why does an increase in cholesterol supply benefit hepatic synthesis of new bile acids?
Why does an increase in cholesterol supply benefit hepatic synthesis of new bile acids?
What effect does lesion or starvation have on protein synthesis in the liver cells?
What effect does lesion or starvation have on protein synthesis in the liver cells?
In which organelle does glycogen degradation occur in liver cells?
In which organelle does glycogen degradation occur in liver cells?
What is the method by which new bile acids are synthesized within liver cells?
What is the method by which new bile acids are synthesized within liver cells?
What is the primary consequence of advanced liver disease on the circulation?
What is the primary consequence of advanced liver disease on the circulation?
Which condition can result from abnormal intrapulmonary vasodilation in hepatopulmonary syndrome?
Which condition can result from abnormal intrapulmonary vasodilation in hepatopulmonary syndrome?
What is a common outcome of renal hypoperfusion in liver disease?
What is a common outcome of renal hypoperfusion in liver disease?
Which factor may contribute to excessive bleeding in chronic liver disease?
Which factor may contribute to excessive bleeding in chronic liver disease?
Which tests are classified under tests of hepatic synthesis?
Which tests are classified under tests of hepatic synthesis?
What is the primary function of transaminases in the liver?
What is the primary function of transaminases in the liver?
Which condition may reflect disruption of hepatic urea synthesis?
Which condition may reflect disruption of hepatic urea synthesis?
A patient with advanced liver disease is found to have increased sensitivity to highly protein-bound drugs. Which physiological factor contributes to this phenomenon?
A patient with advanced liver disease is found to have increased sensitivity to highly protein-bound drugs. Which physiological factor contributes to this phenomenon?
How does liver disease impact the response to inotropes and vasopressors during anesthesia?
How does liver disease impact the response to inotropes and vasopressors during anesthesia?
What should be considered when administering Tylenol to a patient with liver disease?
What should be considered when administering Tylenol to a patient with liver disease?
What innervates the liver and affects its blood reservoir capacity?
What innervates the liver and affects its blood reservoir capacity?
Which receptors are present in the hepatic arteries?
Which receptors are present in the hepatic arteries?
What is the pressure in the hepatic vein leading into the vena cava?
What is the pressure in the hepatic vein leading into the vena cava?
What is a common cause of cirrhosis besides chronic alcohol abuse?
What is a common cause of cirrhosis besides chronic alcohol abuse?
What are the clinical consequences of portal hypertension?
What are the clinical consequences of portal hypertension?
Where might portosystemic shunts form?
Where might portosystemic shunts form?
What is the primary cause of portal hypertension?
What is the primary cause of portal hypertension?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Liver Structure and Function
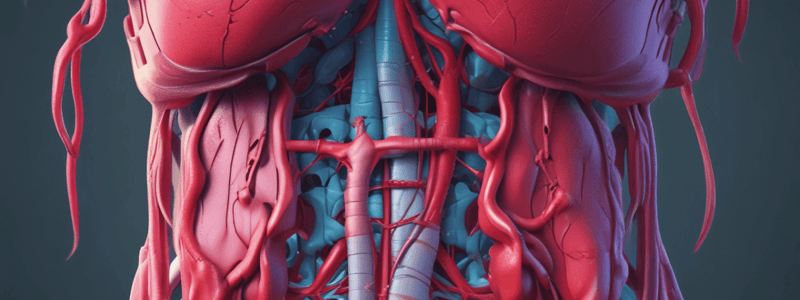
- The liver has a dual vascular supply, receiving 27% of total cardiac output, with high blood flow and low vascular resistance.
- The liver has a dual blood supply:
- Hepatic artery (300 ml/min): 25% of blood supply, mostly stromal, 50% oxygen supply, autoregulates.
- Hepatic portal vein (1050 ml/min): 75% of blood supply, mostly parenchymal, 50% oxygen supply, does not autoregulate.
Bile and Gallbladder
- Bile consists of organic molecules in an alkaline solution, produced by the liver, stored and concentrated in the gallbladder.
- Bile has three functions:
- Assimilation of dietary lipid.
- Excretion of hydrophobic molecules.
- Neutralization of gastric acid.
- Hepatocytes secrete bile into the canaliculi, which coalesce into hepatic ducts prior to the common hepatic duct.
- The cystic duct transmits bile to the gallbladder, where it is concentrated, with a volume of 20-50 ml.
Bile Acid Pool
- Bile acids undergo enterohepatic circulation multiple times per meal/day.
- The pool is insufficient to digest lipids and requires recycling.
- Enterohepatic circulation can be intentionally disrupted as a treatment for high blood cholesterol by ingesting bile-binding resins.
Liver's Location and Movement
- The liver's location, extent, and range of movements are demonstrated.
- Morison's Pouch is a potential space between the liver and right kidney, which can fill with blood or fluid.
Hepatic Synthesis and Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
- Hepatic synthesis of new bile acids requires an increased supply of cholesterol.
- The liver has an intrinsic mechanism to compensate for decreased portal venous flow.
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome is characterized by:
- Restriction-decreased compliance and atelectasis.
- Respiratory alkalosis-compensatory hyperventilation.
- Abnormal intrapulmonary vasodilation-congestion.
Pathophysiologic Consequences of Liver Disease
- Hyperdynamic circulation: low systemic vascular resistance, low blood pressure, increased cardiac output.
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome: restriction, respiratory alkalosis, abnormal intrapulmonary vasodilation.
- Renal hypoperfusion: decreased glomerular filtration rate, increased RAAS, sodium and water retention.
- Hematologic perturbations: decreased clotting factor production, prolonged prothrombin time, increased risk of bleeding.
Liver Function Tests
- Liver function tests can be classified into two categories:
- Hepatocellular damage (AST, ALT).
- Hepatic synthetic function (cholesterol, pseudocholinesterase, PT).
- Liver abnormalities can be divided into two classes based on lab tests:
- Parenchymal disorders (fibrosis, cirrhosis).
- Mechanical biliary obstructive disorders (hepatocellular damage).
Anesthesia Considerations
- Suspect a relative hypovolemia and portal hypertension.
- Assess for high cardiac output and low peripheral vascular resistance.
- May have increased sensitivity to highly protein-bound drugs.
- Lower plasma proteins may affect volume of distribution.
- Suspect esophageal varices, anticipate depressed response to inotropes and vasopressors.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.