Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the thyrocervical trunk in the blood supply to the head?
What is the primary role of the thyrocervical trunk in the blood supply to the head?
- Supplies the face
- Supplies the head
- Supplies the brain
- Supplies the neck (correct)
What is the benefit of the overlap in the arterial blood supply to the head?
What is the benefit of the overlap in the arterial blood supply to the head?
- Decreased oxygenation
- Increased blood pressure
- Collateral blood flow to all areas (correct)
- Reduced blood flow
Which of the following arteries is NOT a primary source of blood supply to the head?
Which of the following arteries is NOT a primary source of blood supply to the head?
- External carotid
- Internal carotid
- Vertebral
- Aorta (correct)
What is the total number of main arteries that supply the head?
What is the total number of main arteries that supply the head?
Which artery is responsible for supplying the brain?
Which artery is responsible for supplying the brain?
What is the term for the connection between different blood vessels that allows for blood flow to continue even if one vessel is compromised?
What is the term for the connection between different blood vessels that allows for blood flow to continue even if one vessel is compromised?
What is the route of the vertebral artery into the skull?
What is the route of the vertebral artery into the skull?
What is the function of the circle of Willis?
What is the function of the circle of Willis?
What is the origin of the vertebral artery?
What is the origin of the vertebral artery?
What is the destination of the merged vertebral arteries?
What is the destination of the merged vertebral arteries?
What is the origin of the thyrocervical trunk?
What is the origin of the thyrocervical trunk?
What are the branches of the thyrocervical trunk?
What are the branches of the thyrocervical trunk?
What is the primary function of the internal carotid artery?
What is the primary function of the internal carotid artery?
Which artery arises from just below the hyoid and descends to supply the thyroid gland?
Which artery arises from just below the hyoid and descends to supply the thyroid gland?
Which two arteries arise from the first part of the subclavian artery?
Which two arteries arise from the first part of the subclavian artery?
What is the destination of the maxillary artery after it runs deep to the zygomatic arch?
What is the destination of the maxillary artery after it runs deep to the zygomatic arch?
What is the path taken by the internal carotid artery to supply the brain?
What is the path taken by the internal carotid artery to supply the brain?
What is the relationship between the branches of the external carotid artery?
What is the relationship between the branches of the external carotid artery?
Which artery runs superiorly to supply the inferior aspect of the thyroid gland?
Which artery runs superiorly to supply the inferior aspect of the thyroid gland?
What is the final destination of the blood drained from the brain tissues?
What is the final destination of the blood drained from the brain tissues?
Which structure does the suprascapular artery pass behind?
Which structure does the suprascapular artery pass behind?
What is the name of the vein that drains the brain tissues into vessels close to the surface?
What is the name of the vein that drains the brain tissues into vessels close to the surface?
What is the name of the sinus that exits through the jugular foramen?
What is the name of the sinus that exits through the jugular foramen?
What is the name of the artery that ascends between the anterior scalene and longus capitis?
What is the name of the artery that ascends between the anterior scalene and longus capitis?
What is the primary route of venous drainage for the anterior aspect of the face?
What is the primary route of venous drainage for the anterior aspect of the face?
What is the final destination of the venous blood from the head, neck, and brain?
What is the final destination of the venous blood from the head, neck, and brain?
Which of the following veins is responsible for draining the brain?
Which of the following veins is responsible for draining the brain?
What is the relationship between the internal and external jugular veins?
What is the relationship between the internal and external jugular veins?
What is the unique feature of the brachiocephalic veins compared to the brachiocephalic arteries?
What is the unique feature of the brachiocephalic veins compared to the brachiocephalic arteries?
Which artery arises from the external carotid artery and supplies the thyroid gland?
Which artery arises from the external carotid artery and supplies the thyroid gland?
Which arteries arise from the first part of the subclavian artery?
Which arteries arise from the first part of the subclavian artery?
Which artery travels through the carotid canal at the base of the skull?
Which artery travels through the carotid canal at the base of the skull?
Which artery supplies the eyes, upper nose, and forehead?
Which artery supplies the eyes, upper nose, and forehead?
Which part of the subclavian artery gives rise to the vertebral and thyrocervical arteries?
Which part of the subclavian artery gives rise to the vertebral and thyrocervical arteries?
Which artery runs deep to the zygomatic arch before branching to provide blood to the deep structures of the face?
Which artery runs deep to the zygomatic arch before branching to provide blood to the deep structures of the face?
What is the significance of the vertebral artery entering the skull through the foramen magnum?
What is the significance of the vertebral artery entering the skull through the foramen magnum?
Which of the following arteries is NOT a branch of the subclavian artery?
Which of the following arteries is NOT a branch of the subclavian artery?
What is the primary function of the internal carotid artery in relation to the circle of Willis?
What is the primary function of the internal carotid artery in relation to the circle of Willis?
What is the relationship between the vertebral arteries and the basilar artery?
What is the relationship between the vertebral arteries and the basilar artery?
Which of the following arteries provides small spinal arteries to surrounding structures?
Which of the following arteries provides small spinal arteries to surrounding structures?
What is the significance of the overlap in the arterial blood supply to the brain?
What is the significance of the overlap in the arterial blood supply to the brain?
Which artery arises directly from the aorta on the left side?
Which artery arises directly from the aorta on the left side?
What is the name of the common branch that gives rise to the common carotid and subclavian arteries on the right side?
What is the name of the common branch that gives rise to the common carotid and subclavian arteries on the right side?
What is the destination of the blood supplied by the external carotid artery?
What is the destination of the blood supplied by the external carotid artery?
Which artery is responsible for supplying the arm?
Which artery is responsible for supplying the arm?
What is the name of the branch that arises from the common carotid artery and supplies the thyroid gland?
What is the name of the branch that arises from the common carotid artery and supplies the thyroid gland?
What is the significance of the brachiocephalic trunk?
What is the significance of the brachiocephalic trunk?
What is the position of the apex of the heart in relation to the body?
What is the position of the apex of the heart in relation to the body?
What is the function of the fibrous pericardium?
What is the function of the fibrous pericardium?
What is the name of the valve that separates the right atrium and ventricle?
What is the name of the valve that separates the right atrium and ventricle?
What is the purpose of the chordae tendineae in the heart?
What is the purpose of the chordae tendineae in the heart?
What is the embryonic remnant that connects the pulmonary trunk and aortic arch in fetal development?
What is the embryonic remnant that connects the pulmonary trunk and aortic arch in fetal development?
What is the name of the artery that supplies the sinoatrial (SA) node?
What is the name of the artery that supplies the sinoatrial (SA) node?
What is the orientation of the heart in the thoracic cavity?
What is the orientation of the heart in the thoracic cavity?
What is the function of the papillary muscles in the heart?
What is the function of the papillary muscles in the heart?
What is the name of the depression in the right atrium that is a remnant of the fetal foramen ovale?
What is the name of the depression in the right atrium that is a remnant of the fetal foramen ovale?
What is the purpose of the semilunar valves in the heart?
What is the purpose of the semilunar valves in the heart?
What is the main function of the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
What is the main function of the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
Which branch of the left coronary artery runs in parallel with the left anterior descending artery?
Which branch of the left coronary artery runs in parallel with the left anterior descending artery?
What is the function of the SA node?
What is the function of the SA node?
Which nerve runs behind the root of the lung and has a branch called the left recurrent laryngeal?
Which nerve runs behind the root of the lung and has a branch called the left recurrent laryngeal?
What is the effect of the sympathetic nervous system on heart rate?
What is the effect of the sympathetic nervous system on heart rate?
Which vessel is the largest in the coronary system?
Which vessel is the largest in the coronary system?
What is the function of the AV node?
What is the function of the AV node?
Which of the following is NOT a branch of the arch of the aorta?
Which of the following is NOT a branch of the arch of the aorta?
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system on heart rate?
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system on heart rate?
Which vessel returns deoxygenated blood from the heart, neck, upper limb, and thoracic wall to the heart?
Which vessel returns deoxygenated blood from the heart, neck, upper limb, and thoracic wall to the heart?
What is the name of the large vessel that runs posterior to the diaphragmatic surface between the atria and ventricles?
What is the name of the large vessel that runs posterior to the diaphragmatic surface between the atria and ventricles?
Which nerve runs in front of the root of the lung in close relation to the fibrous pericardium?
Which nerve runs in front of the root of the lung in close relation to the fibrous pericardium?
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton in the heart?
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton in the heart?
Which branch of the vagus nerve scoops underneath the arch of the aorta?
Which branch of the vagus nerve scoops underneath the arch of the aorta?
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart rate?
What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on the heart rate?
What is the name of the artery that runs in parallel to the posterior interventricular artery?
What is the name of the artery that runs in parallel to the posterior interventricular artery?
Which vein drains the brain tissues into vessels close to the surface?
Which vein drains the brain tissues into vessels close to the surface?
What is the route of the blood flow from the abdomen and lower limbs back to the heart?
What is the route of the blood flow from the abdomen and lower limbs back to the heart?
Which part of the autonomic nervous system increases the heart rate and contractility?
Which part of the autonomic nervous system increases the heart rate and contractility?
What is the name of the artery that arises from the left coronary artery and supplies the lateral aspect of the left ventricle?
What is the name of the artery that arises from the left coronary artery and supplies the lateral aspect of the left ventricle?
What is the main function of the pericardium?
What is the main function of the pericardium?
Which valve is responsible for preventing back-flow from the left ventricle into the left atrium?
Which valve is responsible for preventing back-flow from the left ventricle into the left atrium?
What is the name of the surface of the heart that faces the lungs?
What is the name of the surface of the heart that faces the lungs?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the pericardium?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the pericardium?
What is the name of the valve that separates the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk?
What is the name of the valve that separates the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk?
Where is the apex of the heart located?
Where is the apex of the heart located?
What is the name of the embryonic remnant that connects the pulmonary trunk and aortic arch?
What is the name of the embryonic remnant that connects the pulmonary trunk and aortic arch?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the atrioventricular valves?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the atrioventricular valves?
What is the name of the muscles that contribute to atrial contraction?
What is the name of the muscles that contribute to atrial contraction?
What is the name of the artery that supplies the sinoatrial (SA) node?
What is the name of the artery that supplies the sinoatrial (SA) node?
Flashcards
Heart location
Heart location
The heart is centrally located in the mediastinum, resting on the diaphragm, with the apex angled to the left.
Heart shape
Heart shape
The heart is a tipped pyramid, with the largest part of the left ventricle forming the diaphragmatic surface.
Pericardium layers
Pericardium layers
The pericardium surrounding the heart has three layers: fibrous, parietal, and visceral (epicardium).
Heart's double pump
Heart's double pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood flow (RA)
Blood flow (RA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood flow (RV)
Blood flow (RV)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood flow (lungs)
Blood flow (lungs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood flow (LA)
Blood flow (LA)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood flow (LV)
Blood flow (LV)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood flow (aorta)
Blood flow (aorta)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart valves function
Heart valves function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart sounds
Heart sounds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right atrium features
Right atrium features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right ventricle features
Right ventricle features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left atrium features
Left atrium features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left ventricle features
Left ventricle features
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foramen ovale
Foramen ovale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coronary arteries
Coronary arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Skeleton
Cardiac Skeleton
Signup and view all the flashcards
SA node
SA node
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autonomic regulation
Autonomic regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiovascular system
Cardiovascular system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries vs Veins
Arteries vs Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Branches Subclavian
Branches Subclavian
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Heart Structure and Function
- The heart is located in the middle mediastinum, central to the pleural cavities, and sits on the diaphragm.
- The apex of the heart is displaced to the left, in the 5th intercostal space in the mid-clavicular line.
- The heart has a tipped pyramid shape, with the diaphragmatic surface being the largest part of the LV.
- The anterior surface is the RV, and the pulmonary surfaces face the lungs.
Pericardium
- The heart is surrounded by the pericardium, which is a serous pericardium.
- The pericardium has three layers: parietal, visceral (epicardium), and fibrous pericardium.
- The fibrous pericardium is a strong, fibrous layer of connective tissue that attaches to the diaphragm and sternum.
Blood Flow Through the Heart
- The heart has a double pump, with oxygenated blood on the left and deoxygenated blood on the right.
- Deoxygenated blood enters the RA from the superior and inferior vena cava and coronary sinus.
- Blood flows through the tricuspid valve into the RV, then through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary trunk.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs through the pulmonary veins into the LA, then through the mitral valve into the LV.
- The LV contracts, pumping blood through the aortic valve and into the aorta for distribution to the body.
Heart Valves
- The heart has four valves: tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic.
- The atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) have flexible leaflets, while the semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic) are firmly closed during ventricular relaxation.
- The valves prevent backflow and ensure blood flows in the correct direction.
Heart Sounds
- Heart valves closing produce the "lub-dub" sounds.
- The sounds can be heard at different points on the chest, depending on the valve.
Right Atrium and Ventricle
- The right atrium has an auricle/appendage, pectinate muscles, and a fossa ovalis.
- The right ventricle has an AV orifice, AV valve, IV septum, chordae tendineae, and papillary muscles.
Left Atrium and Ventricle
- The left atrium has an auricle/appendage, pectinate muscles, and a fossa ovalis.
- The left ventricle has chordae tendineae, papillary muscles, trabeculae carnae, and an aortic valve.
Embryonic Remnants
- The foramen ovale is a remnant of fetal development, allowing blood to flow between the RA and LA.
- The ductus arteriosus is another remnant, allowing blood to flow between the pulmonary trunk and arch of the aorta.
Coronary Arteries
- The coronary arteries supply blood to the heart, arising from the aortic sinuses.
- They fill during ventricular diastole, when the valve is closed, and do not fill during ventricular systole.
- The arrangement of the coronary arteries is highly variable, and they are functional end arteries.
Cardiac Skeleton
- The cardiac skeleton is a connective tissue that anchors the valve cusps, prevents over-dilation of the valve openings, and provides a point of insertion for heart muscle bundles.
- It also provides electrical insulation.
Conducting System
- The SA node is the natural pacemaker, releasing electrical stimuli at a regular rate.
- The stimuli propagate through the atria to the AV node, then to the ventricles through the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers.
Autonomic Regulation of the Heart
- The heart rate is regulated by the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
- The parasympathetic nervous system slows the heart rate, while the sympathetic nervous system increases the heart rate and contractility.
The Cardiovascular System
- The cardiovascular system encompasses the heart, capillaries, arteries, and veins.
- The circulatory system includes the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system.
Arteries and Veins
-
Arteries are thicker and hold their structure, while veins are thinner and can collapse.
-
The cardiovascular system includes large elastic conducting arteries, which branch into smaller arteries and arterioles.### Arteries of the Head and Neck
-
Most branches supplying the head and neck are branches of the first part of the subclavian artery.
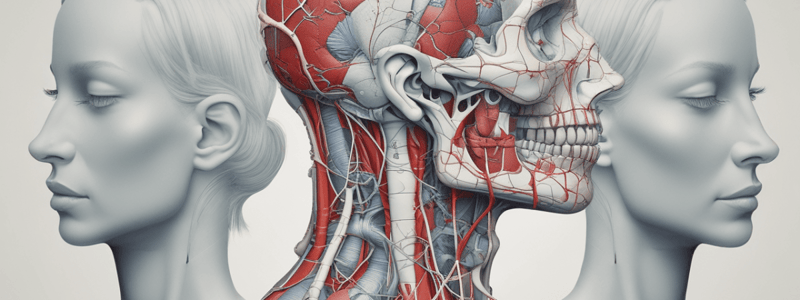
Vertebral Artery
- The vertebral artery originates from the subclavian and proceeds superiorly within the vertebrae, providing small spinal arteries to supply surrounding structures.
- The vertebral artery then enters the skull through the foramen magnum.
Vertebral and Internal Carotid
- Both vertebral arteries merge to form the basilar artery.
- The basilar and internal carotids are the greatest contributors of blood to the brain, forming part of the circle of Willis, a redundancy system of vessels that ensures adequate blood supply to the brain.
Thyrocervical Trunk
- The thyrocervical trunk originates from the subclavian and branches into supplying the thyroid gland and muscles of the neck, including:
- Inferior thyroid artery
- Ascending cervical artery
- Transverse cervical artery
- Suprascapular artery
Branches of the External Carotid Artery
- The external carotid artery provides several branches that target the face and neck, including:
- Superior thyroid artery
- Ascending pharyngeal artery
- Lingual artery
- Facial artery
- Occipital artery
- Posterior auricular artery
- Maxillary artery
- Superficial temporal artery
Internal Carotid
- The internal carotid artery travels much deeper in the neck and has fewer branches.
- It contributes primarily to supplying the brain, after traveling through the carotid canal at the base of the skull.
- It also supplies the eyes, upper nose, and forehead via ophthalmic arteries.
Blood Drainage of the Brain
- The brain is drained into venous sinuses, including:
- Sigmoid sinus
- Superior petrosal sinus
- Ophthalmic vein
- Cavernous sinus
- Great cerebral vein
- Confluence of sinuses
- Straight sinus
- Superior sagittal sinus
- Inferior sagittal sinus
Venous Sinuses Exiting the Skull
- The network of sinuses drains into ever larger sized ones, which then ultimately drain into the sigmoid sinus that exits through the jugular foramen and is continuous with the internal jugular.
Venous Drainage of the Head and Face
- The veins of the face and scalp generally accompany the arteries and have the same name.
- The anterior aspect of the face, including muscles, is drained via a superficial network that ultimately drains into the internal jugular vein.
- The side of the face and scalp is drained into the external jugular vein.
Final Stages of Venous Drainage
- Ultimately, the internal and external jugular, as well as the vertebral veins, descend towards the base of the neck, where venous blood is delivered into the brachiocephalic vein.
- There is a brachiocephalic vein on each side of the body.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers the origins and course of carotid arteries, distribution of major branches, anastomoses, and venous drainage patterns in the head and neck region.